168
Chapter 15: Expressions and The Expression Stack
TI
-
89 / TI
-
92 Plus Developer Guide
Not for Distribution
Beta Version January 26, 2001
Many built-in operators also require exactly two operands, for example,
arithmetic operators, power operators, relational operators, logical operators, the
store operator and the with operator. The arithmetic operators +,
N
, *, /, .+, .
N
, .*,
./, and the store operator
→
, all place the first operand deepest, then the second
operand, and finally the corresponding tag on top.
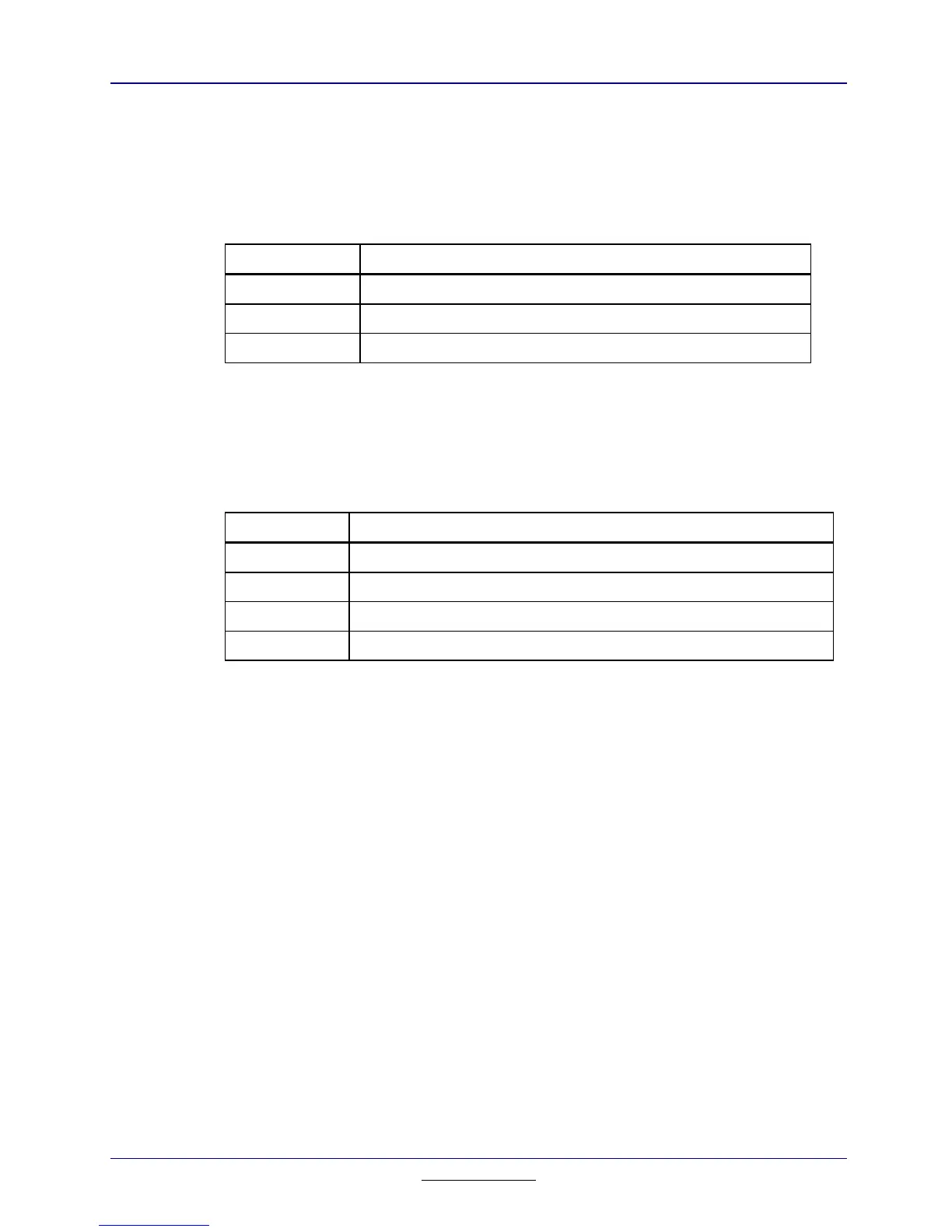
Expression Representation
a + b A_VAR_TAG B_VAR_TAG ADD_TAG
x .* y X_VAR_TAG Y_VAR_TAG DOT_MULT_TAG
π
→
z PI_TAG Z_VAR_TAG STORE_TAG
Table 15.8: Examples of Arithmetic Operations and the Store Operation
The remaining binary operators, the power operators ^ and .^, the relational
operators =, /=, <, <=, >, and >=, the logical operators and, or, and xor, and the
with operator |, all place the tag on top of the first operand on top of the second
operand, just as the functions do.
Expression Representation
x ^ y Y_VAR_TAG X_VAR_TAG EXPONENTIATION_TAG
r > s S_VAR_TAG R_VAR_TAG GT_TAG
a or b B_VAR_TAG A_VAR_TAG OR_TAG
c | d D_VAR_TAG C_VAR_TAG SUCH_THAT_TAG (with)
Table 15.9: Examples of Other Binary Operations
15.2.7. Tags That Take More Than Two or a
Variable Number of Arguments
The tokenized Polish representation of functions that take more than two
arguments is the function tag on top of a tail of arguments. A tail is a sequence of
expressions on top of an END_TAG. The first argument is at the top of the
sequence just below the function tag. The last argument is deepest in the
sequence just above the END_TAG. Thus,
Σ
(m, m, 1, n) is represented as
END_TAG N_VAR_TAG 1 1 NONNEGATIVE_INTEGER_TAG M_VAR_TAG
M_VAR_TAG SUMMATION_TAG.
A tail is also used for functions that accept a variable number of arguments. For
example, the
∫
function will accept 2, 3, or 4 arguments. Therefore,
∫
(ln(x), x) is
represented by END_TAG X_VAR_TAG X_VAR_TAG LN_TAG
INTEGRAL_TAG.
∫
(sin(x), x, 0,
π
) is represented by END_TAG PI_TAG 0
NONNEGATIVE_INTEGER_TAG X_VAR_TAG X_VAR_TAG SIN_TAG
INTEGRAL_TAG.

 Loading...
Loading...


















