Parameter Details
2
2.3 b: Application
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5002A GA500 DRIVE PROGRAMMING 181
■ b4-07: Terminal P2 ON-Delay Time
No.
(Hex.)
Name Description
Default
(Range)
b4-07
(0B34)
Expert
Terminal P2 ON-Delay Time
Sets the delay time until the contact is turned ON after the function set with H2-03 turns ON.
0 ms
(0 - 65000 ms)
■ b4-08: Terminal P2 OFF-Delay Time
No.
(Hex.)
Name Description
Default
(Range)
b4-08
(0B35)
Expert
Terminal P2 OFF-Delay
Time
Sets the delay time to deactivate the contact after the function set in H2-03 deactivates.
0 ms
(0 - 65000 ms)
◆ b5: PID control
The drive has a PID control function. You can control drive output to adjust the proportional gain, integral time, and
derivative time that has an effect on the bias between the target value and the feedback value to match the target value
to the detected value. Use this function to adjust the drive output to accurately match the flow, pressure, and
temperature in the application match the target value.
Use a combination of these controls to increase the performance:
• P control
P control has a proportional effect on the deviation. It outputs the product (the controlled output) proportional to the
deviation. You cannot use only the offset from P control to get to zero deviation.
• I control
I control is the integral of the deviation. It uses an integral value of the deviation to output the product (the
controlled output). I control helps align the feedback value and the target value. If you use only a proportional effect
(P control), it will cause and offset. Use a proportional effect with integral control, and the offset will disappear over
time.
• D control
D control is the derivative of the deviation. D control has an effect on drive output when there are sudden, large
changes in the deviation or feedback value. It quickly returns drive output to the value before the sudden change. It
multiplies a time constant by a derivative value of the deviation (slope of the deviation), and adds that result to PID
input to calculate the deviation of the signal, then it corrects the deviation.
Note:
D control causes less stable operation because the noise changes the deviation signal. Use D control only when necessary.
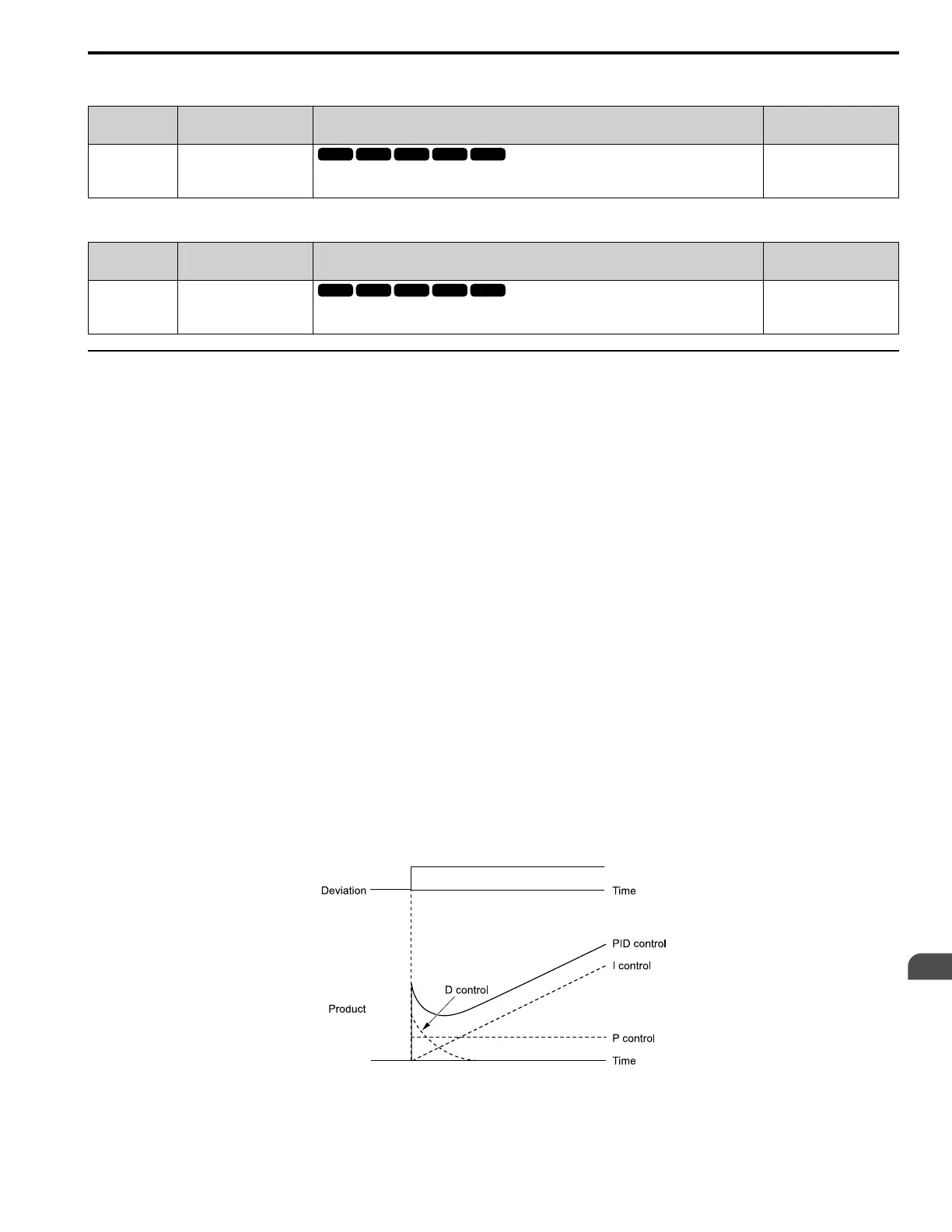
■ PID Control Operation
Figure 2.21 shows PID control operation. The modified output (output frequency) changes when the drive uses PID
control to keep the deviation (the difference between the target value and the feedback value) constant.
Figure 2.21 PID Control Operation

 Loading...
Loading...