10-30
The potential wave form for
OSWV
consists of a square wave superimposed on a
staircase wave form. It can also be viewed as a series of pulses alternating in
direction (hence, the relation to both pulse and A.C. techniques). The current is
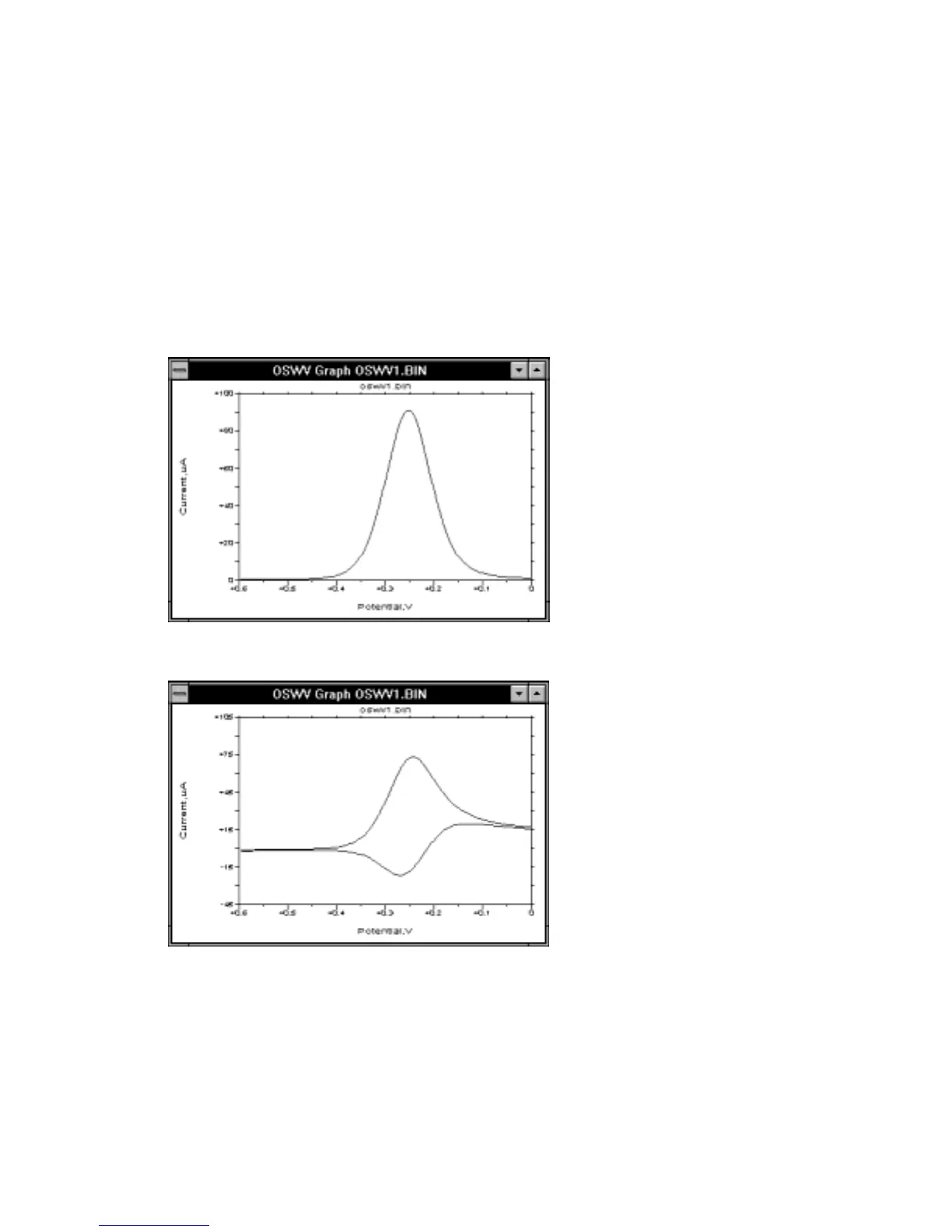
sampled at the end of each of the pulses (or half-cycles). The default current output is
the difference current (Figure 10-18), but the forward current (i
f
) and reverse current
(i
r
) can also be examined (Figure 10-19). For a reversible system, the reverse current
is significant, so the difference current is greater than either the forward or reverse
currents. This is one reason for the greater sensitivity of
OSWV
compared with
DPV/P
. The magnitude of the reverse current can also be used to investigate the
reversibility of the electron transfer.
Figure 10-18.
Difference current response for
OSWV and BSWV/P
.
Figure 10-19.
Forward and reverse current responses for
OSWV
.
The waveform for
BSWV/P
is similar to that for
OSWV
. The main difference is that
the samples are collected and averaged over a number of cycles. In addition, only the
difference current is available (Figure 10-18). Due to the signal averaging,
BSWV/P
is significantly slower than
OSWV
.
 Loading...
Loading...