112 | Chapter 6: Instrument Qualification
compared mean values must be within the accuracy specification for the
instrument.
Example: If the mean value for well A1 in the Normal position is 1.902 with a
specified accuracy of ± 1.0% ± 0.010 OD, then the expected range for the
mean of the same well in its Turnaround (H12) position is 1.873 to 1.931 OD.
1.902 x 0.010 + 0.010 = 0.029; 1.902 - 0.029 = 1.873; 1.902 + 0.029 = 1.931
•
Accuracy Specification. The following accuracy specifications are
applied using Normal mode and a 96-well microplate:
± 1.0% ± 0.010 OD from 0.000 to 2.000 OD
± 3.0% ± 0.010 OD from 2.000 OD to 3.000 OD
Absorbance Liquid Test 2
Materials
• A new 96-well, clear, flat-bottom microplate, such as Corning Costar #3590
• Ten test tubes, numbered consecutively, set up in a rack
• Calibrated hand pipette (Class A volumetric pipette recommended)
• Stock solution A or B (see page 110)
• A 0.05% solution of deionized water and Tween 20
Prepare the Dilutions
Create a percentage dilution series, beginning with 100% of the original concentrated
stock solution (A or B) in the first tube, 90% of the original solution in the second tube,
80% in the third tube, all the way to 10% in the tenth tube. Dilute using the 0.05%
solution of deionized water and Tween 20. This solution can also be made by diluting
the BioTek wetting agent 200:1.
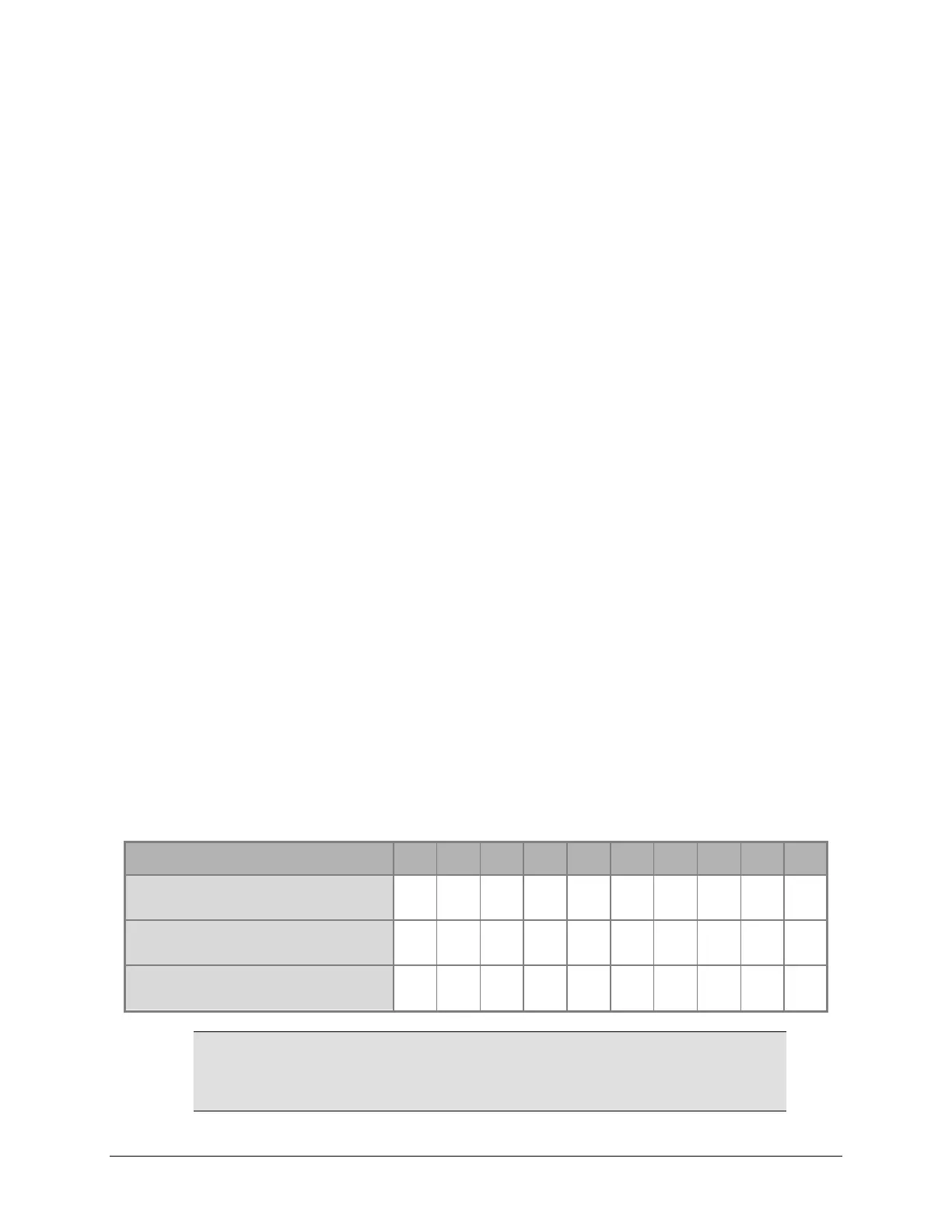
Test Tube Dilutions
Tube Number: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Volume of Original
Concentrated Solution (mL)
20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2
Volume of 0.05% Tween
Solution (mL)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Absorbance expected if original
solution is 2.0 at 200 µL
2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2
The choice of dilutions and the absorbance of the original solution can
be varied. Use this table as a model for calculating the expected
absorbances of a series of dilutions, given a different absorbance of
the original solution.
BioTek Instruments, Inc.

 Loading...
Loading...