and the API called in the container will not be recorded.
Traffic amount: the aggregated advertising packets, the successful connection
requests, and the notification packets of all the gateways managed under this AC.
6.3.
Interface & Protocol
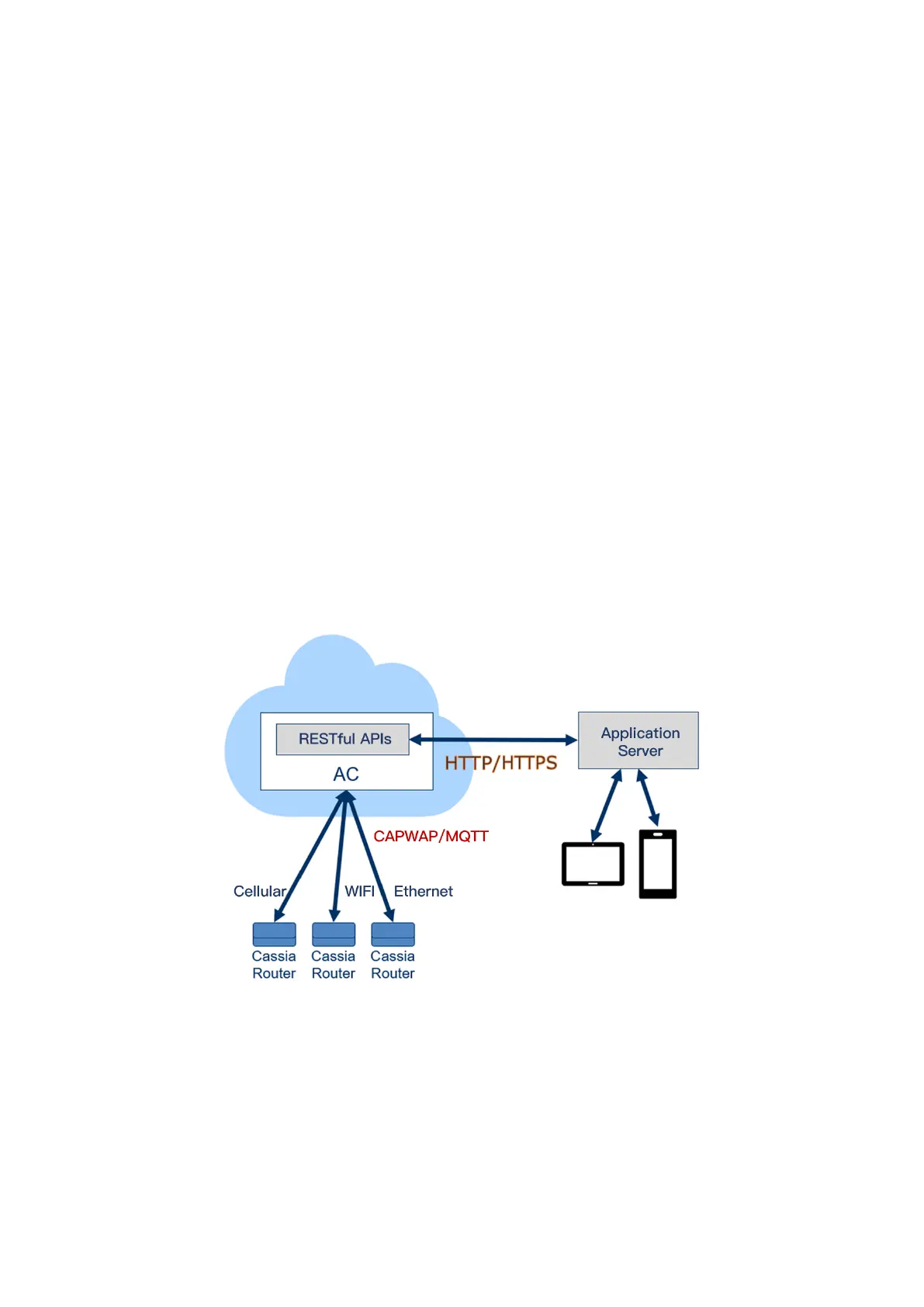
Please see the figure below for the interfaces compatible with the Cassia AC server
Before firmware 2.0.2, the communication between the Cassia Bluetooth gateways
and the AC is over CAPWAP. It is a UDP-based protocol and uses UDP ports 5246 and
5247. It uses DTLS 1.2 to ensure security.
From firmware 2.0, the user can select MQTT to replace CAPWAP. MQTT uses TCP
port 8883 and TLS 1.2. MQTT improves the robustness of gateway and AC
communication and can help the IP packets to pass through the user’s firewall, in
case the firewall doesn’t allow UDP packets to pass. One AC can support MQTT and
CAPWAP at the same time. Please check chapter 4.4 for more information.
The interface between the AC and the application server is using RESTful APIs, on
HTTP (port 80) or HTTPS (port 443). We strongly suggest you to use HTTPS. For
details on Cassia’s RESTful APIs please see the next section.
Compatible Interfaces with Cassia AC
6.4.
Bluetooth Roaming
For cellular and Wi-Fi, roaming occurs when a mobile device switches its association to the
wireless base station with a stronger RF signal when moving from the coverage area of
one base station to the next. A successful roaming is one that doesn’t interrupt the user
data communication during the roaming handoff.
 Loading...
Loading...