MeaningCharacter
The device processing the Multiprotocol Label
Switching (MPLS) echo request is a downstream
device but is not the destination.
R
Replying device is an egress for the destination.
Exclamation mark “!”
Echo request was not successfully transmitted. This
could be returned because of insufficient memory or
more probably because no label switched path (LSP)
exists that matches the Forwarding Equivalence Class
(FEC) information.
Q
Replying device rejected the echo request because it
was malformed.
C
MTU Discovery in an LSP
During an MPLS LSP Ping, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) echo request packets are sent with the
IP packet attribute set to do not fragment. That is, the DF bit is set in the IP header of the packet. This allows
you to use the MPLS echo request to test for the MTU that can be supported for the packet through the label
switched path (LSP) without fragmentation.
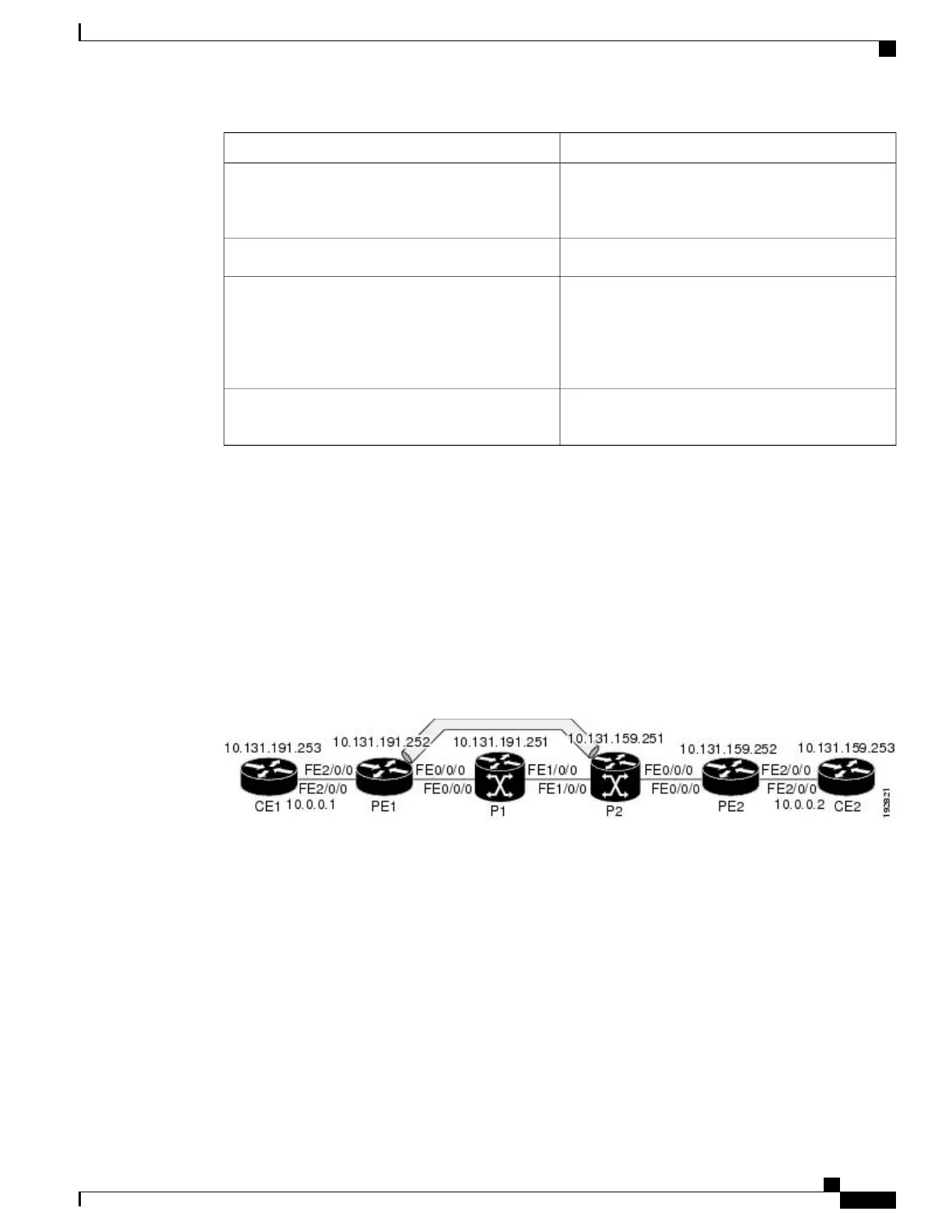
The figure below shows a sample network with a single LSP from PE1 to PE2 formed with labels advertised
by means of LDP.
Figure 10: Sample Network with LSP
—
Labels Advertised by LDP
You can determine the maximum receive unit (MRU) at each hop by tracing the LSP using the MPLS Traceroute
feature. The MRU is the maximum size of a labeled packet that can be forwarded through an LSP. The
following example shows the results of a trace mpls command when the LSP is formed with labels created
by the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP):
Device# trace mpls ipv4 10.131.159.252/32
Tracing MPLS Label Switched Path to 10.131.159.252/32, timeout is 2 seconds
Codes: '!' - success, 'Q' - request not transmitted,
'.' - timeout, 'U' - unreachable,
'R' - downstream router but not target
Type escape sequence to abort.
0 10.131.191.230 MRU 1496 [Labels: 22/19 Exp: 0/0]
R 1 10.131.159.226 MRU 1500 [Labels: 19 Exp: 0] 40 ms
R 2 10.131.159.229 MRU 1504 [implicit-null] 28 ms
! 3 10.131.159.230 40 ms
MPLS Basic Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1 (Cisco ASR 900 Series)
83
MPLS LSP Ping, Traceroute, and AToM VCCV
MTU Discovery in an LSP

 Loading...
Loading...