D-Link Unified Access System Software User Manual
02/15/2011
Page 36 Document 34CS3000-SWUM104-D10
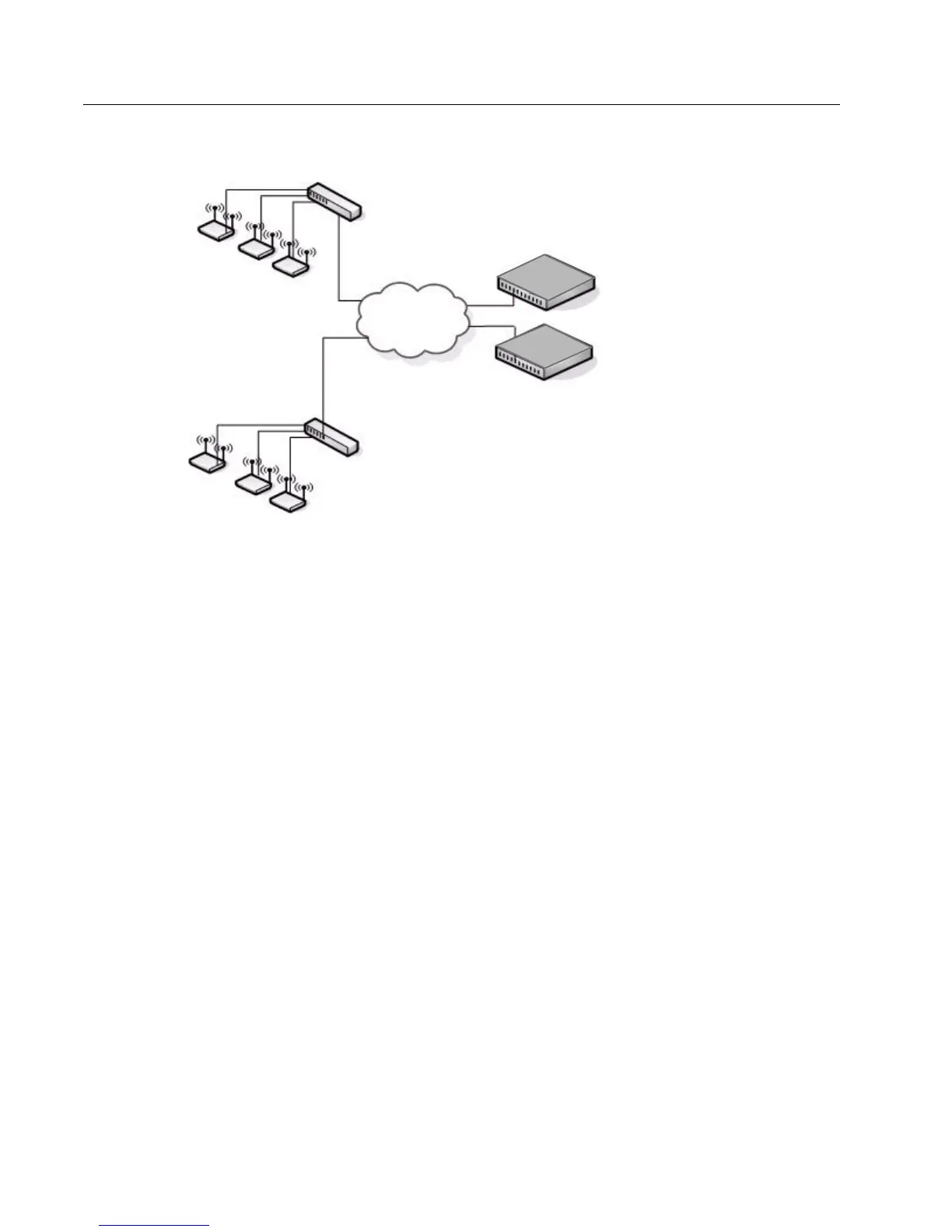
Figure 9: Data Center Topology
The data center topology is a good solution in networks where the goal is to add a wireless LAN to a network with minimal
changes to the existing network. Traffic from wireless clients to the APs is either tunneled through the Unified Switch or
tagged with a VLAN ID by the AP and handled accordingly. If the traffic is tagged, it might not pass through the Unified
Switch.
Access Point-to-Switch Discovery
To enable the AP and Unified Switch to discover each other, you can use one of the following four methods:
• Enter the IP address of the Unified Switch into the AP
• Enter the IP address of the AP into the Unified Switch
• Configure the DHCP server to pass the IP address of the Unified Switch to the AP in DHCP option 43
• Use the D-Link Wireless Device Discovery Protocol
The AP-to-switch discovery method you use depends on your network topology. For example, if the Unified Switch and AP
are in the same Layer 2 multicast domain, we recommend that you use the D-Link Wireless Device Discovery Protocol.
These options are discussed in more detail in “Discovering Access Points and Peer Switches” on page 58.
Access Point Placement
D-Link Access Points can be on the same subnet as the switch or on a different subnet. You can connect the AP directly to
the Unified Switch or to another networking device. The range of the D-Link Access Point is about 100 meters, but the range
is affected by various environmental factors.
To maximize the range, use the following guidelines for the placement of the AP:
• Place the AP in an area where you expect wireless clients will operate.
• Elevated locations, such as on top of a shelf are preferred to increase line-of-sight access.
APs
APs
LAN Switch
LAN Switch
Data Center
Network
Backbone
Unified Switches

 Loading...
Loading...















