Chapter 7: Making Hardware Connections 39
Each Input section has three analog input jacks:
Mic For XLR microphone cables.
Line (TRS) For 1/4-inch Tip-Ring-Sleeve cables
from keyboards, mixers, microphones, and
other line sources.
DI For 1/4-inch Tip-Sleeve cables from guitar,
bass, microphones, or similar sources.
For information about connecting specific au-
dio sources, see “Connecting a Microphone” on
page 39, and “Connecting Instruments to the
Mbox 2” on page 41.
Connecting a Microphone
There are several ways to use Mbox 2 with a mi-
crophone, depending on the type of micro-
phone and cable you use.
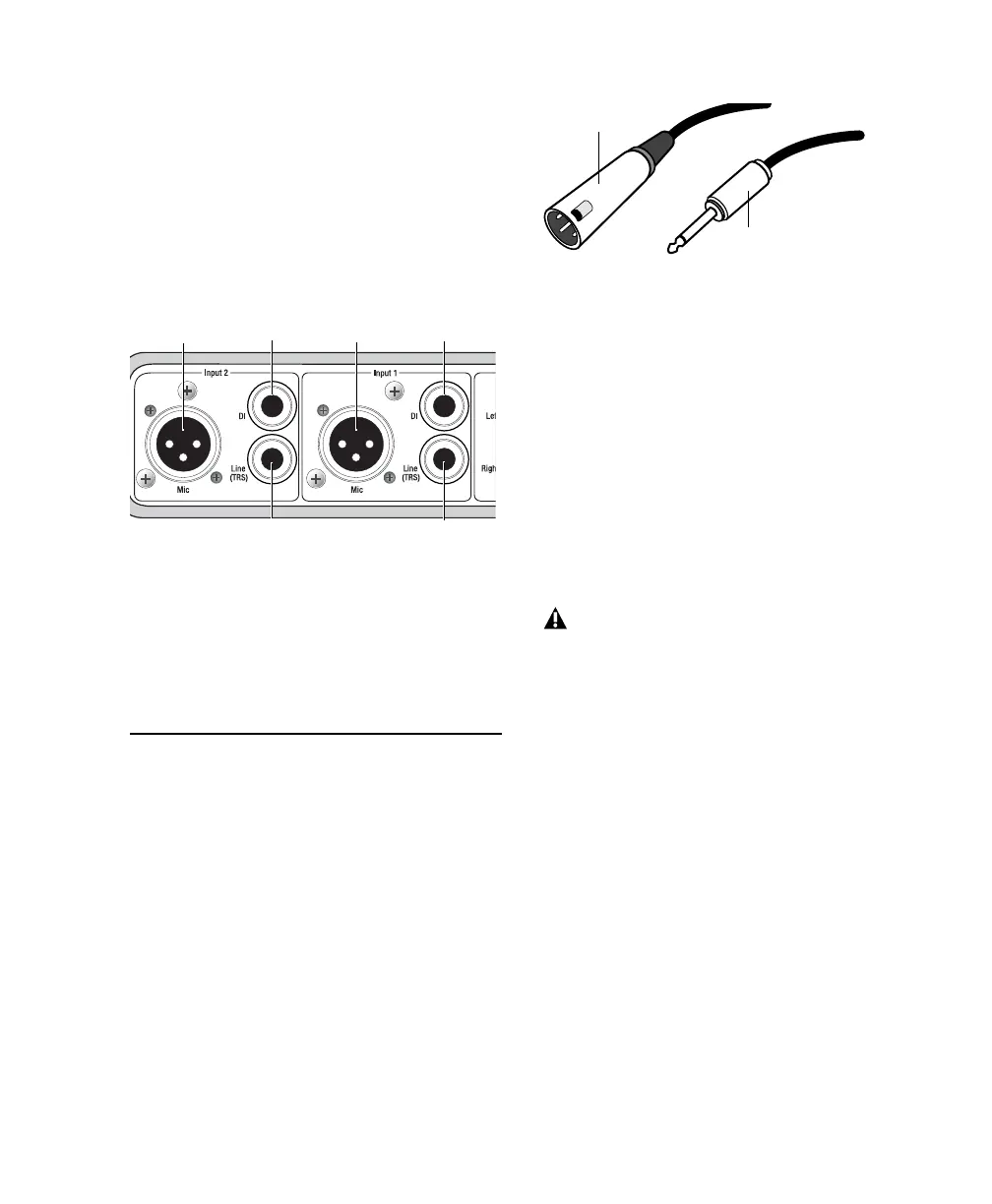
Mic Cables and Connectors
Some microphone cables use an XLR connector
to attach a microphone to an input (such as
those on the Mbox 2); other microphones use a
1/4-inch connector. If you have a choice, use an
XLR connector to connect the microphone to
the Mbox 2 to yield better results.
Phantom Power
Some microphones require power to operate.
This power, called phantom power, is supplied ei-
ther by a battery in the microphone, or through
an audio interface (such as Mbox 2) that can
supply power through the microphone cable.
Most condenser microphones (such as an AKG
C3000) require phantom power to operate. Dy-
namic microphones (such as a Shure SM57) do
not require phantom power to operate, but are
not harmed by it.
The Mbox 2 can only supply power through a
microphone cable with XLR connectors. If you
are not sure about the phantom power require-
ments for your microphone, refer to your micro-
phone’s documentation or contact the manu-
facturer.
Analog input connectors
DI
Line Line
Mic Mic DI
(TRS)(TRS)
XLR and 1/4-inch connectors
Although phantom power can be used
safely with most microphones, it is possible
to damage some ribbon microphones with
it. Always turn off phantom power and
wait at least ten seconds before connecting
a ribbon microphone.
XLR connector
1/4-inch connector
 Loading...
Loading...