CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION
The differential gear system divides the torque
between the axle shafts. It allows the axle shafts to
rotate at different speeds when turning corners.
Each differential side gear is splined to an axle
shaft. The pinion gears are mounted on a pinion
mate shaft and are free to rotate on the shaft. The
pinion gear is fitted in a bore in the differential case
and is positioned at a right angle to the axle shafts.
OPERATION
In operation, power flow occurs as follows:
• The pinion gear rotates the ring gear
• The ring gear (bolted to the differential case)
rotates the case
• The differential pinion gears (mounted on the
pinion mate shaft in the case) rotate the side gears
• The side gears (splined to the axle shafts) rotate
the shafts
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).
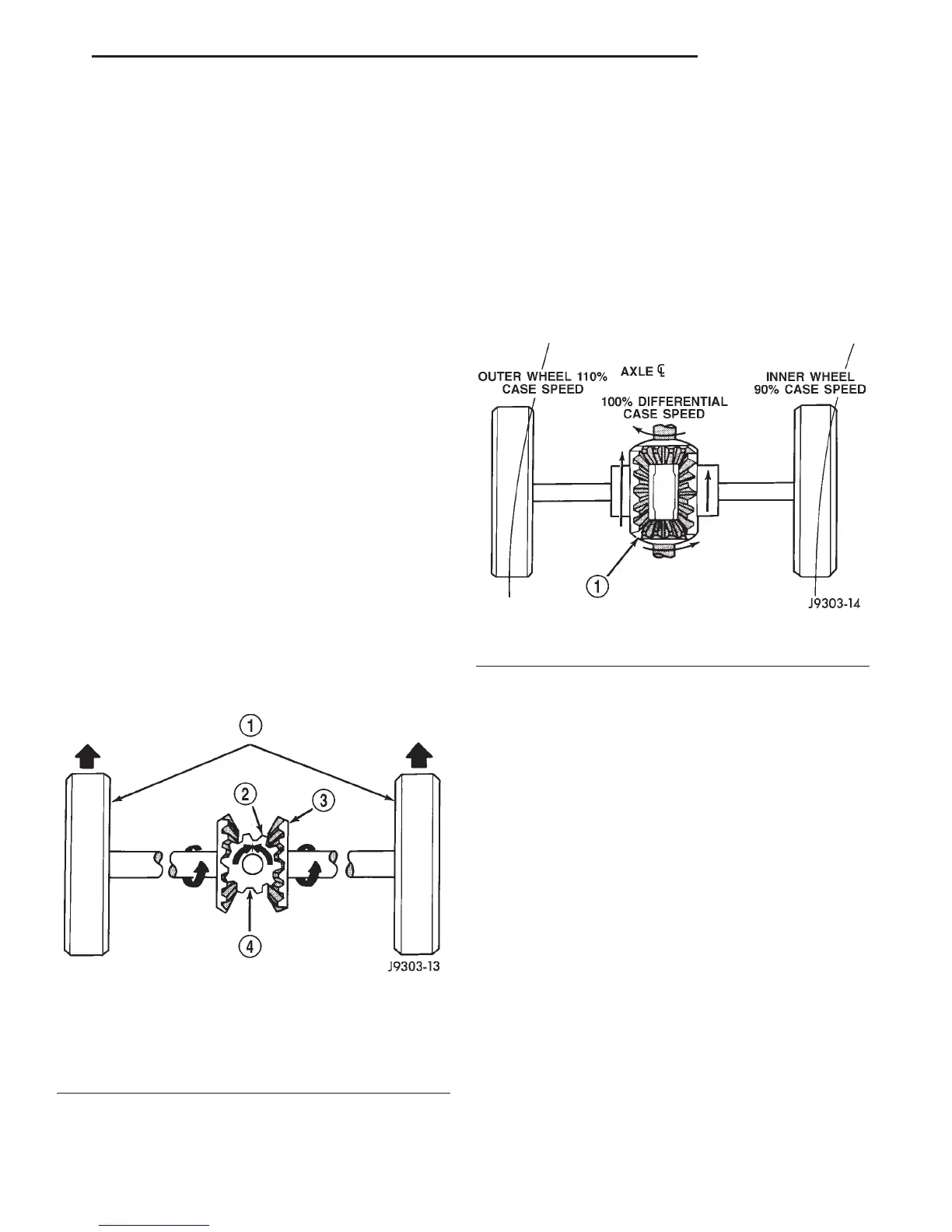
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Axle bearing problem conditions are usually caused
by:
• Insufficient or incorrect lubricant.
• Foreign matter/water contamination.
• Incorrect bearing preload torque adjustment.
• Incorrect backlash.
Axle gear problem conditions are usually the result
of:
• Insufficient lubrication.
• Incorrect or contaminated lubricant.
• Overloading (excessive engine torque) or exceed-
ing vehicle weight capacity.
• Incorrect clearance or backlash adjustment.
Axle component breakage is most often the result
of:
• Severe overloading.
• Insufficient lubricant.
• Incorrect lubricant.
• Improperly tightened components.
• Differential housing bores not square to each
other.
Fig. 1 Differential Operation—Straight Ahead Driving
1 – IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 – PINION GEAR
3 – SIDE GEAR
4 – PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
Fig. 2 Differential Operation—On Turns
1 – PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFT
DN C205F AXLE 3 - 31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
 Loading...
Loading...











