167
WSG-1068 IGNITION SYSTEM
The Fuel Select Switch
In the event that the engine is operated on alternate
fuels such as natural gas, compressed natural gas
(CNG), or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), timing can be
modified with a Fuel Select Switch.
NOTE: Fuel select switch is supplied by the customer.
Sends a signal to the GCP to adjust base timing
for alternate fuel
Is manually controlled.
With this system, the GCP monitors the engine load,
speed, operating temperature, air intake temperature
and decides what degree of spark advance is correct for
all of the operating conditions. Because timing is set for
life inherently in the design of the engine, and there are
no moving parts in the ignition system itself, no
maintenance is required except for periodic spark plug
checks. The system provides for fixed spark advance at
start-up, for cold weather starting, and for “average
value” default settings in case of component failure.
Particular attention has been given to spark optimization
for excellent fuel economy and power in the warm-up
mode.
The spark plugs are paired so that one plug fires during
the compression stroke and its companion plug fires
during the exhaust stroke. The next time that coil is fired,
the plug that was on exhaust will be on compression,
and the one that was on compression will be on exhaust.
The spark in the exhaust cylinder is wasted but little of
the coil energy is lost.
Run Mode
The GCP interprets engine speed above100 RPM as
Run Mode.
The Base Spark Advance (BSA) is calculated by the
(GCP) module processing the engine speed and load
plus sensors mentioned in operation of this section and
Fuel Select Switch.
Inputs to the GCP Effecting the Ignition
The spark strategy is based on sensors and manifold
vacuum input to the GCP module, which include the
following inputs:
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP Sensor)
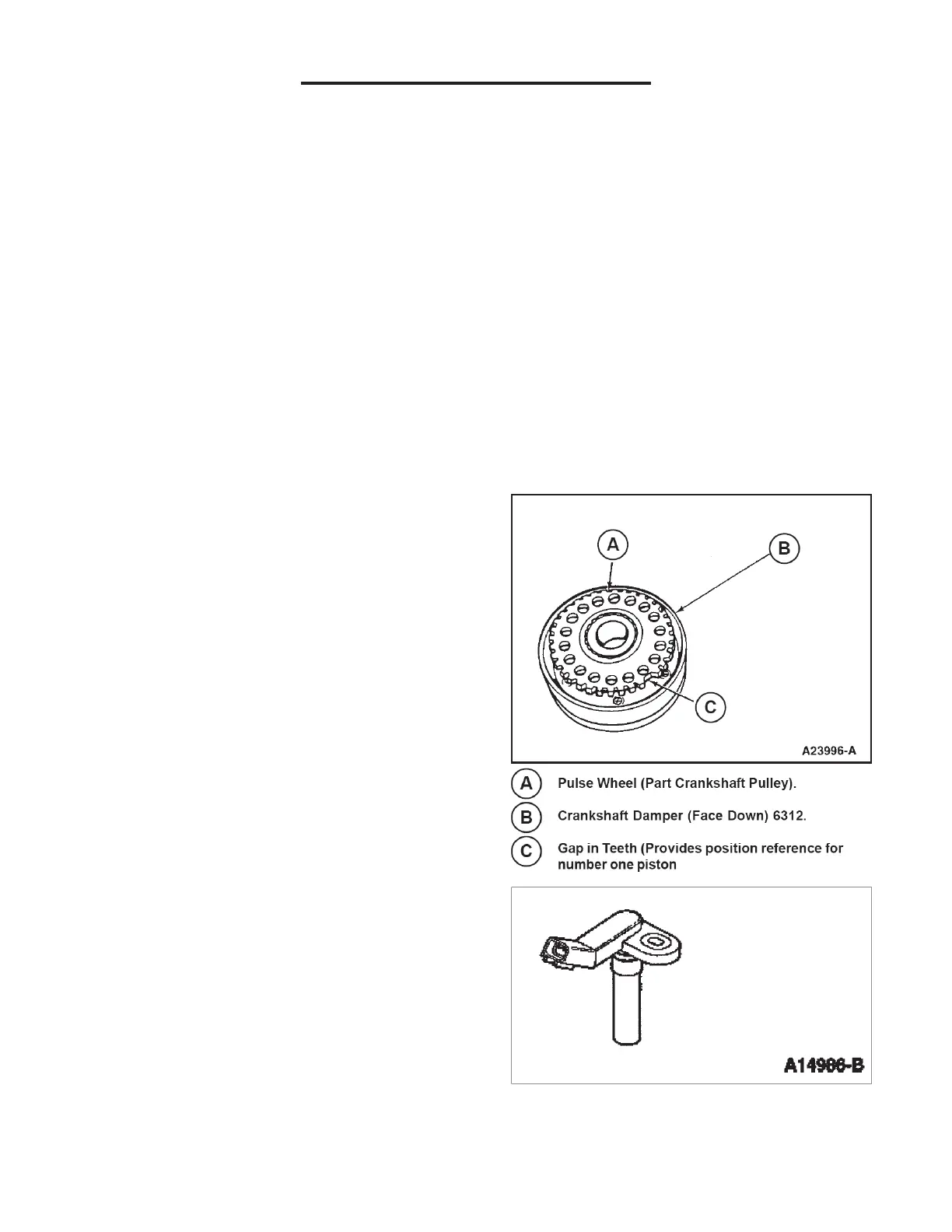
The CKP sensor is a magnetic transducer mounted on
the engine block adjacent to a pulse wheel located on
the crankshaft. By monitoring the crankshaft mounted
pulse wheel A , the CKP is the primary sensor for
ignition information to the GCP. The pulse wheel located
behind the crankshaft pulley B , has a total of 39 teeth
spaced 9 degrees apart with one empty space C for a
missing tooth. An A/C voltage signal is generated which
increases with engine rpm and provides engine speed
and crankshaft position information to the GCP. By
monitoring the pulse wheel, the CKP sensor signal
indicates crankshaft position and speed information to
the GCP. The CKP sensor is also able to identify piston
travel in order to synchronize the ignition system and
provide a way of tracking the angular position of the
crankshaft relative to a fixed reference for the CKP
sensor configuration. GCP also uses the CKP signal to
determine if a misfire has occurred by measuring rapid
decelerations between teeth.
 Loading...
Loading...