7 Operating modes
Festo – GDCP-CMMP-M3/-M0-C-CO-EN – 1510b – English 191
setpoint_acknowledge
new_acknowledge
data_valid
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
Fig. 7.4 Positioning job transmission from a host
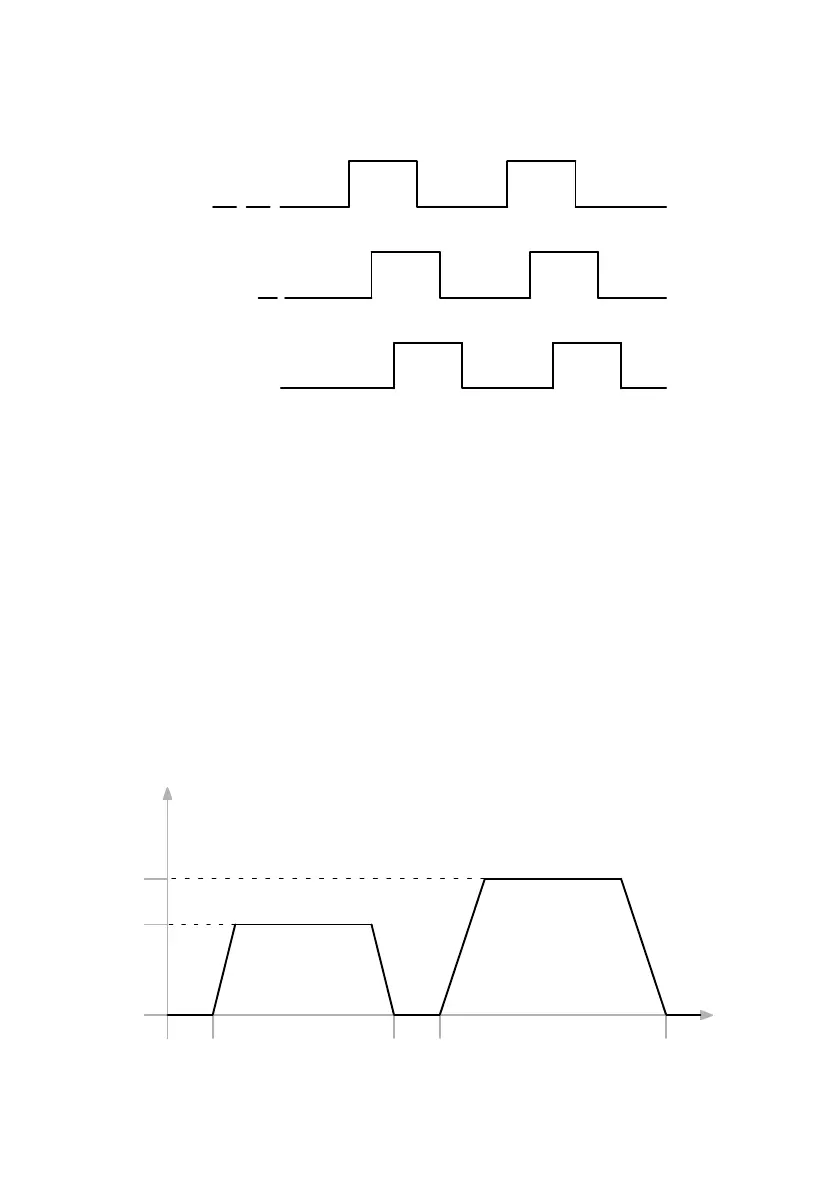
In Fig. 7.4, you can see how the host and the motor controller communicate with each other via the
CAN bus:
First, the positioning data (target position, travel speed, end speed and acceleration) are transmitted to
the motor controller. When the positioning data set has been completely written 1, the host can start
positioning by setting the bit new_set_point in the controlword to “1” 2. After the motor controller
recognises the new data and takes it over into its buffer, it reports this to the host by setting the bit
set_point_acknowledge in the statusword 3.
Then the host can start to write a new positioning data set into the motor controller 4 and delete again
the bit new_set_point 5. Only when the motor controller can accept a new positioning job 6 does it
signal this through a “0” in the set_point_acknowledge bit. Before this, no new positioning may be
started by the host 7.
In Fig. 7.5, a new positioning task is only started after the previous one has been completely finished.
To determine this, the host evaluates the bit target_reached in the object statusword.
Time
t
0
v
2
v
1
t
1
t
2
t
3
Velocity
Fig. 7.5 Simple positioning task

 Loading...
Loading...











