GE
D
IRECTION 5535208-100, REV. 2 LOGIQ E9 SERVICE MANUAL
Chapter 5 Components and Functions (Theory) 5 - 29
5-7-5 Shear Wave (SWAVE) Option
What is Shear Wave?
A Shear wave is a transverse wave that occurs in an elastic medium when it is subjected to periodic
shear.
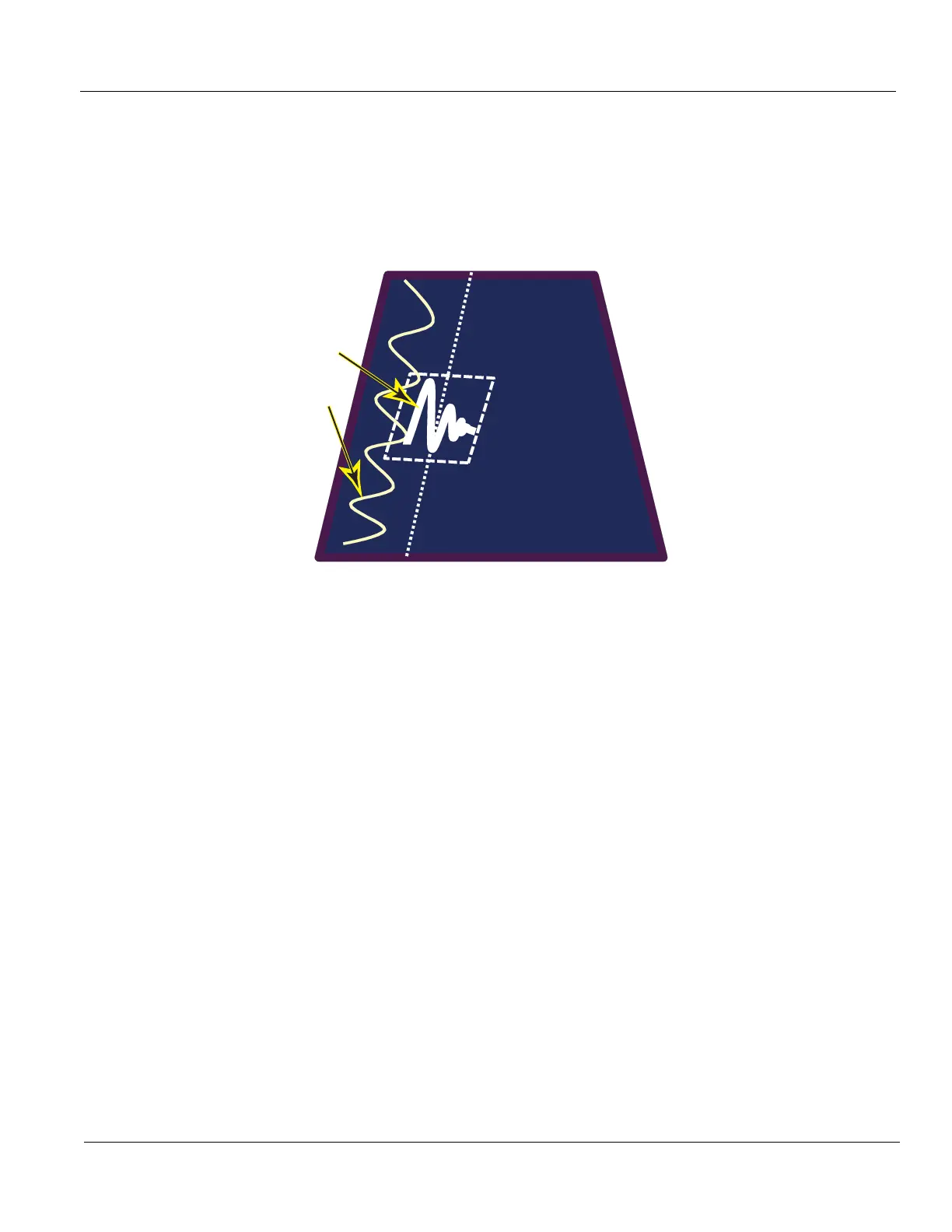
A = Ultrasound “push“ pulse applied. B = Shear Wave response.
There are basically two methods of creating shear waves in tissue.
• External, low frequency vibrator applied to the body of the patient. Used in Magnetic Resonance
Elastography (MRE).
• Generating shear waves in tissue using a diagnostic ultrasound transducer. Shear waves "push"
the tissue at a low frequency in either a single burst of high amplitude, long duration pulses or a
series of such pulses.
Where is it used?
Because elasticity, stiffness, viscosity and a number of other Properties of certain tissue types change
with disease states, there is a clinical need of a quantitative method for assessing elasticity of tissue in
order to help detect potentially cancerous masses and help diagnose diffuse soft tissue diseases like
liver fibrosis.
Pre-SWAVE Mode
• Intermediate mode between B mode scanning and a single point analysis technique.
• During this pre-mode, the previous B-mode imaging mode is still active.
Figure 5-19 SWAVE Visually Explained
A
B
 Loading...
Loading...