Page 12-2
To define the functions f(x,y) and g(x,y,z), in ALG mode, use:
DEF(f(x,y)=x*COS(y)) ` DEF(g(x,y,z)=√(x^2+y^2)*SIN(z) `
To type the derivative symbol use ‚¿. The derivative ,
for example, will be entered as ∂x(f(x,y))
` in ALG mode in the screen.
Multiple integrals
A physical interpretation of the double integral of a function f(x,y) over a
region R on the x-y plane is the volume of the solid body contained under
the surface f(x,y) above the region R. The region R can be described as R
= {a<x<b, f(x)<y<g(x)} or as R = {c<y<d, r(y)<x<s(y)}. Thus, the double
integral can be written as
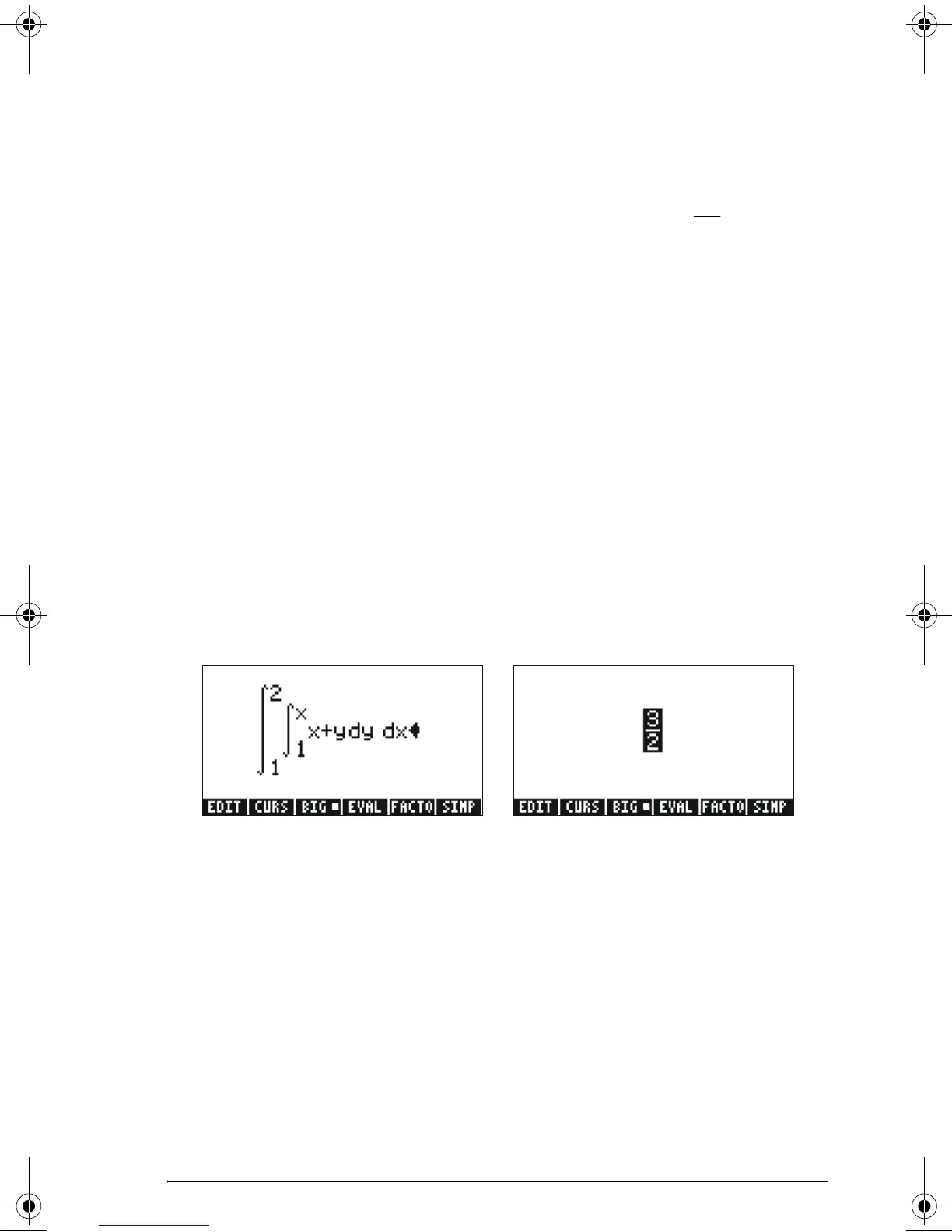
Calculating a double integral in the calculator is straightforward. A
double integral can be built in the Equation Writer (see example in
Chapter 2 in the user’s guide), as shown below. This double integral is
calculated directly in the Equation Writer by selecting the entire expression
and using function
@EVAL. The result is 3/2.
Reference
For additional details of multi-variate calculus operations and their
applications see Chapter 14 in the calculator’s user’s guide.
)),(( yxf
x∂
∂
∫∫∫∫∫∫
φ=φ=φ
d
c
)y(s
)y(r
b
a
)x(g
)x(f
R
dydx)y,x(dydx)y,x(dA)y,x(
SG49A.book Page 2 Friday, September 16, 2005 1:31 PM

 Loading...
Loading...




