Page 14-1
Chapter 14
Differential Equations
In this Chapter we present examples of solving ordinary differential
equations (ODE) using calculator functions. A differential equation is an
equation involving derivatives of the independent variable. In most cases,
we seek the dependent function that satisfies the differential equation.
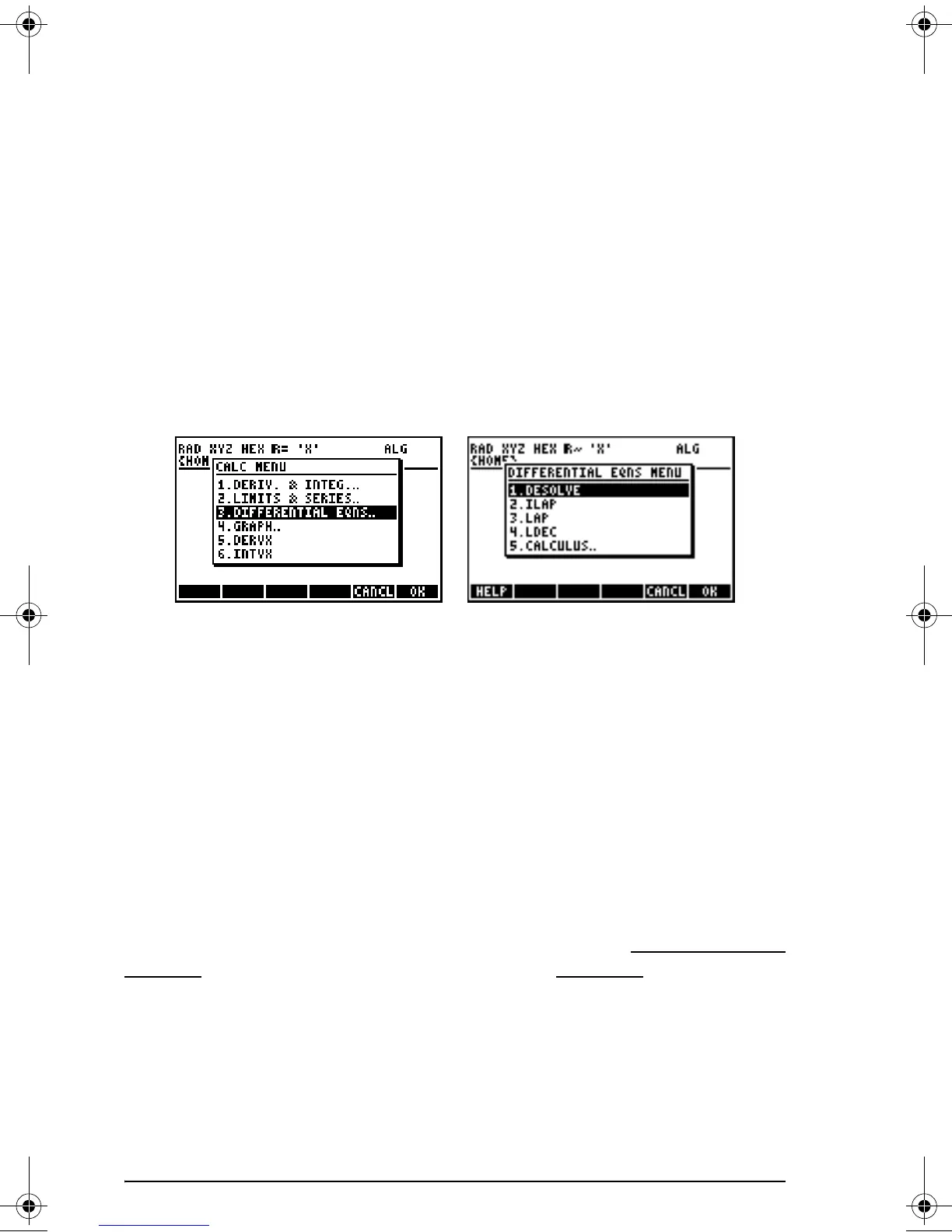
The CALC/DIFF menu
The DIFFERENTIAL EQNS.. sub-menu within the CALC („Ö) menu
provides functions for the solution of differential equations. The menu is
listed below with system flag 117 set to CHOOSE boxes:
These functions are briefly described next. They will be described in more
detail in later parts of this Chapter.
Solution to linear and non-linear equations
An equation in which the dependent variable and all its pertinent
derivatives are of the first degree is referred to as a
linear differential
equation. Otherwise, the equation is said to be non-linear.
Function LDEC
The calculator provides function LDEC (Linear Differential Equation
Command) to find the general solution to a linear ODE of any order with
constant coefficients, whether it is homogeneous or not. This function
requires you to provide two pieces of input:
DESOLVE: Differential Equation SOLVEr, solves differential equations,
when possible
ILAP:
Inverse LAPlace transform, L
-1
[F(s)] = f(t)
LAP: LAPlace transform, L[f(t)]=F(s)
LDEC: Linear Differential Equation Command
SG49A.book Page 1 Friday, September 16, 2005 1:31 PM

 Loading...
Loading...




