Page 11-48
In RPN mode, function MAD generate a number of properties of a square
matrix, namely:
• the determinant (stack level 4)
• the formal inverse (stack level 3),
• in stack level 2, the matrix coefficients of the polynomial p(x) defined
by (x⋅I-A) ⋅p(x)=m(x)⋅I,
• the characteristic polynomial of the matrix (stack level 1)
Notice that the equation (x⋅I-A)⋅p(x)=m(x)⋅I is similar, in form, to the
eigenvalue equation A⋅x = λ⋅x.
As an example, in RPN mode, try:
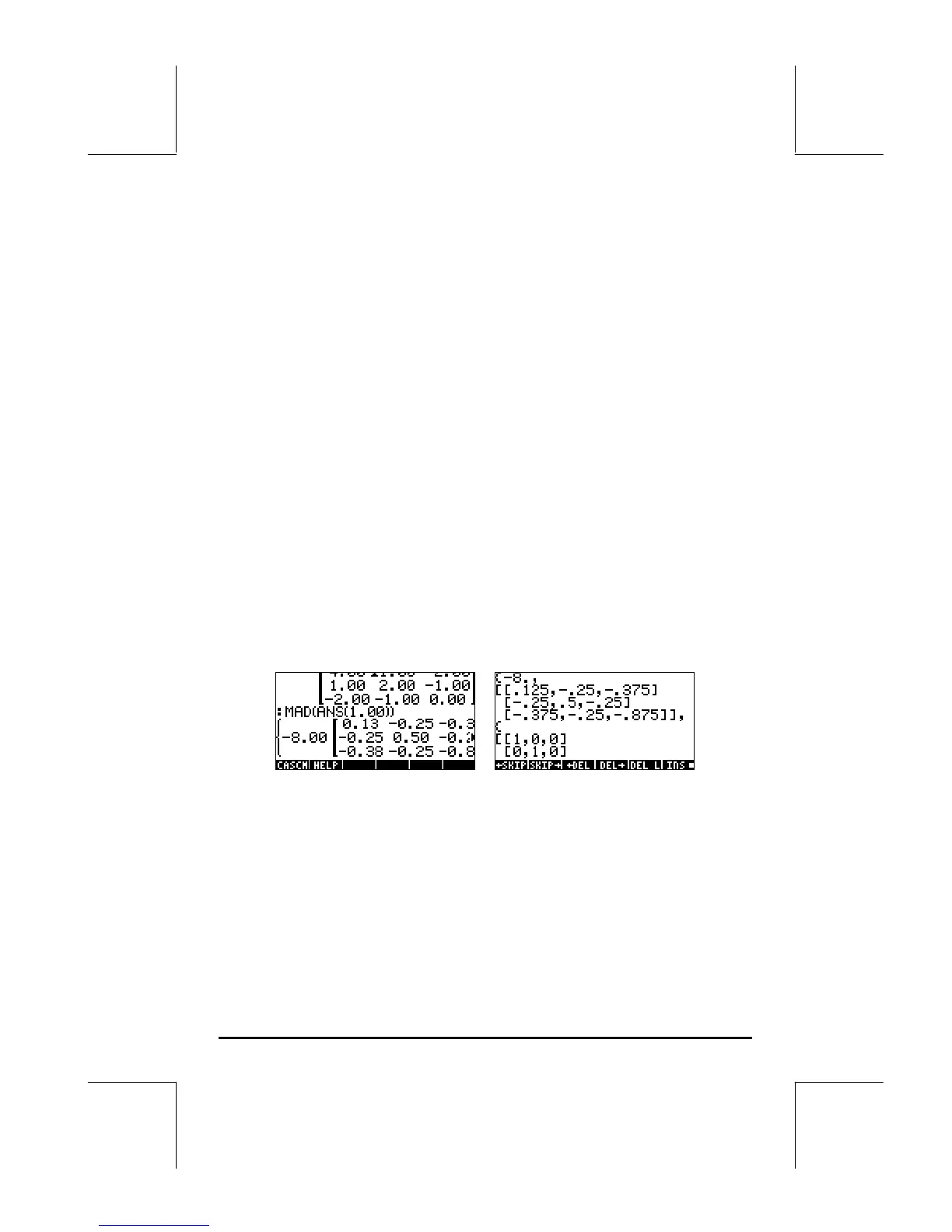
[[4,1,-2] [1,2,-1][-2,-1,0]] MAD
The result is:
4: -8.
3: [[ 0.13 –0.25 –0.38][-0.25 0.50 –0.25][-0.38 –0.25 –0.88]]
2: {[[1 0 0][0 1 0][0 0 1]] [[ -2 1 –2][1 –4 –1][-2 –1 –6] [[-1 2 3][2 –4 2][3 2 7]]}
1: ‘X^3+-6*x^2+2*X+8’
The same exercise, in ALG mode, will look as follows:
Matrix factorization
Matrix factorization or decomposition consists of obtaining matrices that when
multiplied result in a given matrix. We present matrix decomposition through
the use of Functions contained in the matrix FACT menu. This menu is
accessed through „Ø.

 Loading...
Loading...