Page 15-4
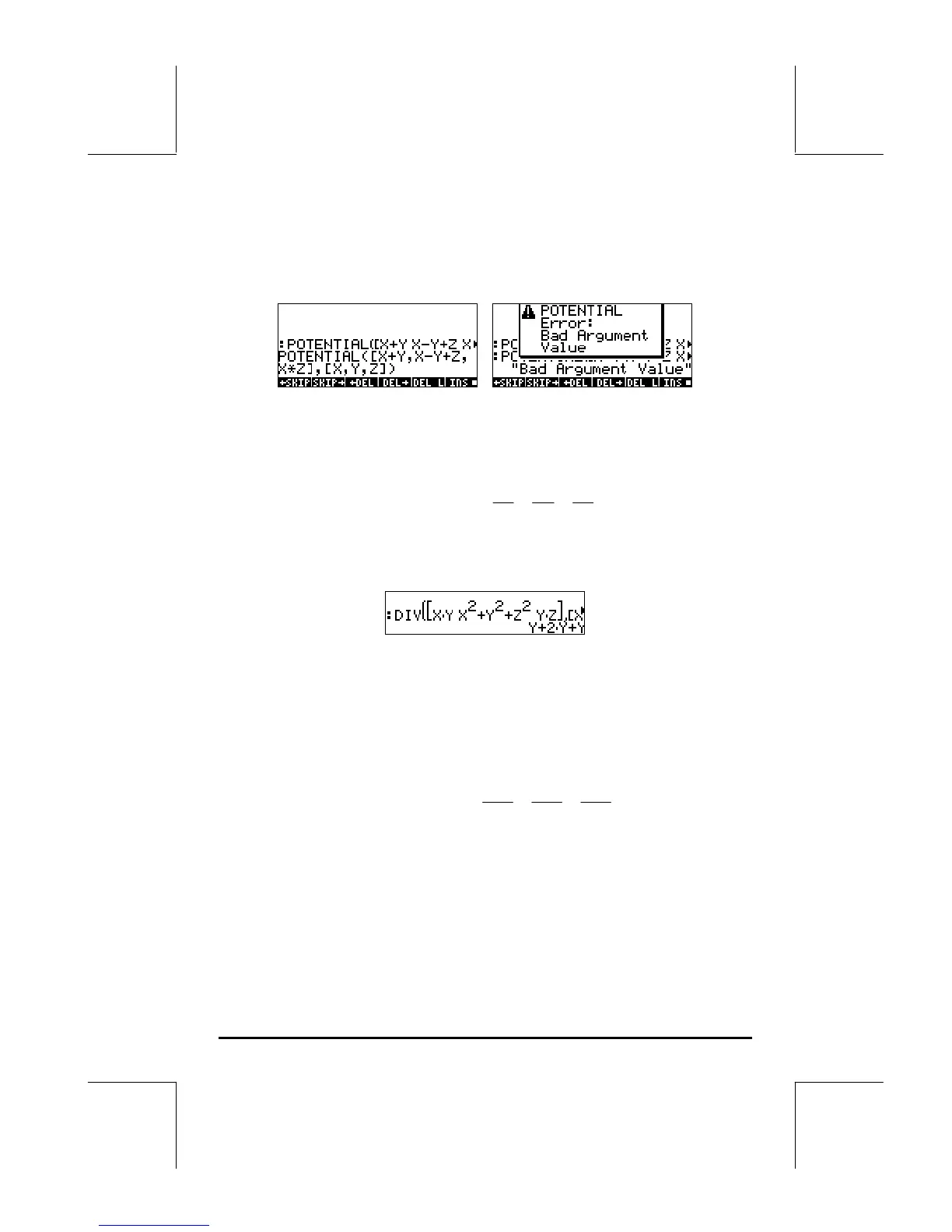
function φ(x,y,z) does not exist. In such case, function POTENTIAL returns an
error message. For example, the vector field F(x,y,z) = (x+y)i + (x-y+z)j +
xzk, does not have a potential function associated with it, since, ∂f/∂z ≠
∂h/∂x. The calculator response in this case is shown below:
Divergence
The divergence of a vector function, F(x,y,z) = f(x,y,z)i+g(x,y,z)j+h(x,y,z)k,
is defined by taking a “dot-product” of the del operator with the function, i.e.,
z
h
y
g
x
f
FdivF
∂
∂
+
∂
∂
+
∂
∂
=•∇=
Function DIV can be used to calculate the divergence of a vector field. For
example, for F(X,Y,Z) = [XY,X
2
+Y
2
+Z
2
,YZ], the divergence is calculated, in
ALG mode, as follows:
Laplacian
The divergence of the gradient of a scalar function produces an operator
called the Laplacian operator. Thus, the Laplacian of a scalar function φ(x,y,z)
is given by
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
∂
∂
+
∂
∂
+
∂
∂
=∇•∇=∇
φφφ
φφ
The partial differential equation ∇
2
φ = 0 is known as Laplace’s equation.
Function LAPL can be used to calculate the Laplacian of a scalar function. For
example, to calculate the Laplacian of the function φ(X,Y,Z) = (X
2
+Y
2
)cos(Z),
use:

 Loading...
Loading...