IPv4 Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Configuring and Assigning an ACL
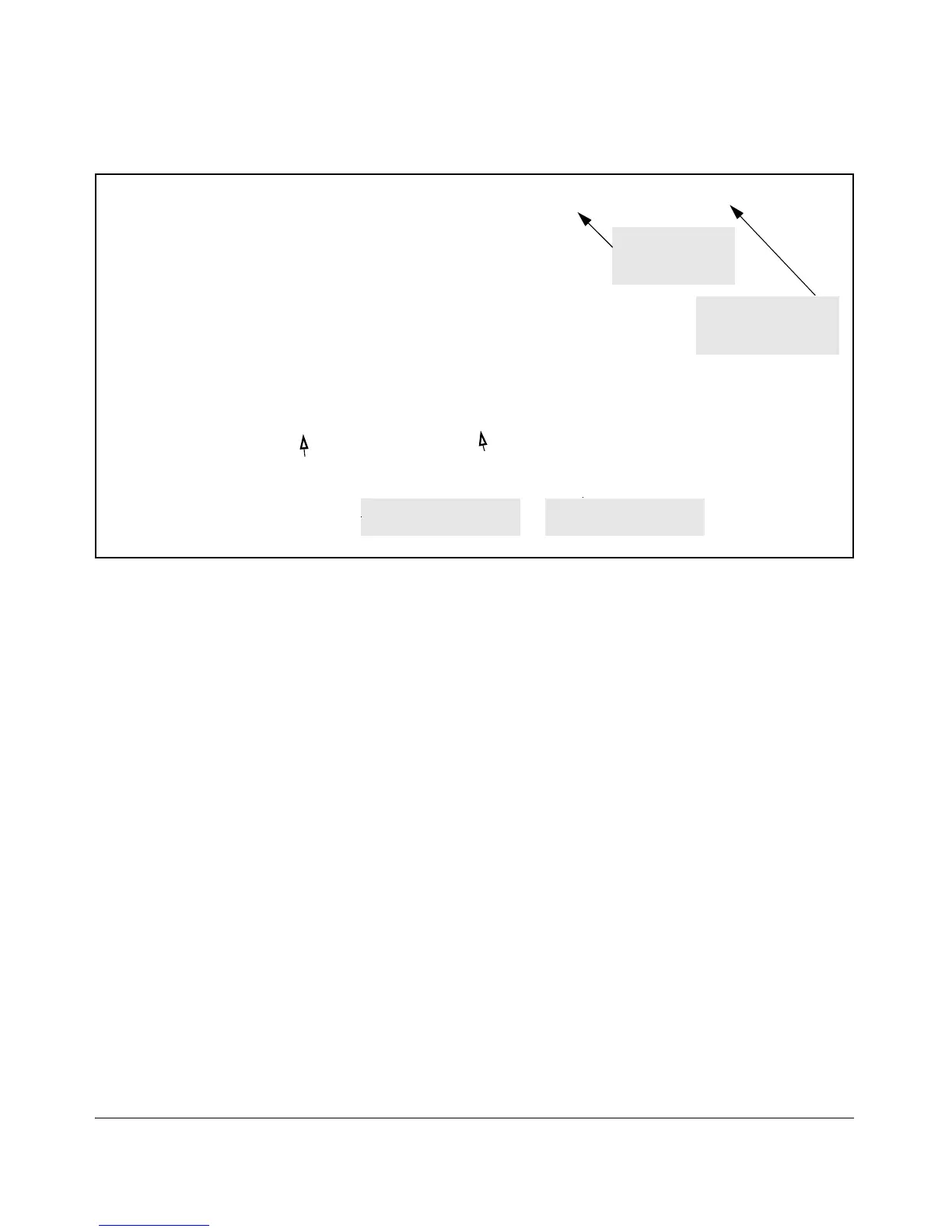
ProCurve (config)# ip access-list extended 150
ProCurve (config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp host 10.10.20.200 10.10.10.1/24 eq
telnet
ProCurve (config-ext-nacl)# exit
Command Entry for
ProCurve (config)# write mem
Source IP Address
ProCurve (config)# interface 12 ip access-group 150 in
and Mask
ProCurve (config)# show config
Command Entry for
Destination IP Address
Startup configuration:
and Mask
; J9085A Configuration Editor; Created on release #A.14.03
hostname "ProCurve Switch"
ip access-list extended "150"
permit tcp 10.10.20.100 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.255 eq 23
exit
snmp-server community "public" Unrestricted
.
.
Configured Source IP Configured Destination IP
.
Address and Mask Address and Mask
Figure 9-17. Using the “Named ACL” Context To Configure an ACL
Enabling or Disabling ACL Filtering on an Interface
You can configure one ACL to filter inbound traffic on multiple interfaces. For
limits and operating rules, refer to “ACL Configuration and Operating Rules”
on page 9-25.
Syntax: [no] interface < port-list > ip access-group < ascii-string > in
where: < ascii-string > = either a ACL name or an ACL ID number.
Assigns an ACL to a physical interface, which can be any
combination of ports and/or trunks that do not already have
an ACL assignment. You can use either the global
configuration level or the interface context level to assign
an ACL to an interface or remove an ACL from an interface.
9-53

 Loading...
Loading...














