Chapter 4. IBM System Storage DS planning and configuration 187
You have two methods to define hot spare drives:
Automatic assignment
Manual assignment
For an array that has FDE drives that are not secured, the hot-spare drive can be either an
unsecured FDE drive or a non-FDE drive.
For an array that has secured FDE drives, the hot-spare drive should be an unsecured FDE
drive of the same or greater capacity. After the unsecured FDE hot-spare drive is used as a
spare for a failed drive in the secured RAID array, it is security enabled.
Automatic assignment
For automatic hot spare assignment, follow these steps:
1. To automatically create the hot spare coverage using the drives that are available, select
Automatically assign drives, as shown in Figure 4-50. The recommended quantity of
spares drives needed for your configuration are created automatically.
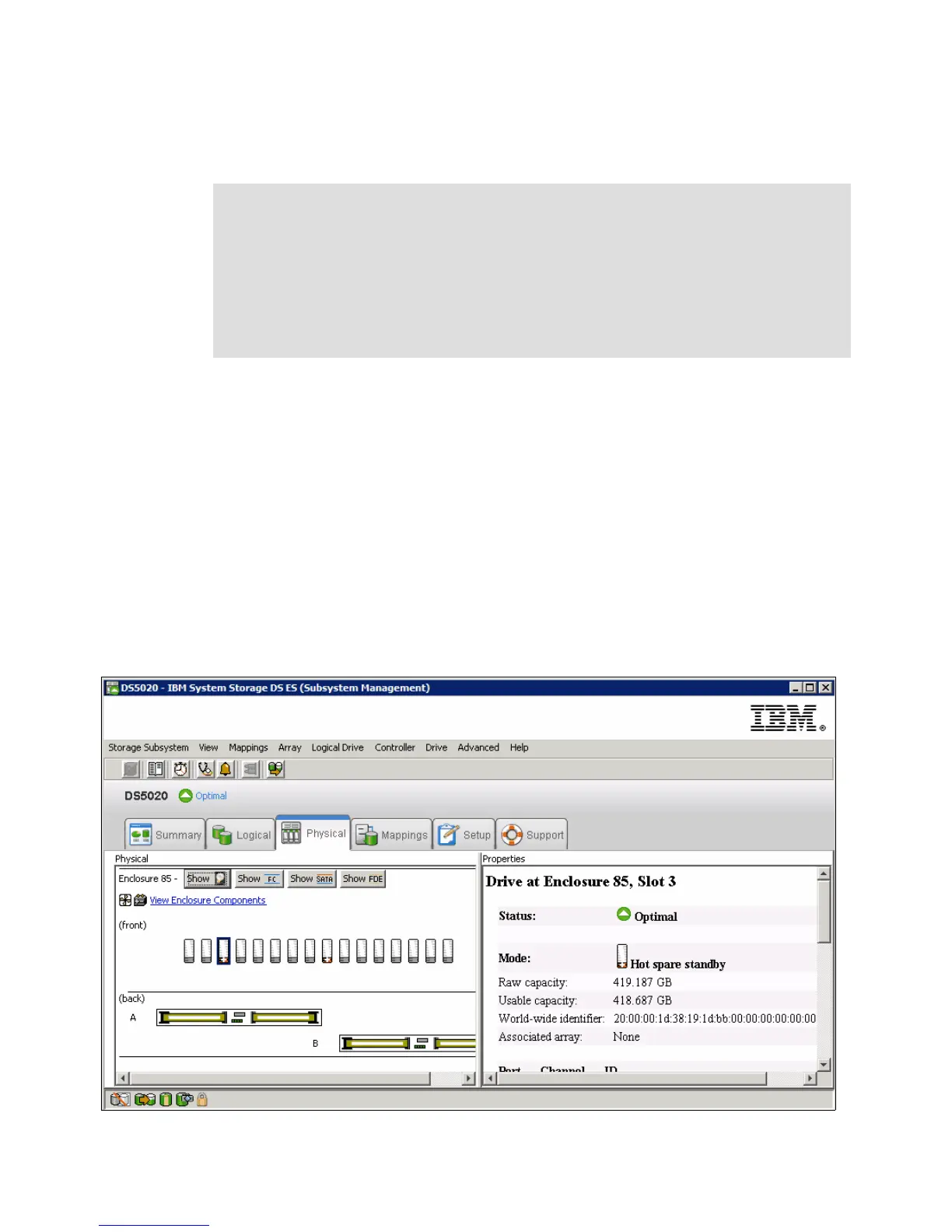
2. Select the Physical tab to view the results of the automatic hot spare creation. You see
the drives assigned in Figure 4-51.
Figure 4-51 Automatic hot spare creation
Tip: Select drives of equal or greater size than the total capacity of the largest disk in the
storage subsystem.
Especially in large configurations with arrays containing many drives, it might be necessary
to define multiple hot spares, because the reconstruction of a failed drive to a hot spare
can take a long time.
Consider having spares for each type of disk drives, that is, FC, SATA, and security
enabled FDE.

 Loading...
Loading...











