Chapter 4. IBM System Storage DS planning and configuration 235
Once the procedure is started, it cannot be stopped, as the subsystem needs to redistribute
the data contained in the array to all drives, including the new ones. There is a performance
impact during this operation, but the logical drives of the array remain available to the host
systems.
4.10.2 Defragment an array
A logical drive can be deleted anytime to free the space in the array. The free space might be
fragmented within the array in different free space nodes.
New logical drives cannot spread across several free space nodes, so the logical drive size is
limited to the greatest free space node available, even if there is more free space in the logical
drive. The array needs to be defragmented first to consolidate all free space nodes to one free
space node for the array. Then, all new logical drives can use the whole available free space.
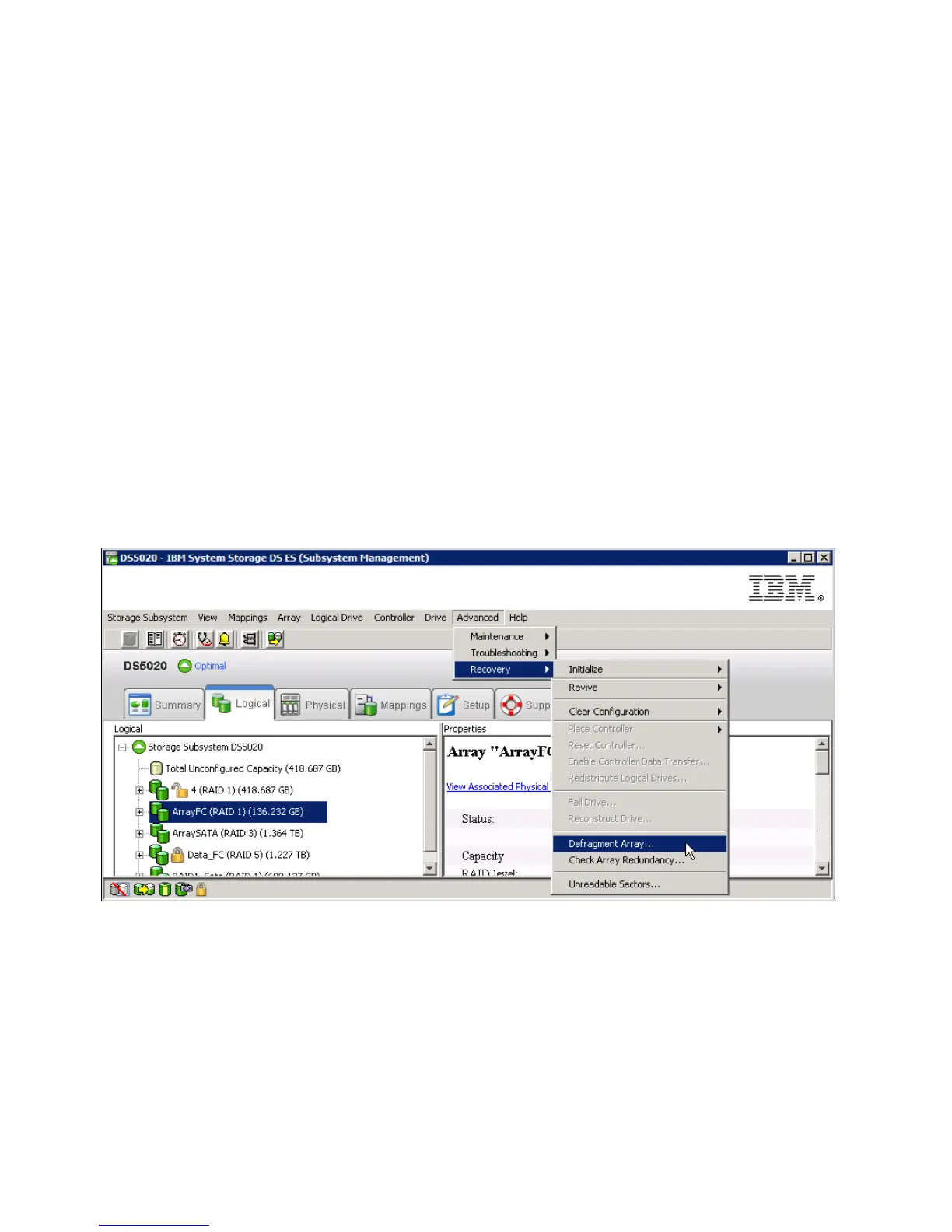
To accomplish this task, open the Subsystem Management window, highlight the array to
defragment, and select Advanced Recovery Defragment Array to start the procedure,
as shown in Figure 4-102. The defragmentation can run concurrently with normal I/O, but it
impacts performance because the data of the logical drives must be moved within the array.
Depending on the array configuration, this process continues to run for a long period of time.
Once the procedure is started, it cannot be stopped again. During this time, no configuration
changes can be performed on the array.
Figure 4-102 Defragment an array
The defragmentation done on the DS5000 storage subsystem only applies to the free space
nodes on the array. It is not connected to a defragmentation of the file system used by the
host operating systems in any way.

 Loading...
Loading...











