Appendix A. Overview of IBM System Storage DS5000 RAID types 511
Table A-2 shows the RAID 6 details.
Table A-2 RAID 6 details
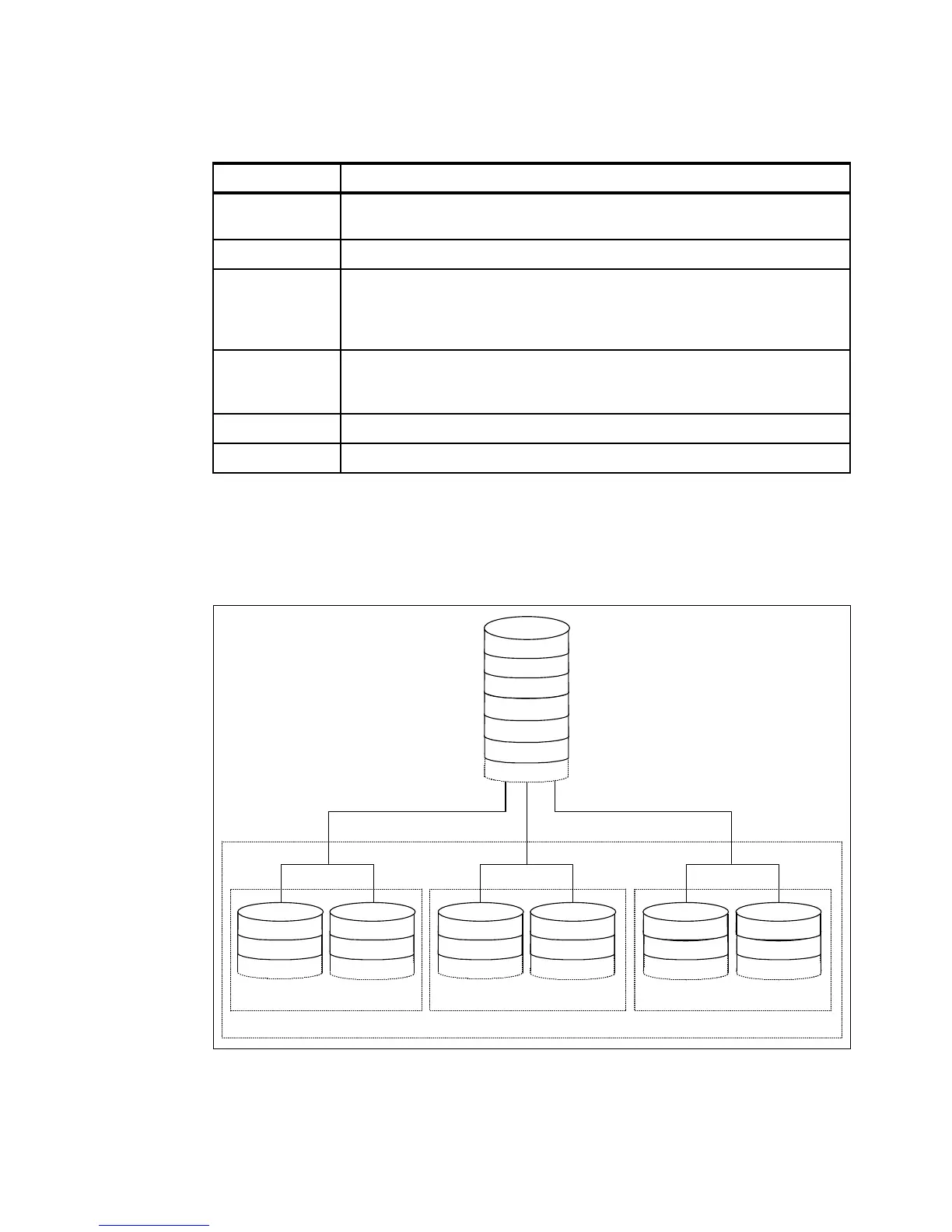
RAID 10: Higher performance than RAID 1
RAID 10 (Figure A-5), also known as RAID 1+0, implements block interleave data striping and
mirroring. In RAID 10, data is striped across multiple disk drives, and then those drives are
mirrored to another set of drives.
Figure A-5 RAID 10
Feature Description
Definition Distributed parity; Disk striping and two independent parity blocks per stripe
Can survive the loss of two disks without losing data
Benefits Data redundancy, high read rates, and good performance.
Considerations Requires two sets of parity data for each write operation, resulting in a significant
decrease in write performance.
Additional costs because of the extra capacity required by using two parity blocks
per stripe.
Uses Any application that has high read request rates and average write request rates.
Transaction servers, Web servers, data mining applications, and Exchange
servers.
Drives Minimum of three.
Fault Tolerance Yes.
Stripeset
etc.
Block 5
Block 4
Block 3
Block 2
Block 1
Block 0
Logical Drive
Host View
Controller
internal
mapping
Actual
device
mappings
Block 6
Block 3
Block 0
Disk 1
Block 6
Block 3
Block 0
Disk 2
Block 7
Block 4
Block 1
Disk 3
Block 7
Block 4
Block 1
Disk 4
Block 8
Block 5
Block 2
Disk 5
Block 8
Block 5
Block 2
Disk 6
Disk Array #1 Mirrorset
Disk Array #2 Mirrorset
Disk Array #3 Mirrorset

 Loading...
Loading...











