7 PROGRAMMING A ROBOT WITH IRC
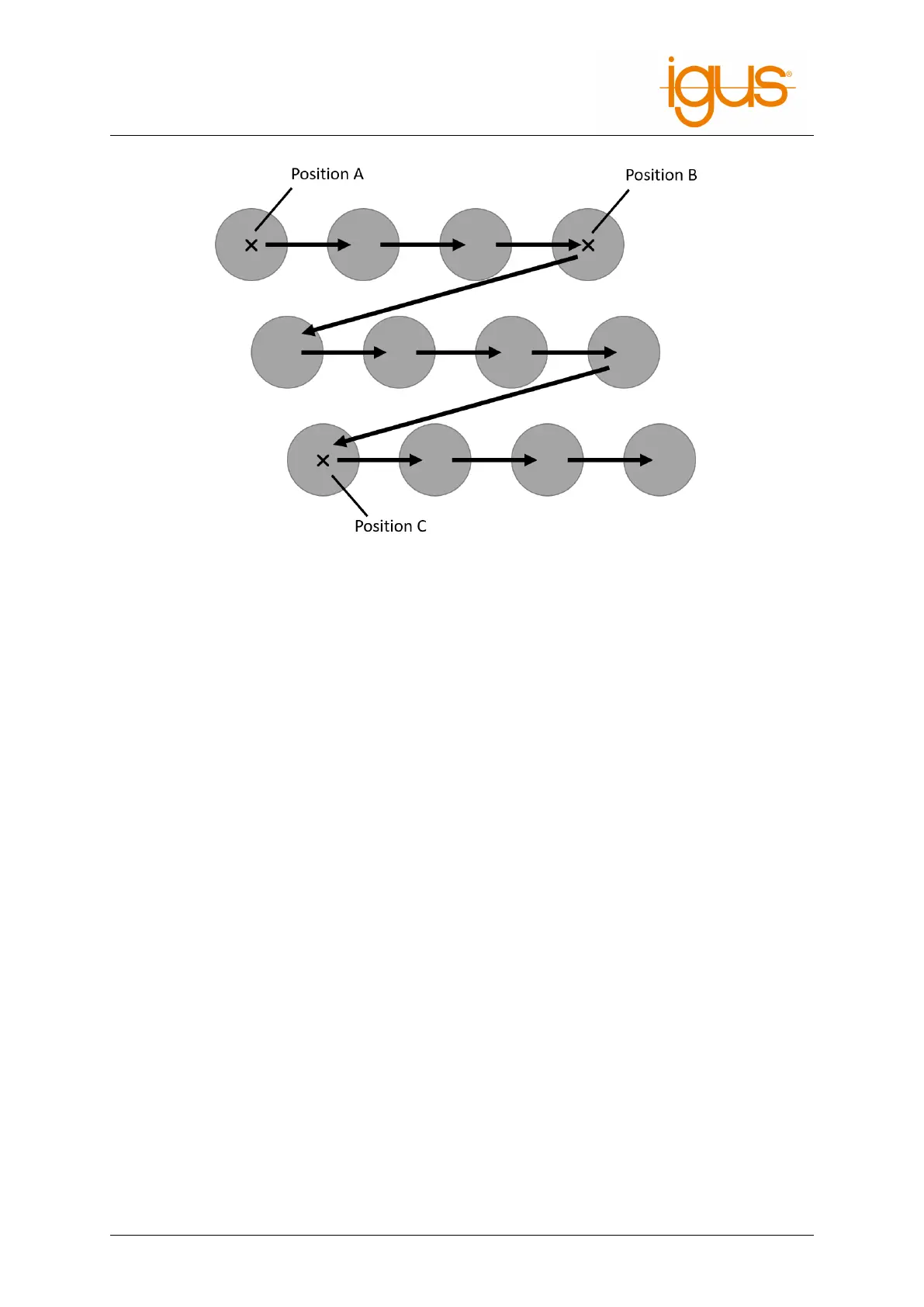
Figure 17: The matrix movement is from point A to B, then offset in direction C
.
7.5.8 Subprograms
Subprograms can be executed using the Sub command.
The path to the subroutine file is specified under "Filename". It is relative to the subfolder "Pro-
grams" of the iRC folder "Data". The command can be invoked from the menu item "Programflow"
→ "Subprogram".
7.6 Variables and Variable Access
Programs for iRC and TinyCtrl support two types of variables:
• Number variables: These can be used to store integer or floating point numbers.
• position variables: These can be used to store cartesian and joint positions. Whether such a
variable is interpreted as cartesian or joint depends on the context.
The cartesian components x, y, z are in mm, the euler angles A, B, C are in degrees. The joint
values are measured in mm or degrees depending on the type of axis.
7.6.1 User-defined Variables
It is possible to define variables with the Store command, which is accessible in the program editor
through the menu items under "Special" → "Variable definition".
Three types of store operations can be selected:
• "Current position":
A position variable is initialized with the cartesian and axis position of the robot when the com-
mand is executed.
• "NumberConstant":
A number variable is initialized with the constant specified in "value" (see 20).
• "PositionConstant":
A position variable is initialized with the constants specified in "Cartesian Position", "Joint Po-
©2022 igus® GmbH 32
 Loading...
Loading...