Basic Operation
2. Based on the above formula conversion relationship, calculate the M (slope
coefficient) and b (offset) values of the voltage setting value.
For example: When the instrument voltage input range is 0-100V, the user
needs a 0-10V analog signal to control the setting value of 0-100V. Then, M
is: 100–0/10–0=10, and b is: 0–0=0
3. Press the composite keys [Shift]+[P-set] (System) on the front panel to en-
ter the system menu.
4. Use knob or Up/Down key to select Ext-Program and press [Enter].
5. Set the Ext-Program→On / Off to On to turn on the analog function.
6. Use Up/Down key or knob to select the menu item CV, and set the M and b
values in CV mode.
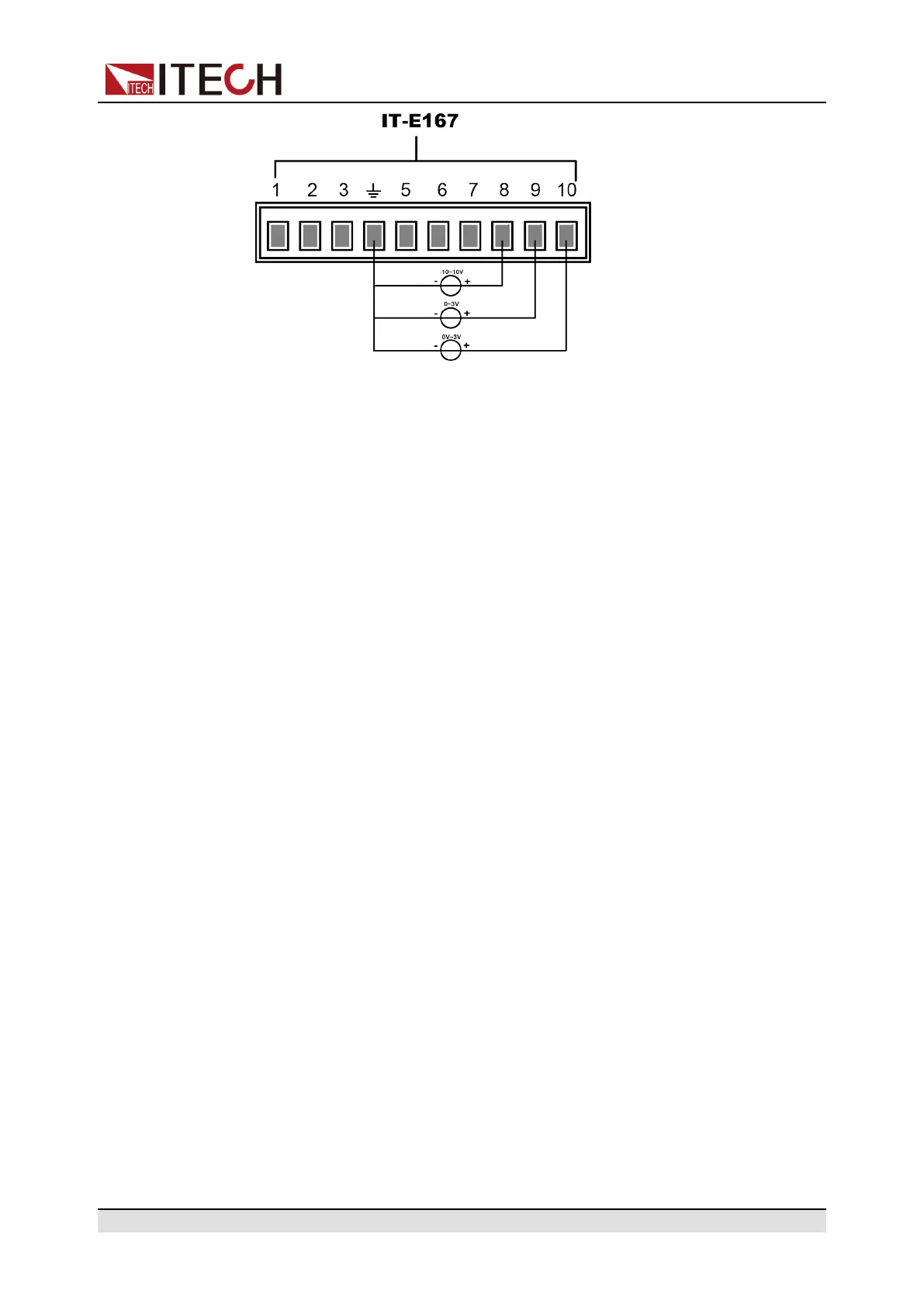
7. Input low-level voltage 1V in Pin 9, and input high-level voltage 3V in Pin 10.
Switch the existing mode to CV mode. For detailed mode definition, refer to
the description of analog quantity interface.
8. Input 0-10V voltage in Pin 8, and control the setting value of the input voltage
of this instrument.
For example, when the input voltage of Pin 8 is 1V, the setting value of the
input voltage of this instrument is 10V; when the input voltage of Pin 8 is 5V,
the setting value of the input voltage of this instrument is 50V. The corre-
sponding relationship meets the calculation relationship of y=Mx+b.
Voltage Monitoring and Current Monitoring
The analog interface can monitor the existing input voltage and input current.
Connect a digital voltmeter between Pin 5 and Pin 6 of the analog interface and
ground wire 4. The connection method is as shown below. The voltage reading
from -10 to 10V corresponds to the zero to full-scale voltage/current setting of
the instrument. The connection diagram is as shown below.
Copyright © Itech Electronic Co., Ltd.
102

 Loading...
Loading...