72 Chapter 3
Theory of Operation
Waveform Playback
segments. Each waveform segment is played out according to its segment and
sequence definition. A total of 1 million (220) loops can be defined for each
segment. After the last segment loop is executed, the entire sequence can repeat
continuously or for the predefined number of times.
Advanced Sequencing
NOTE Advanced sequencing is only available through the programatic interfaces.
Advanced sequencing enables the grouping of sequences into scenarios in a way
that is similar to how segments are grouped in sequencing. With scenarios you gain
more control of waveform playback.
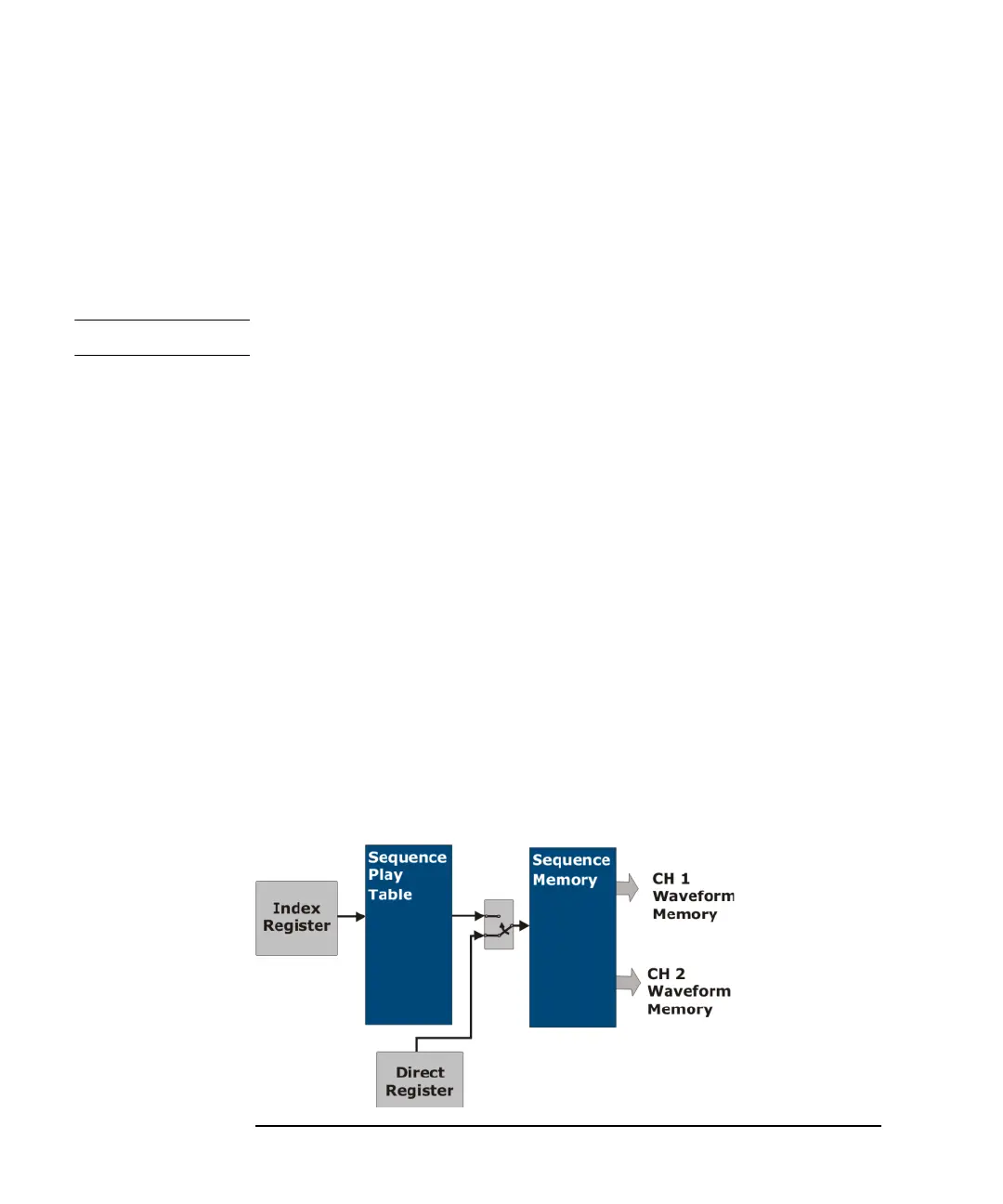
Scenario Pointer Source
There are two ways to choose which sequence to play.
• Index
A register is written to by the host processor that addresses entries in the
sequence play table. This register can be written to at any time including while a
sequence is playing. A valid Start trigger or Jump trigger starts the sequence
specified by the index in the register. The valid sequence index range is 0-16383.
Selecting invalid sequence indexes causes indeterminate behavior.
• Direct
The user can directly address waveforms in the sequencer memory completely
bypassing the play table. The next sequence pointer can be written to while a
sequence is being played. A valid Start trigger or Jump trigger starts the
sequence specified by the new pointer in the register. Addressing undefined
sequences causes indeterminate behavior.

 Loading...
Loading...











