59
Basic functions
Combination mode
Pitch page
Transpose, Detune (BPM Adjust)
These parameters adjust the pitch of the timbre.
• In a layer-type combination, you can set two or
more timbres to the same program, and create a
richer sound by using “Transpose” to shift their
pitch apart by an octave or by using “Detune” to
create a slight difference in pitch between the two.
• In split-type combinations, you can use
“Transpose” to shift the pitch (in semitone units) of
the programs specified for each key zone.
• If you wish to change the playback pitch of a drum
program, use “Detune.” If you change the
“Transpose” setting, the correspondence between
notes and drum sounds will change.
Adjusting the BPM of multisamples or samples cre-
ated in Sampling mode (requires the EXB-SMPL
option be installed)
If a timbre program uses multisamples or samples that
you created in Sampling mode (or loaded in Media
mode) to a specific BPM value, you can use the Utility
“Detune BPM Adjust” to call up a new specified BPM
value. This changes the BPM by changing the playback
pitch. (
☞PG p.38)
Note timing and scale settings
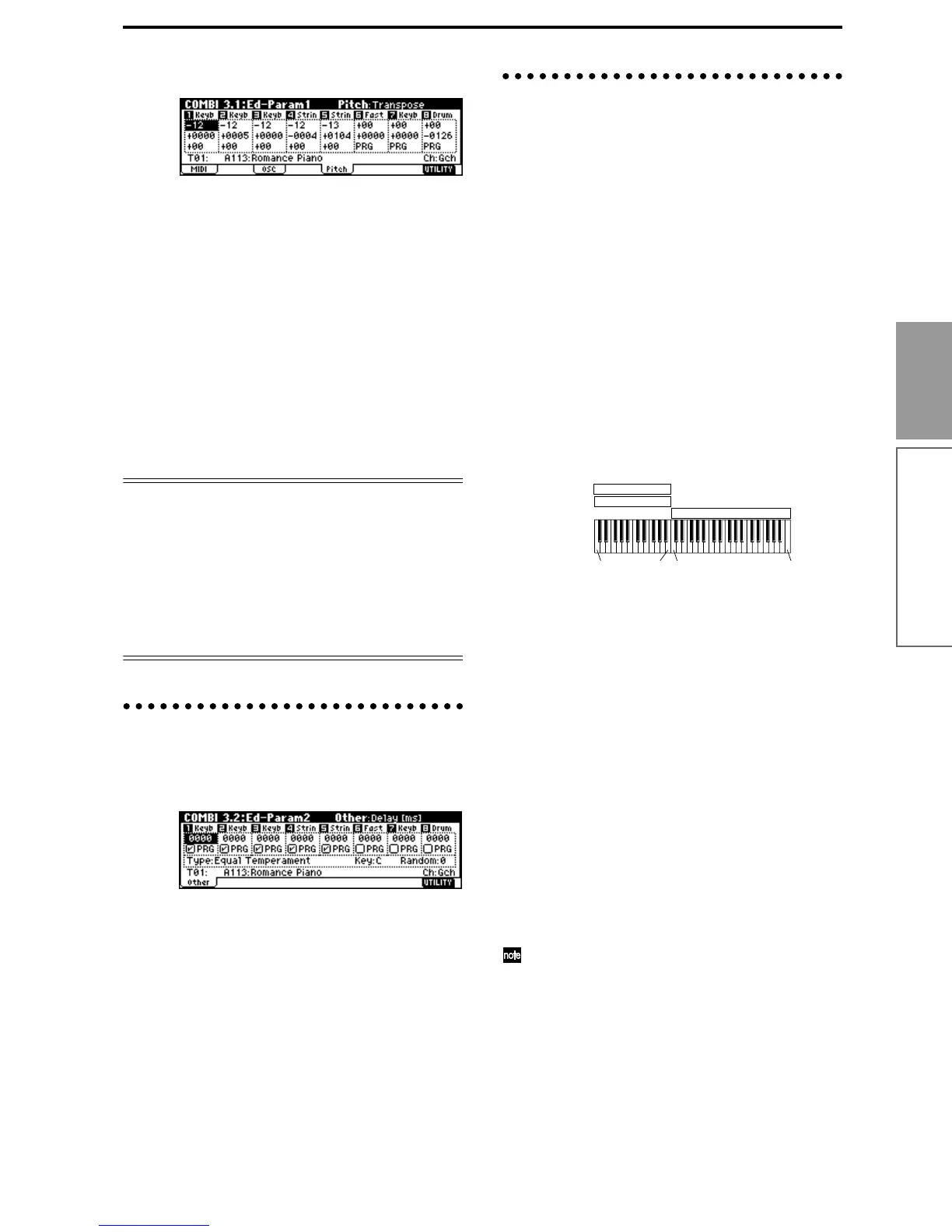
3.2: Ed–Param2
Other page
Delay [ms]
Specifies the timing at which the program of each tim-
bre will sound. Specify the time from when you play
the keyboard until the program will sound.
If you select KeyOff for this parameter, the timbre will
sound when the note is released.
Use Prog’s Scale, Combi’s Scale
Specifies the scale for each timbre. If you check “Use
Prog’s Scale,” the scale specified by the program will
be used. Timbres for which this is not checked will use
the “Combi’s Scale” setting.
Layer and split settings
3.3: Ed–Key Zone
Indicates settings such as layer, split, and keyboard
crossfade.
Key page
Specifies the range of notes that will sound each tim-
bre. Each area that sounds a timbre is referred to as a
Key Zone. By setting key zones, you can create a com-
bination in which different programs sound in differ-
ent areas of the keyboard.
By combining key zones specified for each timbre, you
can create layered or split combinations.
The upper and lower limits for the key zone of each
timbre are set by the “Top Key” and “Bottom Key”
respectively.
For example in the following diagram, timbres 1–3 are
set to create a layered and split combination. This is
specified by the key zone settings.
Timbres 2 and 3 create a layer. Timbre 1 and timbres 2/
3 are split between the B3 and C4 note numbers.
As an example here, we will explain how to create a
combination like the one shown above.
1 In the 1.1: Play, Prog page or the 2.1: Ed-Prog/Mix,
Prog page, use the “Program Select” area to select
the program that will be used for each timbre 1–3.
Select a piano program for timbre 1.
Select a brass program for timbre 2.
Select a strings program for timbre 3.
2 In the MIDI page of 3.1: Ed-Param1, set “Status” to
INT for all the timbres that you wish to use, and
set “MIDI Channel” to either Gch or to match the
global MIDI channel (a “G” will be displayed
after the channel number).
3 In the Key page of 3.3: Edit-Key Zone, set “Top
Key” and “Bottom Key.”
Set timbre 1 to a “Top Key” of G9 and a “Bottom
Key” of C4.
Set timbres 2 and 3 to a “Top Key” of B3 and a “Bot-
tom Key” of C–1.
You can also enter these values by holding down
the [ENTER] key and playing a note on the key-
board of this instrument.
Slope page
Here you can specify the range of keys over which the
original volume will be reached, starting at the top key
and bottom key.
In the case of the above example, you could set the key
zones so that a portion of timbres 1 and 2 overlaps (i.e.,
is layered) with timbre 3, and set “Top Slope” and
“Bottom Slope” so that the sound changes gradually,
instead of changing suddenly between B3 and C4.
PianoTimbre 1
Brass
Timbre 2
Strings
Timbre 3
C–1 C4 G9B3

 Loading...
Loading...
















