THEORY OF OPERATION
MOTOMAN 3-5 Spot Welding Manual for Medar
3.3.6 Primary Current
Primary current indicates the average amount of buss current that is required to
make a weld. This value is read directly from a current pickup coil within the weld
control cabinet. Together with the turns ratio, the secondary current can be
determined with the primary current as follows:
I secondary = I primary X Turns Ratio
3.4 AC Welding
In AC spot welding, AC line power is stepped down to low voltage/high current by
a transformer (transgun). The weld control “fires” the power to the gun and
controls the weld sequence in units of cycles (1/60 seconds). The control includes
a sophisticated feedback loop to ensure that weld power is adjusted for line power
variations.
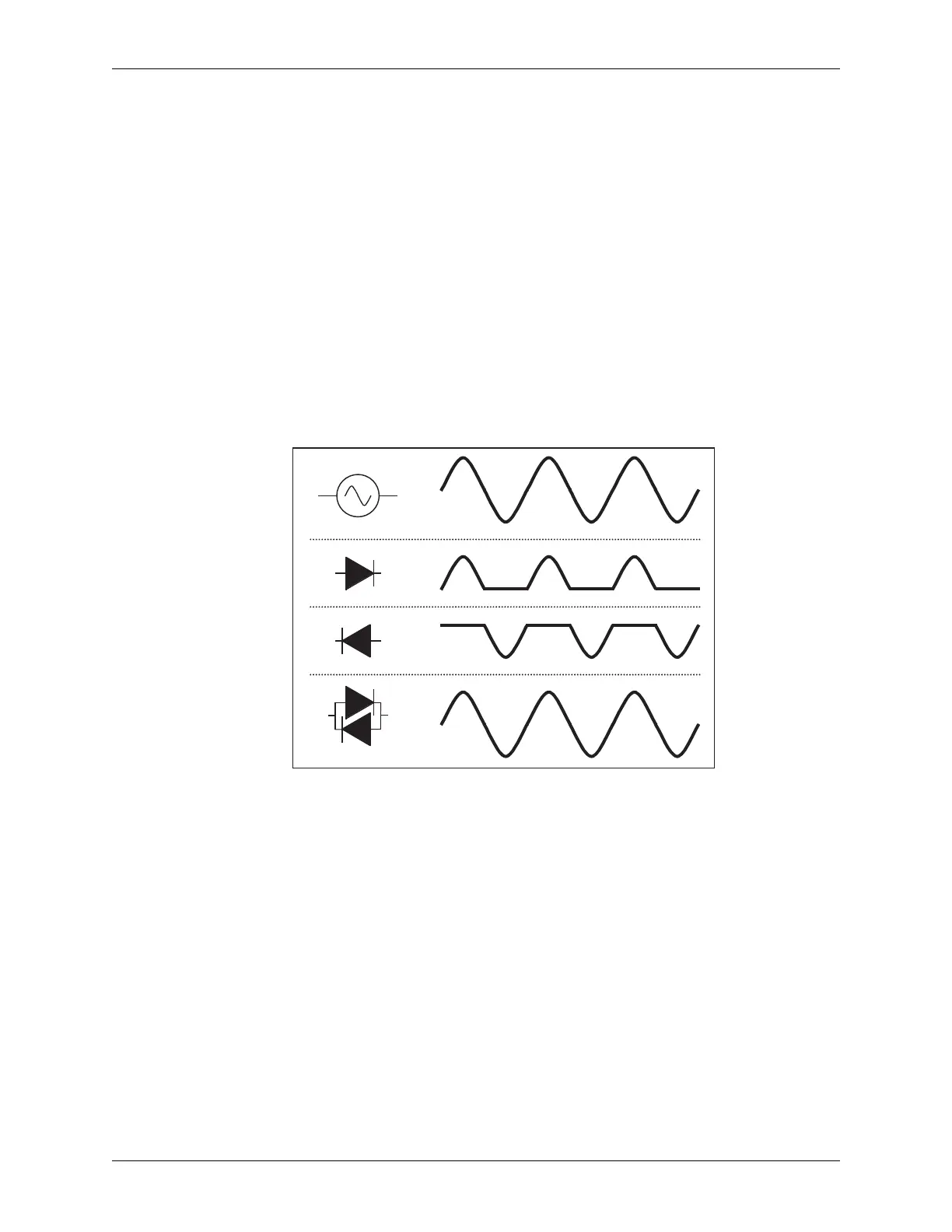
Modern AC welding power sources use silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) as the
main current control contactors. These are essentially gate-controlled diodes, and
work as shown in Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-4 AC Welding
Current is regulated by enabling the SCR of different sine wave angles, as
illustrated in Figure 3-5. More current is delivered as more of the sine wave is
allowed to conduct.
 Loading...
Loading...