THEORY OF OPERATION
MOTOMAN 3-7 Spot Welding Manual for Medar
Resistance to electrical current causes heat. More resistance generates more heat.
Heat is bad for a welding system. Therefore, there should be as little resistance as
possible on the secondary circuit in order to avoid generating heat. The greatest
amount of resistance must be concentrated where the parts to be welded are joined,
since this is where the most heat is required. As resistance increases in the circuit,
otherwise usable power is converted to waste heat that is diverted away from the
weld point.
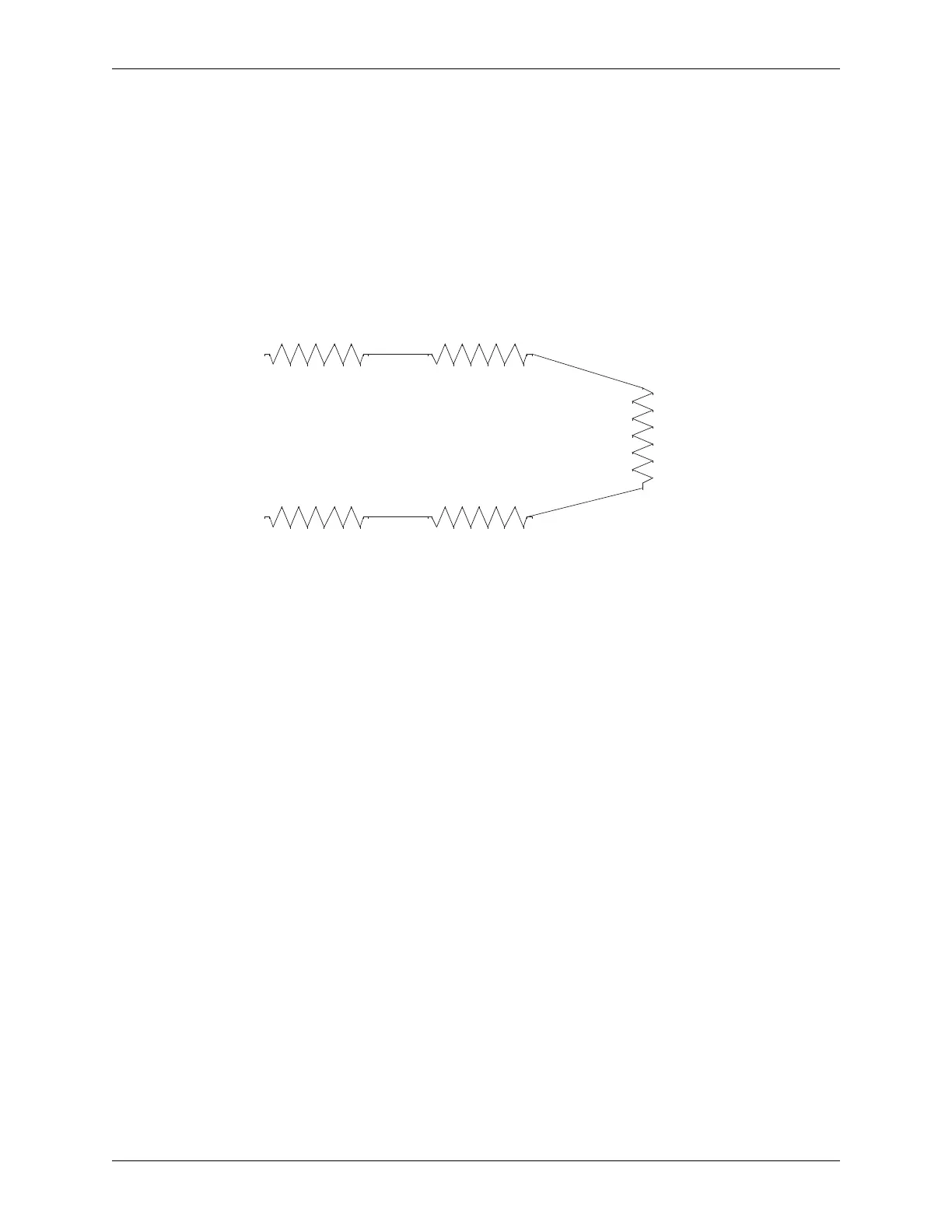
Figure 3-6 shows what happens to the heat when resistance is high in places other
than the part contact area. In this simple circuit, only 40 percent of the current is
used for welding.
Figure 3-6 Welding Circuit with Heat Loss
200µΩ
Part
100µΩ
50µΩ
50µΩ
100µΩ
 Loading...
Loading...