TROUBLESHOOTING
Spot Welding Manual for Medar 5-4 MOTOMAN
5.3 Troubleshooting Welding Problems
Table 5-2 identifies common problems that occur during resistance welding. To
troubleshoot your system, identify the type of problem and look for it in the
PROBLEM column. Next to this column is a list of PROBABLE CAUSES.
Be aware that sometimes more than one problem can occur at the same time. After
identifying and resolving a problem, test the system thoroughly to make sure no
other problems exist.
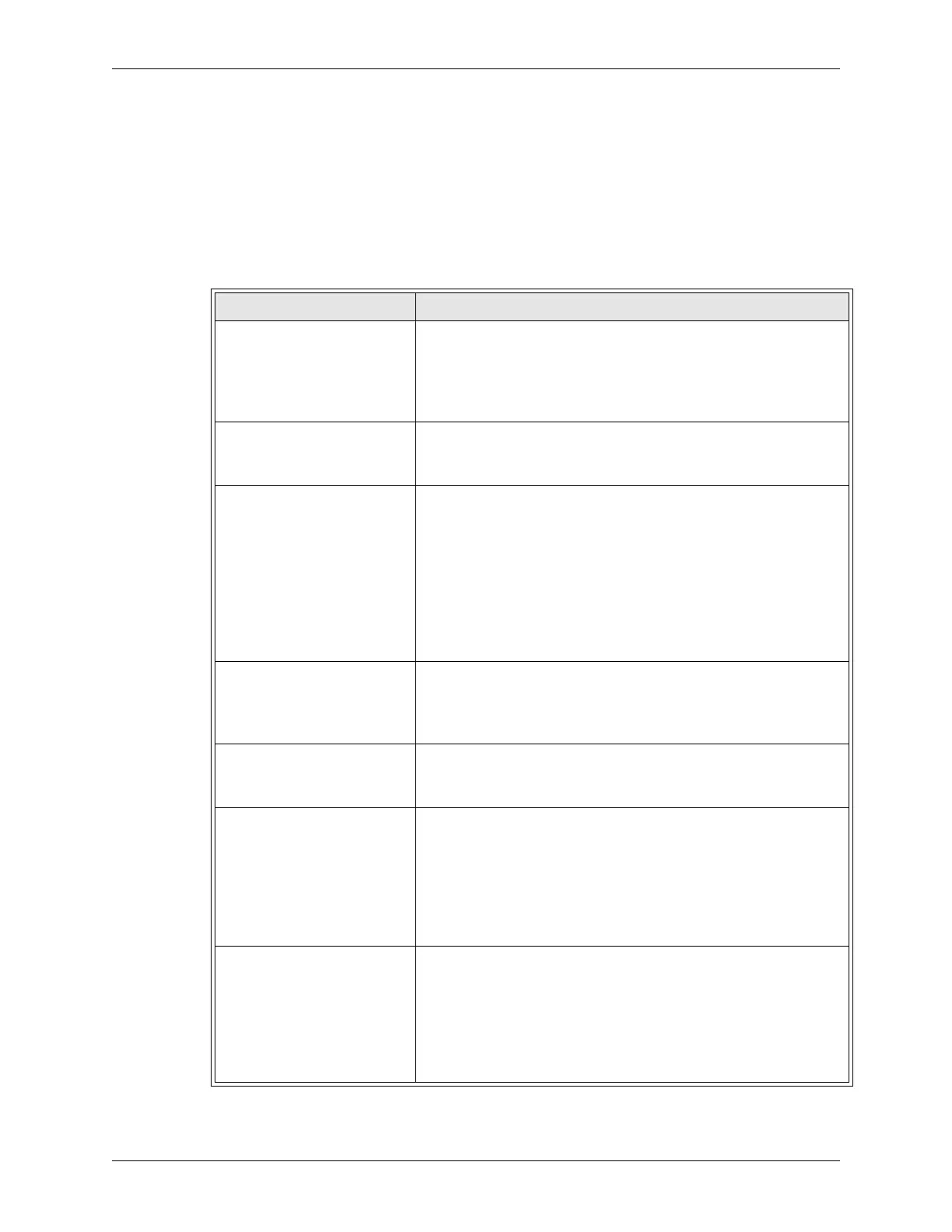
Table 5-3 Welding Troubleshooting Chart
Problem Probable Causes
Excessive indentation Weld force too high, weld current too high, or weld time too long.
Electrode face too small.
Fit up is poor.
Speed regulator on cylinder is missing.
Pressure regulation is poor.
Electrode is mushrooming Weld force too high, weld current too high, or weld time too long.
Electrode face too small.
Insufficient electrode cooling.
Weld nugget is undersized Weld force is too high.
Weld current is too low.
Weld Time is too short.
Fit up is poor.
Heat balance is poor.
Weld spacing is too close.
Weld is too close to edge of part.
Shunt path is in secondary.
Excess ferrous material in throat.
Weld nugget is offset Electrodes are not flat and parallel.
Electrodes are misaligned.
Fit up is poor.
Heat balance is poor.
Misshapen weld nugget Electrodes are not flat and parallel.
Electrodes are misaligned.
Fit up is poor.
Expulsion at weld surface Weld force too low, weld current too high, or weld time too long.
Electrode face too small.
Electrodes are not flat and parallel.
Fit up is poor.
Material is dirty.
Squeeze time is too short.
Follow up is poor.
Expulsion at interface Weld force too low, weld current too high, or weld time too long.
Electrode face too small.
Fit up is poor.
Weld is too close to edge of part.
Material is dirty.
Squeeze time is too short.
Follow up is poor
 Loading...
Loading...