OMICRON 33
Introduction to capacitance and dissipation factor measurement
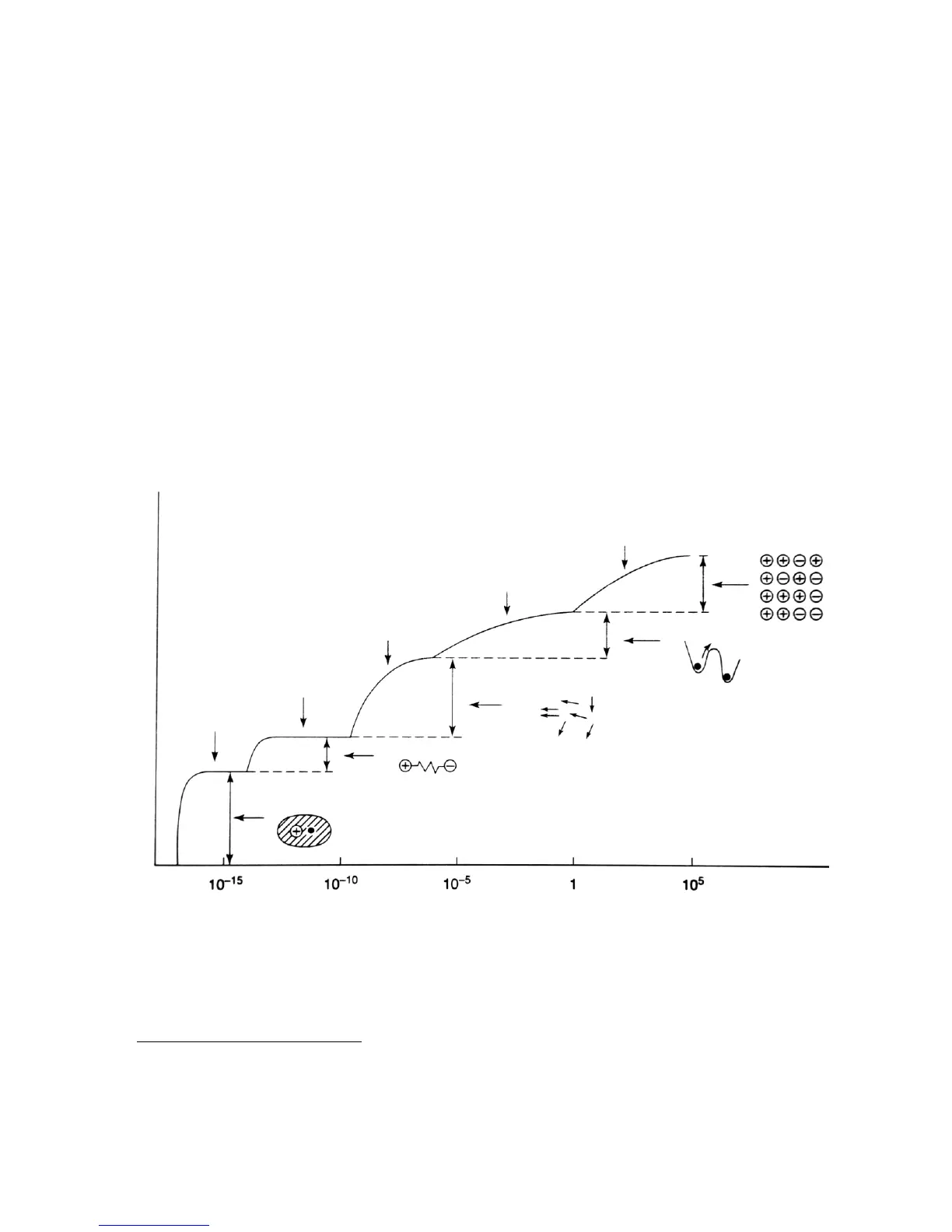
The dielectric losses in the insulation are caused by polarization and conduction phenomena. The
different polarization mechanisms are caused by various physical processes:
[1]
• Electronic polarization: Shifting of the (negative) atomic shell charge concentration towards the
(positive) nucleus charge concentration.
• Ionic Polarization: Shifting of positive and negative ions relative to each other.
• Orientation polarization: Alignment of permanent dipoles due to the applied electrical field.
• „Hopping“ polarization: „Hopping“ polarization is caused by movement of so called „hopping charge
carriers“. These charge carriers are stationary most of the time but at times change their position
through tunneling or thermal activation.
[2]
• Space Charge Polarization: If different dielectrics with different permittivities and conductivities are
present in a material, this can lead to accumulations of charge carriers at the boundary surfaces of
these dielectrics.
Figure 4-4: Polarization mechanisms an their respective time constants
[3]
1. Zaengl, W.: Dielectric Spectroscopy in Time and Frequency Domain for HV Power Equipment, Part I: Theoretical
Considerations. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, Vol. 19, No. 5, 2003, pp. 5-19
2. Jonscher, A.K.: Dielectric Relaxation in Solids. Chelsea Dielectric Presss, 1983, ISBN: 0950871109
3. Kao, K.-C.: Dielectric Phenomena in Solids. Academic Press; 1st edition, 2004, ISBN 0123965616

 Loading...
Loading...