3-9
3 EtherCAT Communications
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherCAT Port User’s Manual (W505)
3-3 State Transitions for EtherCAT Communications
3
3-3-1 Self Diagnosis at Startup
3-3 State Transitions for EtherCAT
Communications
The EtherCAT master executes the following self-diagnosis when the power is turned ON.
The results of self-diagnosis are provided in the following system-defined variables as EtherCAT mas-
ter errors if errors are detected.
Refer to Error Descriptions in Errors in the EtherCAT Master Function Module in the NJ/NX-series Trou-
bleshooting Manual (Cat. No. W503-E1-19 or later) for details on error types.
EtherCAT communications provides four control states. Communications is controlled by moving
between these states.
After the power is turned ON, the communications master and slaves go from the Init state to the Pre-
operational state, Safe-operational state, and then Operational state before starting EtherCAT commu-
nications. Afterwards, EtherCAT communications are performed while the state changes automatically
between these states according to error occurrence and other conditions.
3-3-1 Self Diagnosis at Startup
Diagnosis Detected error type System-defined variables
Diagnosis of network configuration
information
Network configuration information error _EC_NetCfgErr
Diagnosis of communications port MAC address error _EC_MacAdrErr
Communications controller error _EC_LanHwErr
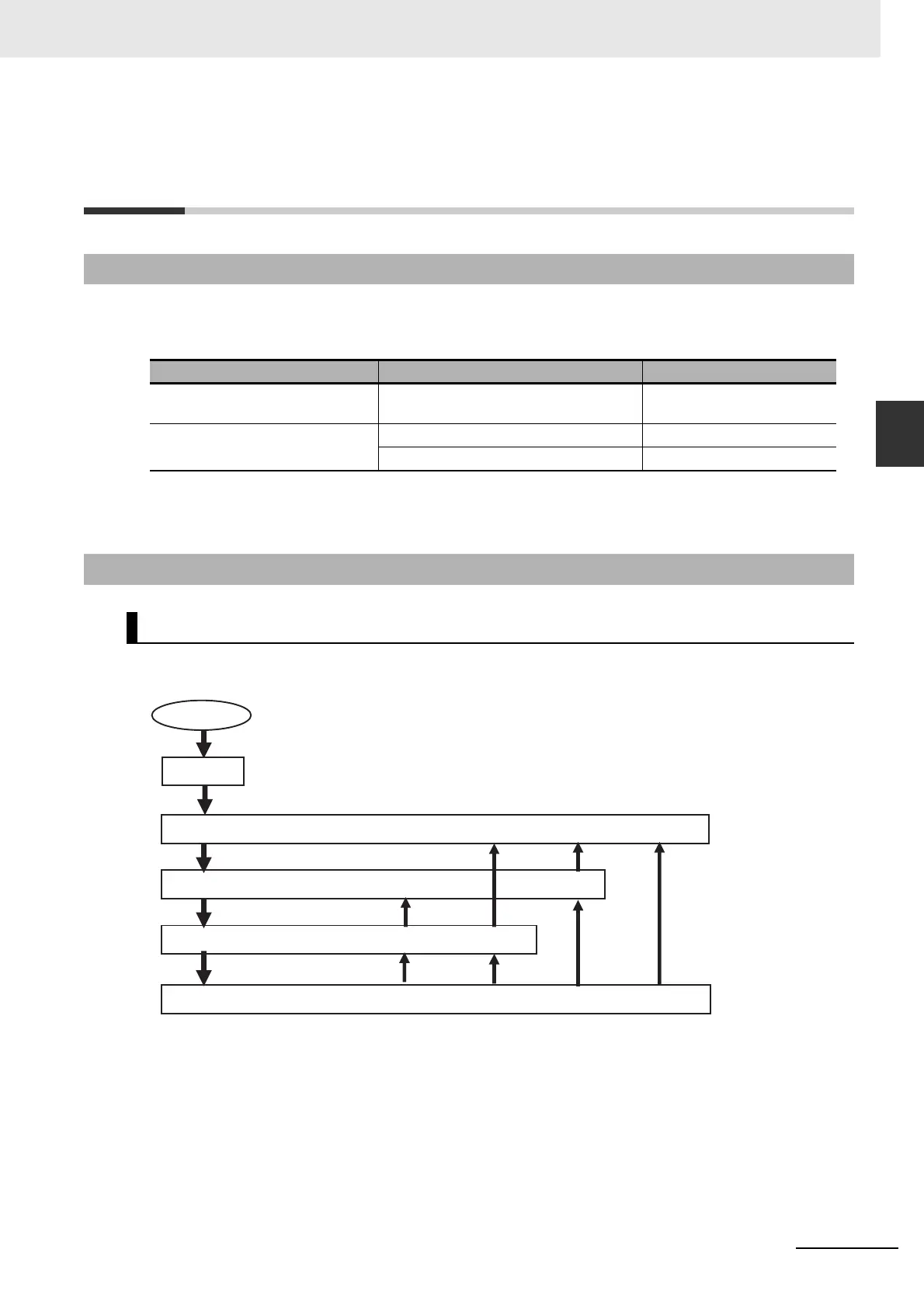
3-3-2 Control States for EtherCAT Communications
Control State Machine
Power ON
Self-diagnosis
4. Operational state (I/O for process data communications and SDO communications are possible.)
3. Safe operational state (Inputs for process data communications and
SDO communications are possible.)
2. Pre-operational state (Only SDO communications is possible.)
1. Init state (Process data communications and SDO communications are not possible.)

 Loading...
Loading...