3-11
3 EtherCAT Communications
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherCAT Port User’s Manual (W505)
3-3 State Transitions for EtherCAT Communications
3
3-3-3 CPU Unit Status in Relation to EtherCAT
I/O Refreshing
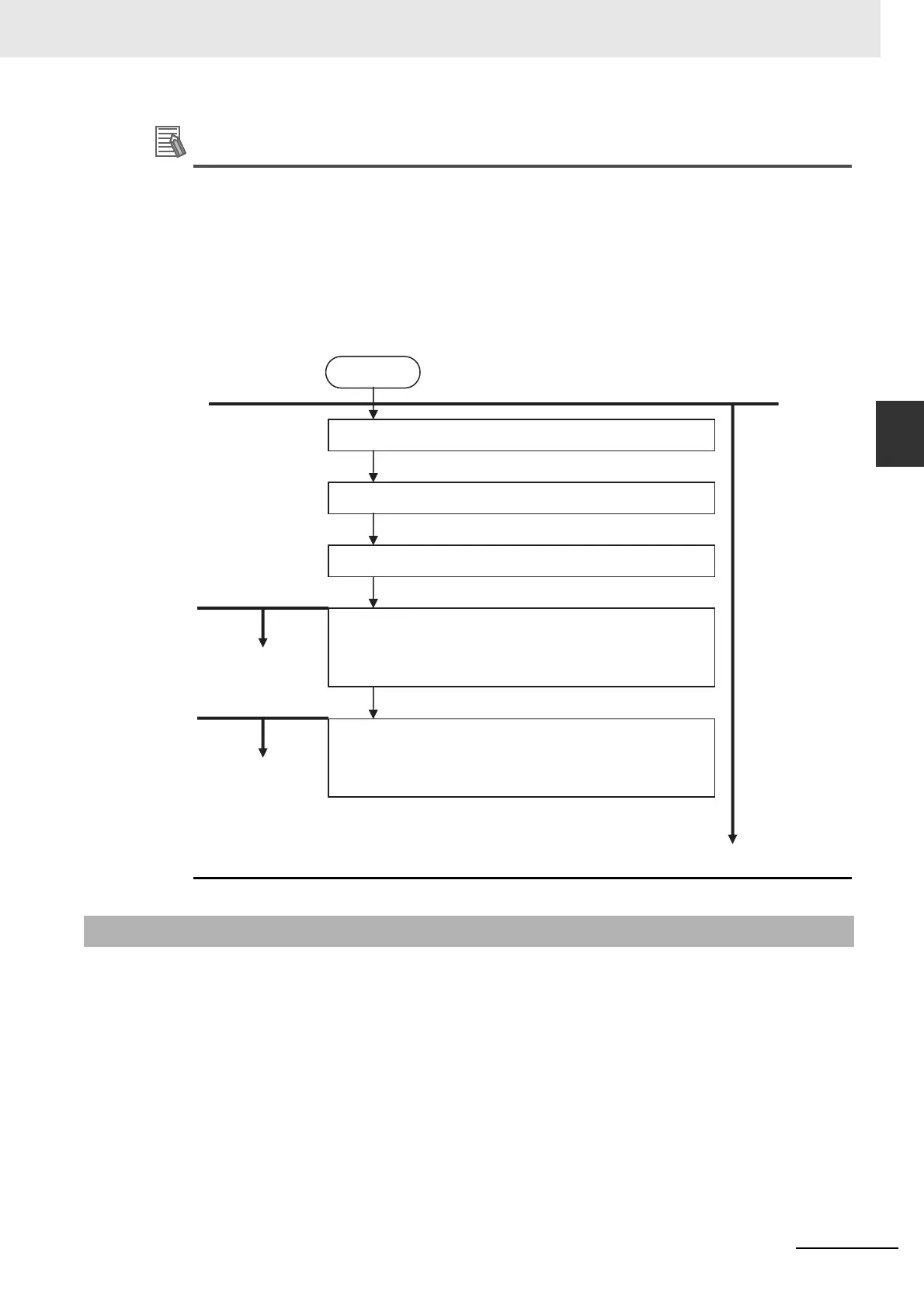
The procedure from startup of the EtherCAT network until process data I/O can be refreshed is
shown below. There is no correlation between the startup of the EtherCAT network and the exe-
cution of the user program. Design the user program by adding the system-defined variables* for
the relevant slaves to the interlock conditions of the device variables for the slaves.
* _EC_ActSlavTbl[1..n], _EC_MBXSlavTbl[1..n], _EC_PDSlavTbl[1..n], _EC_DisconnSlavTbl[1..n], and
_EC_DisableSlavTbl[1..n]
Here, n is the maximum value of the settable node address. Refer to 1-3-1 Performance Specifications for
the maximum value of the settable node address.
Refer to A-1 EtherCAT Status in Relation to CPU Unit Status for details on the following: memory
related to the EtherCAT master, the ability to download master settings and slave settings, and the sta-
tus of slaves according to the CPU Unit operating mode and the status of Controller errors.
3-3-3 CPU Unit Status in Relation to EtherCAT
START
I/O refreshing started
for the relevant slave.
User program executed.
Applicable slave
parameters can be set.
5. When the system-defined variable _EC_PDSlavTbl for the
relevant slave changes to TRUE, I/O refreshing for the relevant
slave is enabled.
4. When the system-defined variable _EC_MBXSlavTbl for the
relevant slave changes to TRUE, message communications for
the relevant slave are possible.
3. The program waits for slaves to join the EtherCAT network.
2. Slaves initialized based on network configuration information.
1. EtherCAT master initialized.
Power ON

 Loading...
Loading...