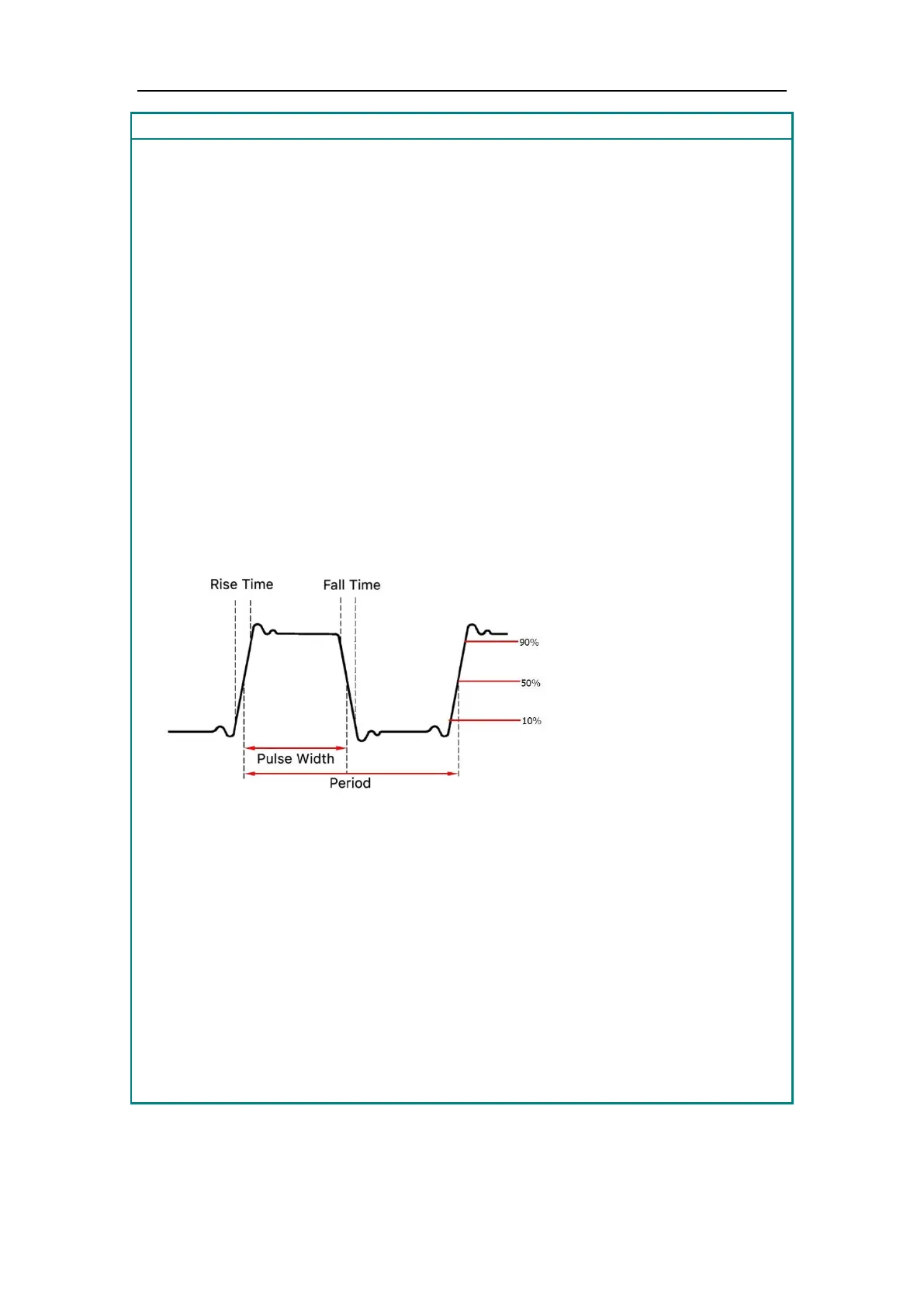
Pulse Width
PW is an abbreviation for pulse width and is divided into positive pulse width
and negative pulse width.
The positive pulse width is the time interval from 50% of the rising edge to 50%
of the adjacent falling edge.
The negative pulse width is the time interval from 50% of the falling edge to
50% of the adjacent rising edge.
The pulse width is determined by the period and duty cycle of the signal. The
calculation formula is pulse width = period * duty cycle.
Duty Cycle
In a series of ideal pulse sequences (such as a square wave), the ratio of the
duration of the positive pulse to the total pulse period.
Pulse/Duty Cycle
The pulse width is defined as the time interval from the 50% threshold of the
amplitude of the rising edge of the pulse to the 50% threshold of the amplitude
of the next falling edge, as shown in the following figure.
⚫ The settable range of pulse width is limited by the "minimum pulse width"
and "pulse period"
Pulse width ≥ minimum pulse width
Pulse width ≤ pulse period - minimum pulse width
⚫ The pulse duty cycle is defined as the pulse width as a percentage of the
pulse period.
⚫ The pulse duty cycle is associated with the pulse width, and modifying one
of the parameters will automatically modify the other parameter. The pulse
duty cycle is limited by the "minimum pulse width" and "pulse period".
Pulse duty cycle ≥ minimum pulse width ÷ pulse period × 100%
Pulse duty cycle ≤ (1 - 2 × minimum pulse width ÷ pulse period) × 100%

 Loading...
Loading...