Reference MVI69E-MBTCP ♦ CompactLogix Platform
User Manual Modbus TCP/IP Enhanced Communication Module
Page 124 of 150 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
June 28, 2017
In the above example, the client's Modbus command to transmit inside the
Modbus packet is as follows.
In this example, the client's Modbus packet contains the data byte and data word
counts that have been doubled from the amount specified by Reg Count due to
the Float flag set to Y. Some servers look for the byte count in the data packet to
know the length of the data to read from the wire. Other servers know at which
byte the data begins and read from the wire the remaining bytes in the packet as
the data the client is sending.
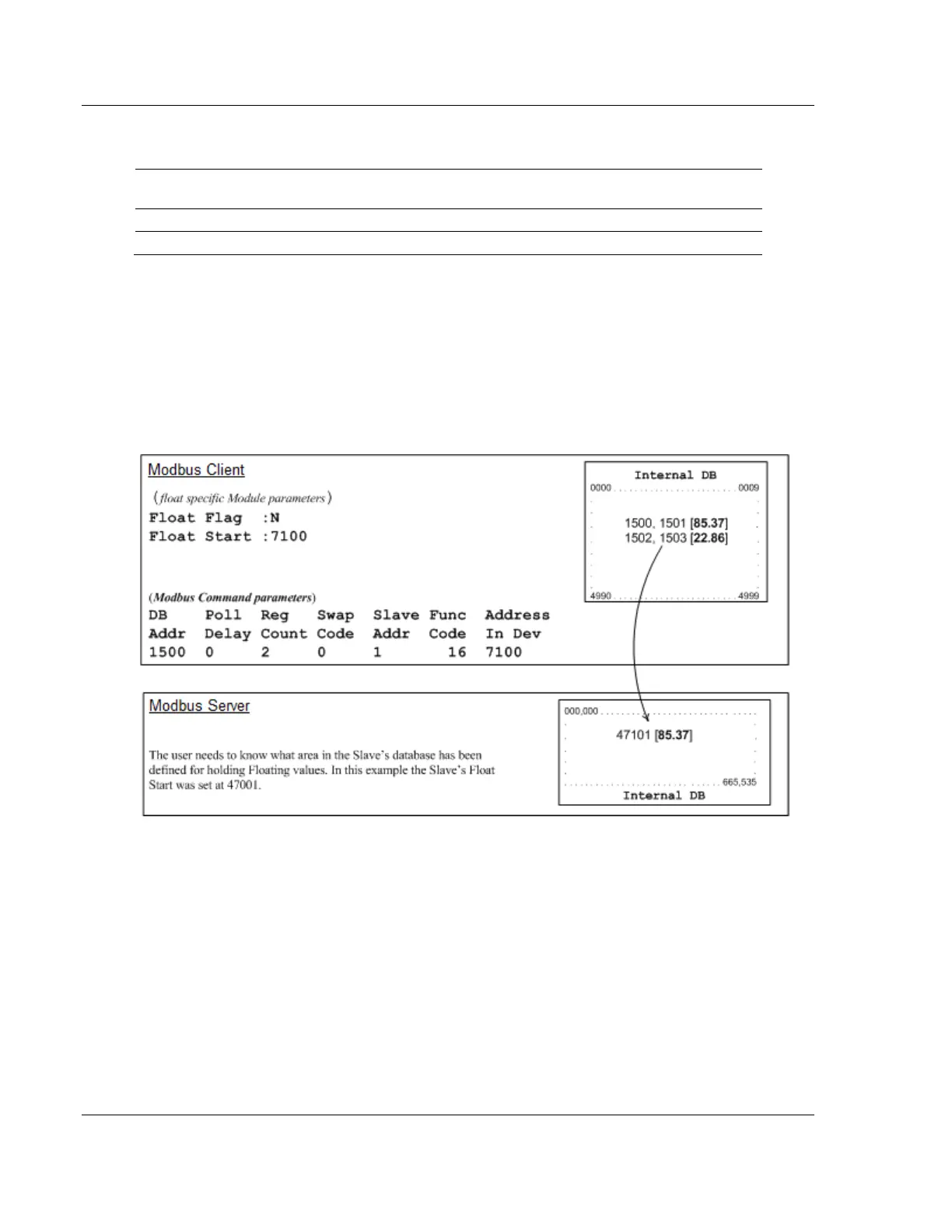
Example #2: client is issuing Modbus command with FC 16 (with Float Flag: No) to transfer
Float data.
Float Flag: "N" tells the client to ignore the floating values and treat each
register data as a data point composed of 1 word, 2 bytes or 16 bits.
Float Start: Ignored.
DB Addr - same as when Float Flag: Y.
Reg Count - Tells the client how many data points to send to the server.
Swap Code - same as when Float Flag: Y.
Func Code - same as when Float Flag: Y.
Addr in Dev - same as when Float Flag: Y as long as the server's Float Flag = Y.
 Loading...
Loading...