Page 28
Example 2 Alternating Control (pump down)
Example 2 Alternating Control (pump down)Example 2 Alternating Control (pump down)
Example 2 Alternating Control (pump down)
A sump is typically used to temporarily hold water or effluent, and when the
level reaches a specific point, the sump is pumped down, with the fluid
being transferred to another process.
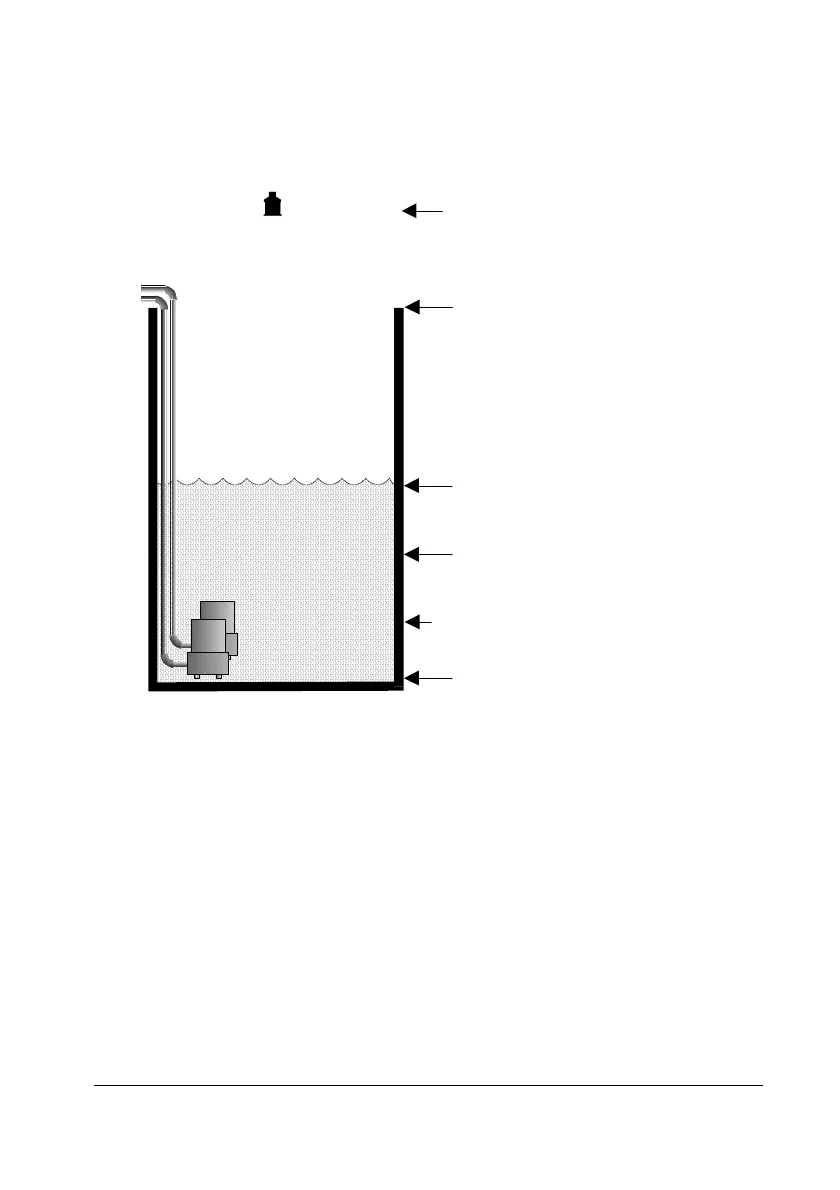
empty distance (P105), 5.0m
100%, span (P106), 4.7m
(output = 5VDC)
pump 1+ 2 off (P214, 224), 0.5m
0% , empty level (output = 0VDC)
pump 2 on (P 223), 1.4m
pump 1 on (P 213), 1.0m
In this example a blackbox with dB6 is being used to control pumps on a
pump down application, there are two pumps, and the duty pump is to be
alternated between the pumps.
This will operate as follows. During normal operation, pump 1 will come
on at 0.8 m, and pump down to 0.5 m. The setpoints are then shifted to
pump 2, which will come on first next time.
During peak periods, when pump 1 cannot cope, pump 1 will come on at
1.0m, pump 2 will come on at 1.4 m, and pump down to 0.5 m. The
setpoints are then shifted to pump 2, which will come on first next time.
The 0 to 5VDC output will be representative of level.
 Loading...
Loading...