Model 3095FB Multivariable Transmitter with Modbus Protocol
Modbus Protocol Guide
Page 9 of 79
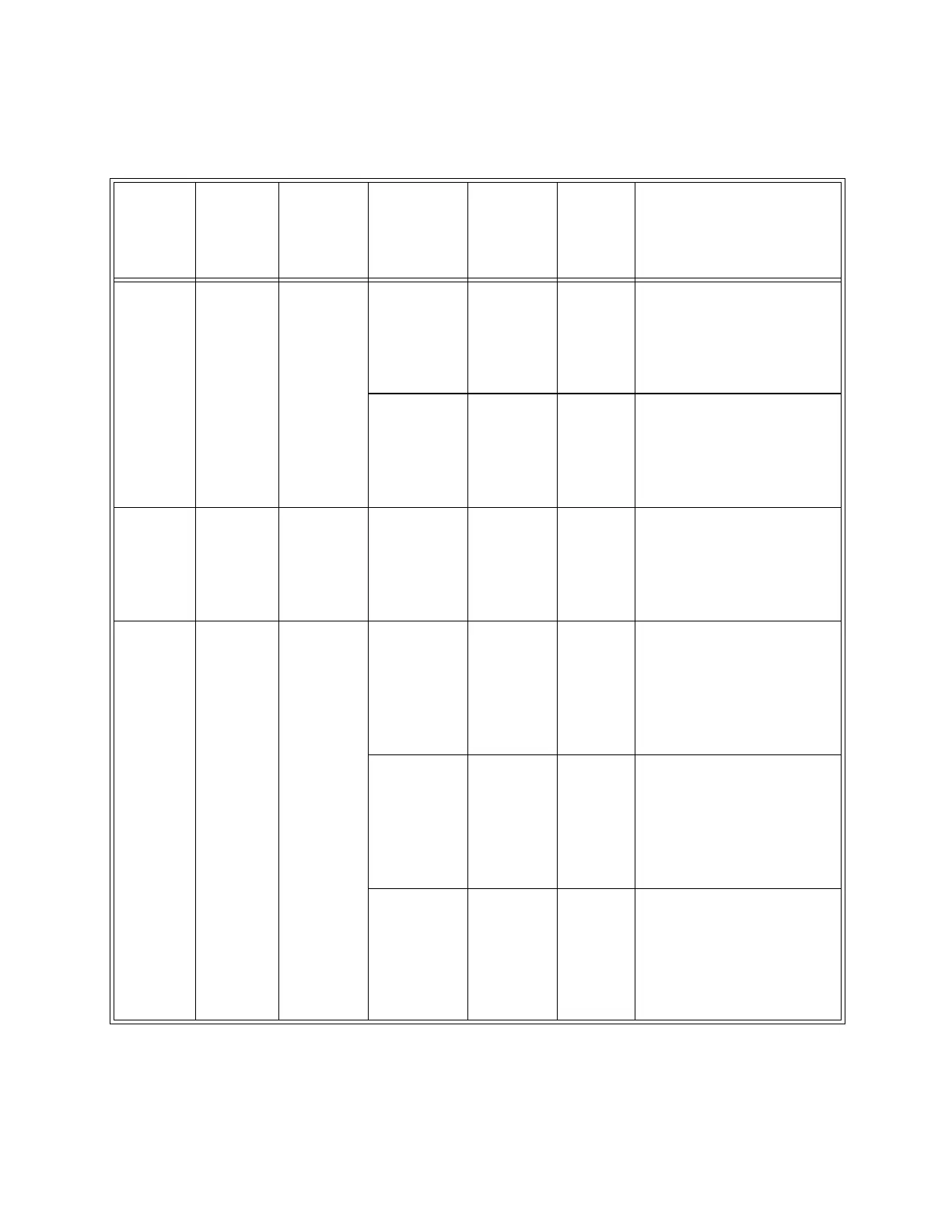
Table 2-2 Data Types According to Function Code and Mapped Address
Address
start
register
Address
end
register
Register
size in
bits
Accessible
via
function
codes
Address
type
Access Description
1 *
1001
10001
86 *
1086
10086
1
1
1
01, 02, 05 Coil Read/
write
Single ON/OFF bit per coil
(Boolean). Shares the same
register range with the Dis-
crete Inputs. See Section
2.3.2.
01, 02 Discrete
input
Read-
only
Single ON/OFF bit per coil
(Boolean). Shares the same
register range with the Dis-
crete Inputs. See Section
2.3.2.
401 *
7401
20401
488 *
7444
20488
16
32
16
03, 04,
06**, 16,
69, 70
Floating
point reg-
ister
Read-
only and
read/
write
IEEE 754 floating point
number. Accessed as either
two 16-bit registers or one
32-bit register. See Section
2.3.1.
1 *
3001
30001
40001
50001
214 *
3214
30214
40214
50214
16
16
16
16
16
03, 04 Input reg-
isters
Read-
only
One 16 bit unsigned integer
per register. Shares the
same register range with
the Holding registers and
ASCII registers. See Sec-
tion 2.3.1.
03, 04, 06,
16
Holding
register
Read/
write
One 16 bit unsigned integer
per register. Shares the
same register range with
the Input registers and
ASCII registers. See Sec-
tion 2.3.1.
03, 04, 06,
16
ASCII
characters
Read/
write
Two ASCII characters per
16 bit register. Shares the
same register range with
the Input registers and
Holding registers. See Sec-
tion 2.3.1.
* Base Address. The other register ranges are duplicate addresses for the base registers. Reading and
writing to these duplicates is the same as reading and writing to the base registers.
** Floating Point numbers can only be written with function code 6 if the register is a 32-bit register.
 Loading...
Loading...











