Date Code 20010518 Message Strings 8-7
SEL-2020 Instruction Manual
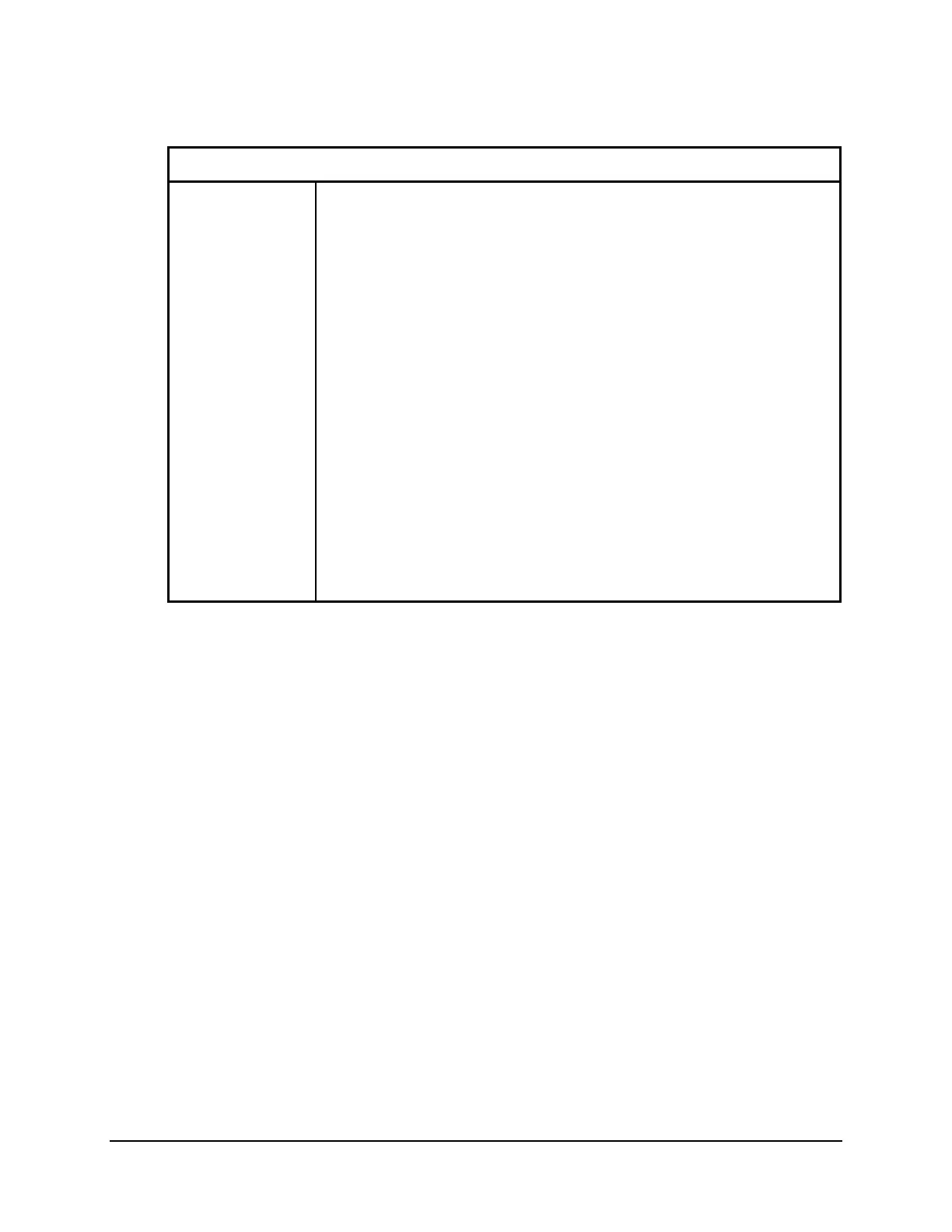
Table 8.3: Special Parsing Sequences for Strings
Character Comments
\At/ Register address. For READ and WRITE settings only.
t specifies the address format.
b=binary (2 bytes).
a=ASCII-hexadecimal (4 digits).
\Dt/ Data item. For WRITE setting only.
t specifies the data format.
b=binary word (2 bytes).
h=ASCII-hexadecimal word (4 digits).
c=binary bytes (1 byte).
g=ASCII-hexadecimal byte (2 digits).
\Pt/ Port number. For TRANS, READ, and WRITE settings only.
t specifies the Port number format.
b=binary (1 byte).
a=ASCII-hexadecimal (2 digits).
\X[X]/ Ignore character. \X/ indicates ignore one character. \XX/ indicates
ignore all characters following until the next defined character is
encountered.
The following are examples of using special parsing sequences in strings:
CMD1=“In the\XX/” The CMD1 bit will assert whenever a
string that begins with “In the” is
received at the SEL-2020 Port set with
this user-defined message.
WRITE=“W\Pa/@\Aa/=\Dh/” Creates a write command that the
SEL-2020 uses to recognize data in a
special format. In this example, the
string containing the data must begin
with a W, followed by a Port number,
an @ symbol, a database address, an =
character, and finally the data. For
instance, to write 0 (zero) to Port 8,
address F800h, you would have to send
the string “W08@F800=0000” to the
SEL-2020.
PRE-DEFINED STRINGS
When working with SEL relays, the SEL-2020 includes some pre-defined strings you can use in
SET A auto-messages to collect data. The SEL-2020 also includes four pre-defined strings you
can enter as SET U user-defined commands to recognize automatic messages sent from an SEL
 Loading...
Loading...