IM Machine Name Rev.: END 19
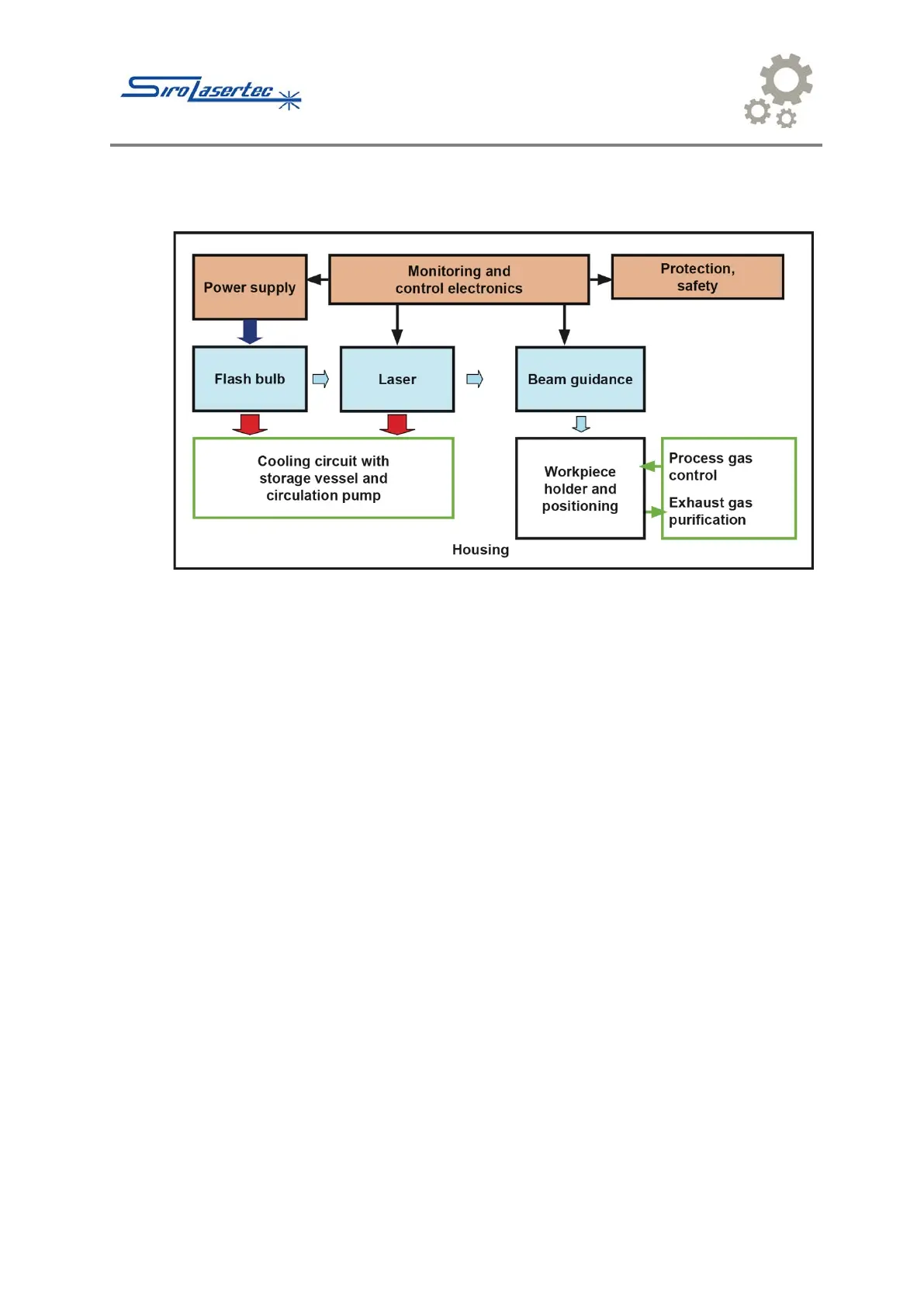
3.2 Construction of the Welding laser system
Illustration 3 Construction Block Diagram - In the picture, left to right, top to bottom: Power supply,
Monitoring and control electronics, Protection and safety, Flashbulb, Laser, Beam guidance, Cooling
circuit with storage vessel and circulation pump, Workpiece holder and positioning, Process gas control,
Exhaust gas purification, Housing.
All functions for the operation of the SL 10 welding laser system are integrated in the
housing.
The core of the welding laser system is the solid-state laser. It receives its energy
from a flashbulb that is operated by a power supply unit with high electrical efficiency.
The laser flash is guided through the observation microscope on to the workpiece via
a carefully coordinated beam path.
In the closed cooling water circuit, the cooling water is pumped through the pump
chamber of the laser and cools down the flashbulb and the laser rod. The heat
generated is dissipated into the ambient air via a heat exchanger and a fan.
The shielding gas, for example, argon, required for the protection of the weld seam is
externally supplied via a connection fitted on the back of the device. The shielding
gas can be routed directly to the weld point via a rigid as well as a flexible supply line
in the work chamber. The gas flow is controlled via the foot switch.
The welding fumes generated during the welding are extracted out of the welding
chamber.
 Loading...
Loading...