4.2.10. PID-algorithm for BLDC engine control
Algorithm description
BLDC engine is controlled by the PID regulator, with the coordinate as the controlled parameter. The controlled coordinate changes
according to motion settings and incoming commands to provide motion capability. We will call controller coordinate the running
position. Output current is the control signal of the regulator.
The control action is calculated according to the following formula:
, where:
- is the control action
- is difference between the running coordinate and the current motor coordinate
- are proportional, integral and differential coefficients of the regulator. Regulator coefficients are set on PID settings
page of the XiLab program or programmatically by calling set_pid_settings() function of the libximc library (see Programming guide).
The effects different PID components (Kp, Ki, Kd) have are same for BLDC and DC motors. See PID-algorithm for DC engine control
PID regulator manual tuning
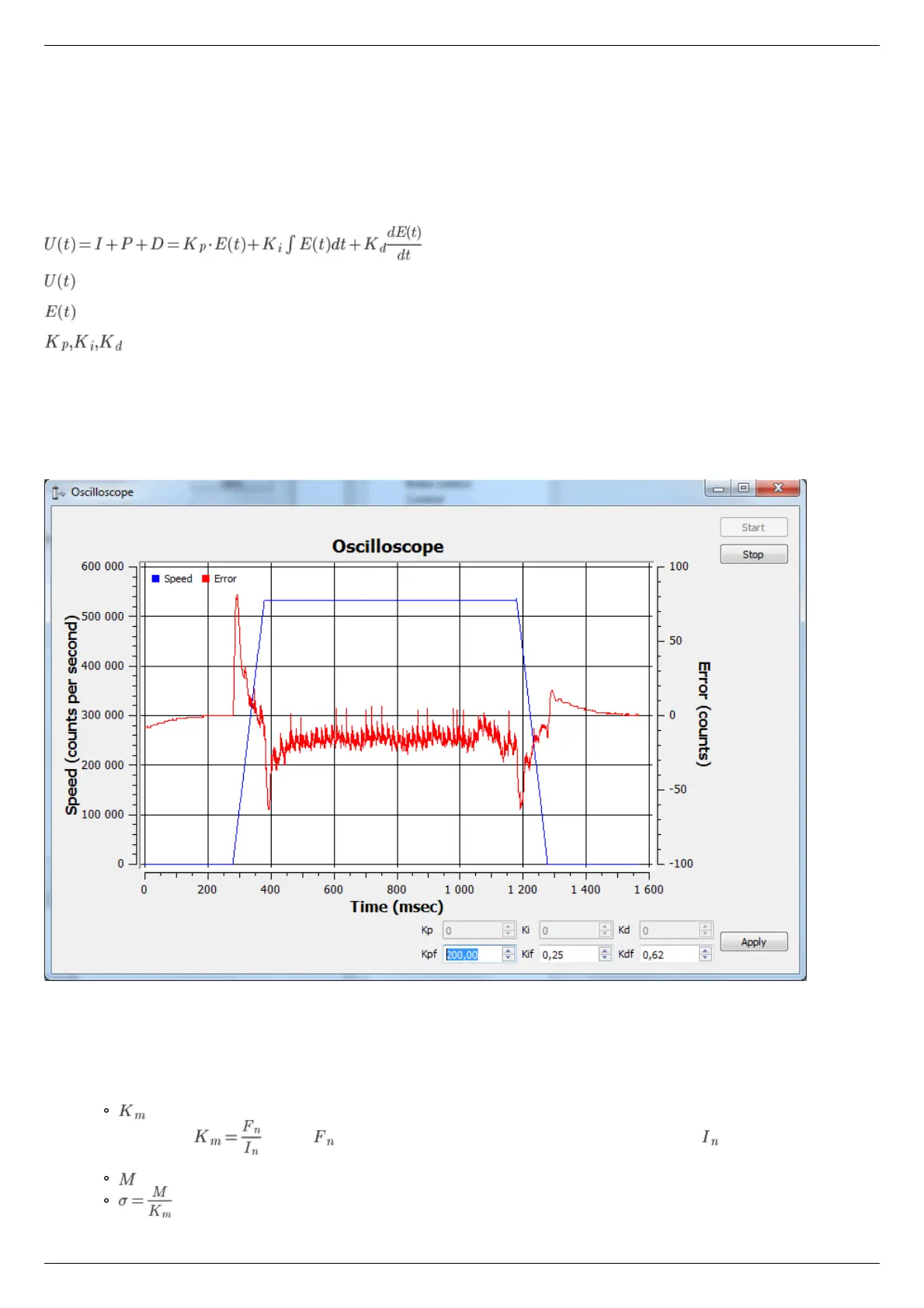
We provide a special XiLab extension for the manual adjustment of the PID regulator coefficients. The time dependence of the speed of
the BLDC engine and the speed retention error is shown in a special window, see the screenshot below.
The PID regulator tuning window
The stable position retention is necessary for the correct engine operation.
Steps to adjust the coefficients:
1. First, you need to evaluate the PID coefficients. Given the structure of the managed system, they can be calculated from
simplified formulas. For this, the parameters from the documentation for the appropriate motor and positioner are used.
- electromechanical motor coefficient [H / A] (the torque generated by the current strength is 1 A). Can be calculated
as the ratio , where is the nominal (maximum) force generated by the motor, is the rated (maximum)
current strength.
- weight of load (kg).
.
 Loading...
Loading...