Note. Sync in settings may be saved in controller flash (non-volatile) memory. In this case everything related to
synchronization may also be said about autonomous controller operation. For example, you may set up shift on offset
on syncin pulse with syncout pulse on movement stop and connect the controller to a standalone measurement
device, which starts measurements on its own input sync pulse and outputs a sync pulse on measurement end. Then
you can run such a system without a PC, because after the first sync pulse all measurements and movements will
happen automatically.
Connection
The controller is supplied with two TTL-sync channels on the BPC connector.
Sync in
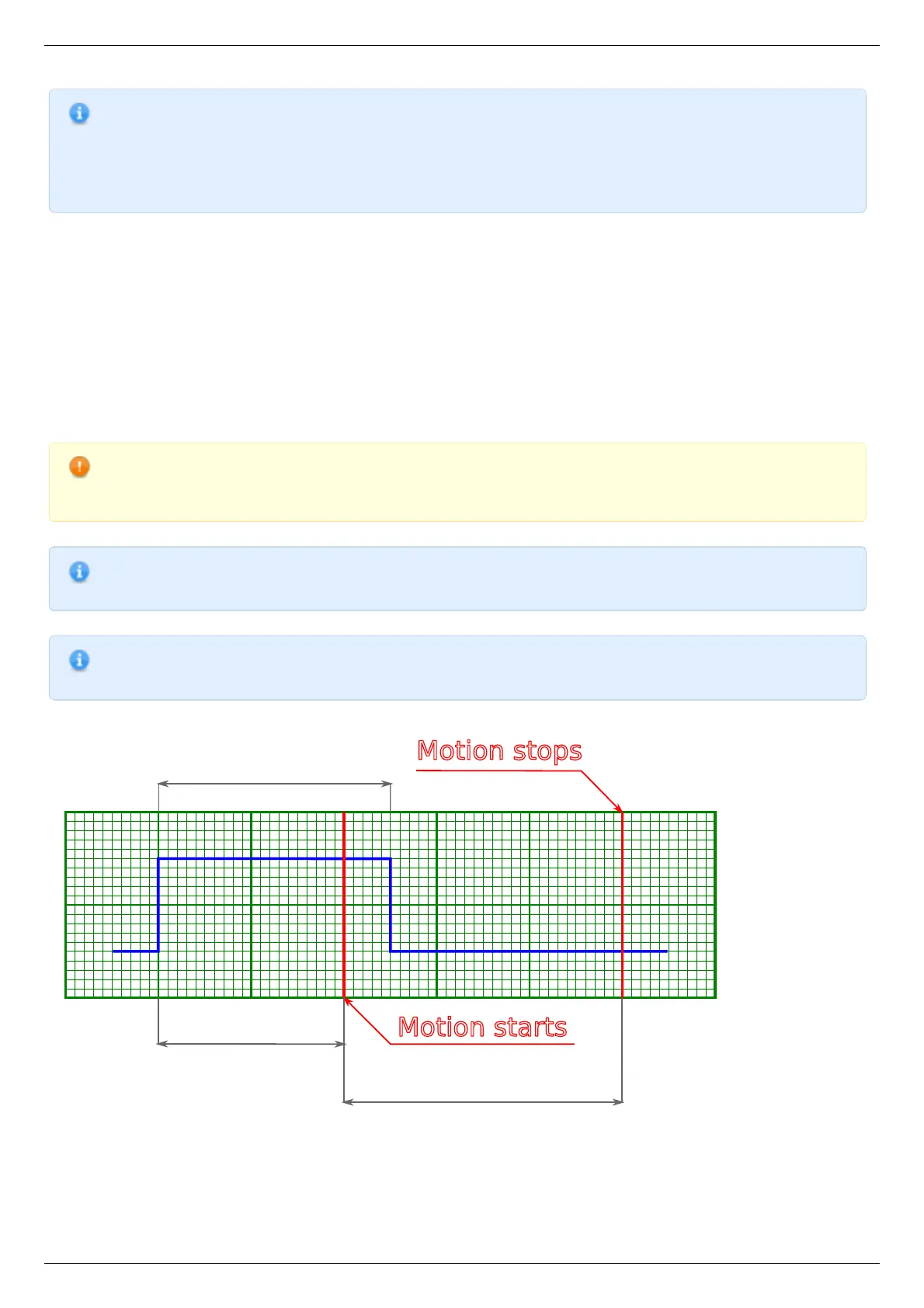
Syncronization input has a setting, which defines minimum syncin pulse length which may be registered. This length is measured in
microseconds. Use this setting to decrease controller sensitivity to noise. Synchronization input may be turned on or off. If it is on, then
a sync in pulse will lead to a situation as if Predefined displacement mode command has taken place, which takes its Position and
Speed from syncin settings. If syncin settings are changed during the time the movement takes place it will not change current
movement parameters. Movement parameters will change on the next front on syncronization input. This designed deliberately to
allow one to set up next shift parameters in multiaxis systems during movement.
WARNING. When you turn on or reboot the controller at the input voltage level of the synchronize input is present,
which is considered to be active, the controller interprets it as if Predefined displacement mode command has taken
place.
Note. Position and Speed are two separate variables which also may be saved in non-volatilve controller memory.
They are used only with synchronization input.
Note. Syncin movement obeys acceleration, max speed settings and all other settings which are related to motion.
Their incorrect setting may disrupt coordinated movement in multiaxis system.
 Loading...
Loading...