66 S100 User Guide – Rev. D – June 2005
SyncServer S100
• Real-Time Clock, or RTC, synchronizes the oscillator to the 1PPS signal from the
timing engine itself
Mode - How time is being acquired.
Time Format - The timing engine uses Binary code time.
Year - Set the year here. (Note: You must enter the year if you are using IRIG as the primary
reference source).
Local Offset - Allowed values are -16 through +16, and can include half-hour offsets.
Propagation Delay - If there is any propagation delay from the reference source, the timing
engine will adjust for it. Values range from -9999999 to +9999999.
Current Leap Seconds - This figure accounts for the local offset.
Scheduled Leap Event Time - This is a 32-bit binary value corresponding to the number of
seconds elapsed since 0 hour January 1, 1970 UTC.
Scheduled Leap Event Flag - This will alert you to an upcoming leap event.
GPS Time Format - UTC is the default.
IEEE Daylight Savings Flag - This alerts you to an upcoming Daylight Savings Time event.
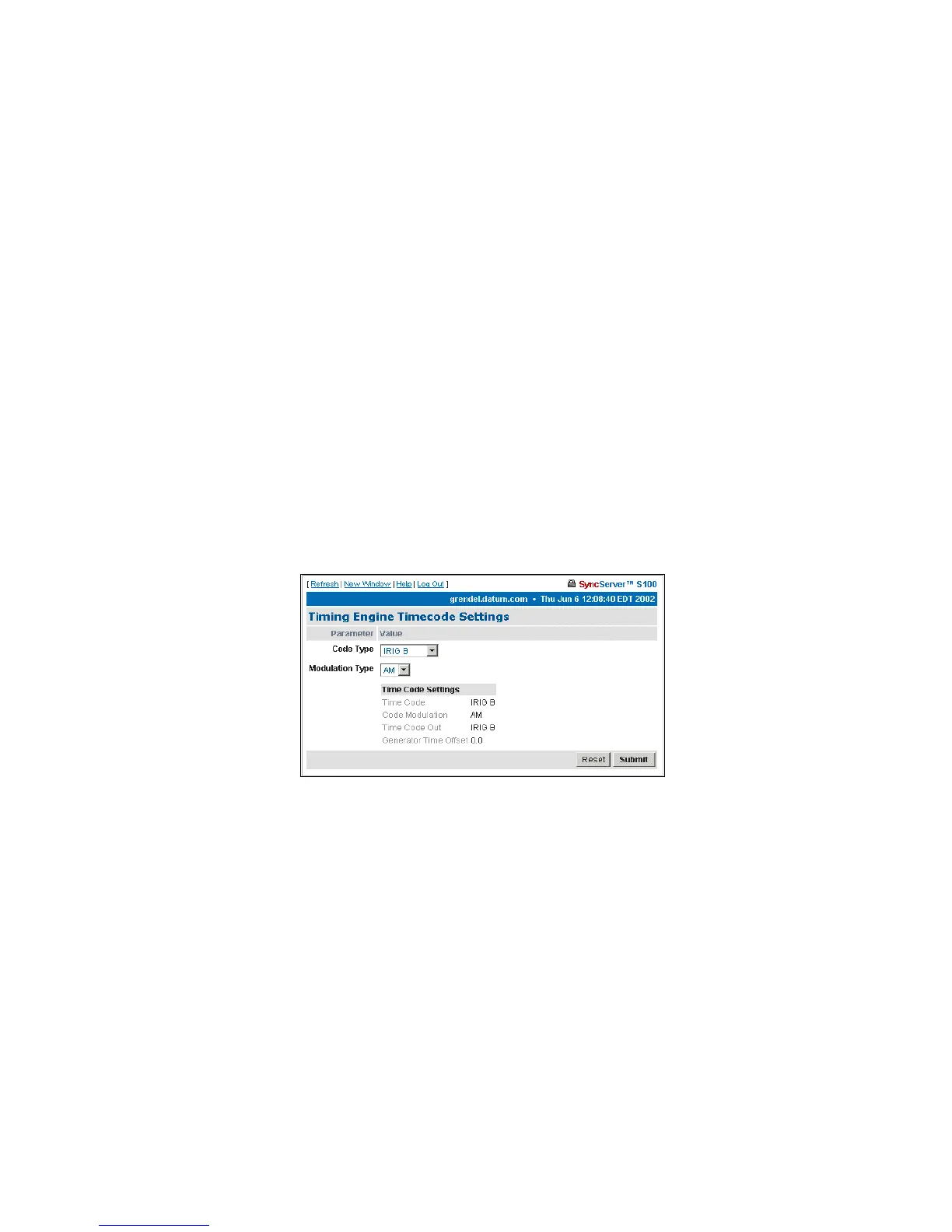
Timecode Settings
Code type choices in the drop-down list box are:
• IRIG-A
• IRIG-B
• IEEE 1344
• NASA 36
Code Type - This identifies the time code in setting.
Modulation Type - The type associated with the time code signal:
• AM, for amplitude modulated
• DC, for direct current level shift, or digital IRIG
Figure 4-13: Timecode Settings
 Loading...
Loading...