Appendix A: Functions and Instructions 837
Return CATALOG
Return [
expression
]
Returns
expression
as the result of the function. Use
within a
Func
...
EndFunc
block, or
Prgm
...
EndPrgm
block.
Note: Use
Return
without an argument to exit a
program.
Note: Enter the text as one long line on the Home
screen (without line breaks).
Define factoral(nn)=Func
:local answer,count:1! answer
:For count,1,nn
:answerù count! answer:EndFor
:Return answer:EndFunc
¸ Done
factoral(3)
¸ 6
right() MATH/List menu
right(
list1
[,
num
]) ⇒
list
Returns the rightmost
num
elements contained in
list1
.
If you omit
num
, returns all of
list1
.
right({1,3,ë 2,4},3)
¸
{3 ë 2 4}
right(
sourceString
[,
num
])
⇒
string
Returns the rightmost
num
characters contained in
character string
sourceString
.
If you omit
num
, returns all of
sourceString
.
right("Hello",2)
¸ "lo"
right(
comparison
)
⇒
expression
Returns the right side of an equation or inequality
.
right(x<3)
¸ 3
rotate() MATH/Base menu
rotate(
integer1
[
,
#ofRotations
]
) ⇒
integer
Rotates the bits in a binary integer. You can enter
integer1
in any number base; it is converted
automatically to a signed, 32-bit binary form. If the
magnitude of
integer1
is too large for this form, a
symmetric modulo operation brings it within the
range.
In Bin base mode:
rotate(0b1111010110000110101)
¸
0b10000000000000111101011000011010
rotate(256,1) ¸ 0b1000000000
If
#of Rotations
is positive, the rotation is to the left. If
#of Rotations
is negative, the rotation is to the right.
The default is
ë
1 (rotate right one bit).
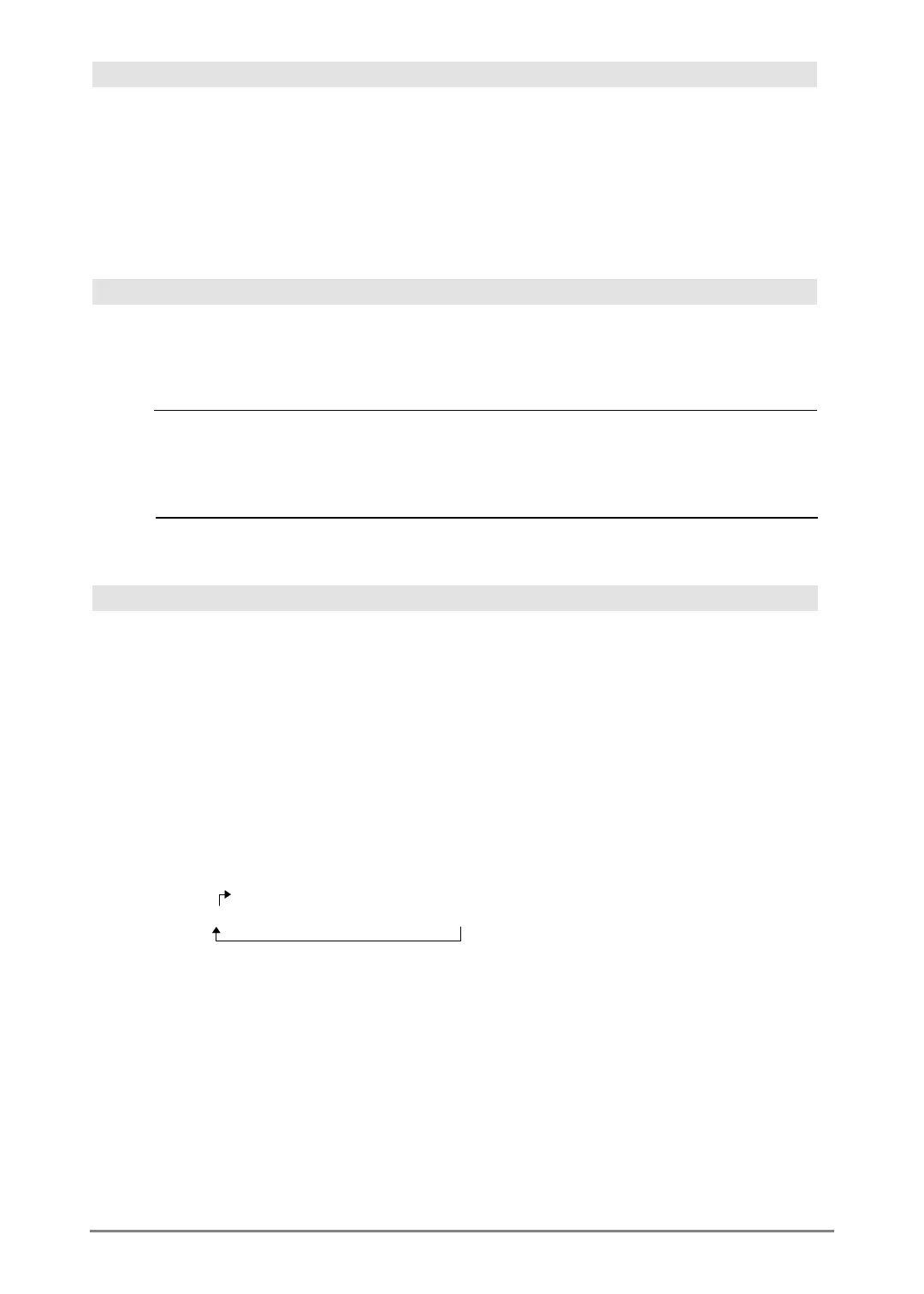
For example, in a right rotation:
In Hex base mode:
rotate(0h78E) ¸ 0h3C7
rotate(0h78E,ë 2) ¸0h800001E3
rotate(0h78E,2) ¸ 0h1E38
0b00000000000001111010110000110101
produces:
0b10000000000000111101011000011010
The result is displayed according to the
Base
mode.
Important: To enter a binary or hexadecimal
number, always use the 0b or 0h prefix (zero,
not the letter O).
Rightmost bit rotates to leftmost.
Each bit rotates right.
 Loading...
Loading...











