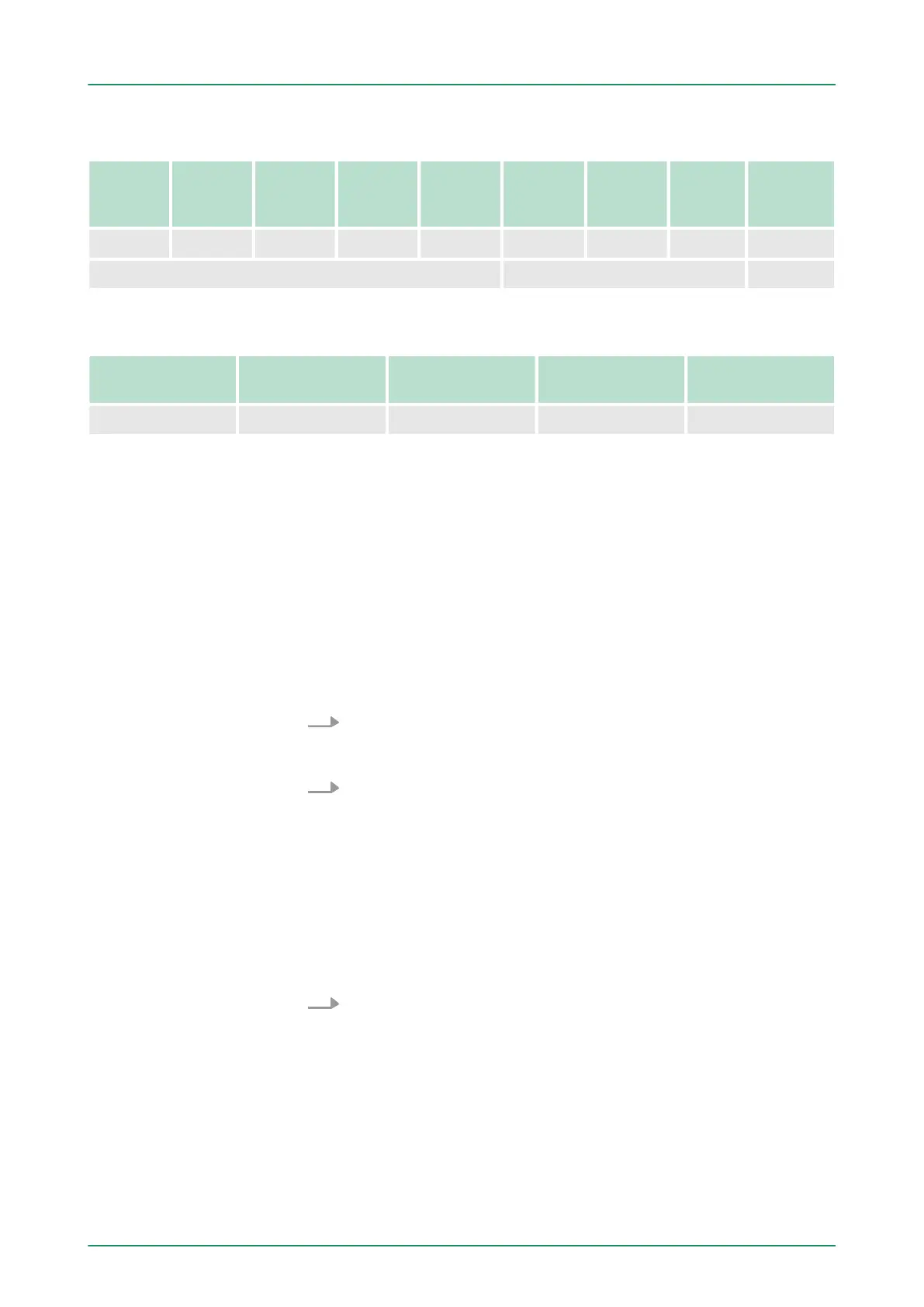
Command telegram
Slave
address
Func-
tion
code
Address
1. word
Number
of
words
Number
of bytes
Data 1.
word
Data 2.
word
... Check
sum
CRC/LRC
1byte 1byte 1word 1word 1byte 1word 1word 1word 1word
max. 125words
Respond telegram
Slave address Function code Address 1. word Number of
words
Check sum
CRC/LRC
1byte 1byte 1word 1word 1word
7.8 Modbus - Example communication
The example establishes a communication between a master and a
slave via Modbus. The following combination options are shown:
n CPU 31xS as Modbus RTU master
n CPU 21xSER-1 as Modbus RTU slave
n Siemens SIMATIC Manager and possibilities for the project
transfer
n Modbus cable connection
1. Assemble a Modbus system consisting of a CPU 31xS as
Modbus master and a CPU 21xSER-1 as Modbus slave and
Modbus cable.
2. Execute the project engineering of the master! For this you
create a PLC user application with the following structure:
n OB 100:
Call SFC 216 (configuration as Modbus R
TU master) with
timeout setting and error evaluation.
n OB 1:
Call SFC 217 (SER_SND) where the data is send with error
evaluation. Here you have to build up the telegram according
to the Modbus rules. Call SFC 218 (SER_RECV) where the
data is received with error evaluation.
3. Execute the project engineering of the slave! The PLC user
application at the slave has the following structure:
n OB 100:
Call SFC 216 (configuration as Modbus R
TU slave) with
timeout setting and Modbus address in the DB and error
evaluation.
n OB 1:
Call SFC 217 (SER_SND) for data transport from the slave
CPU to the output buffer. Call SFC 218 (SER_RECV) for the
data transport from the input buffer to the CPU. Allow an
according error evaluation for both directions.
Overview
Approach
VIPA System 300SDeployment PtP communication
Modbus - Example communication
HB140 | CPU | 314-6CF03 | GB | 16-43 192
 Loading...
Loading...