Undesirable Effects 47
5
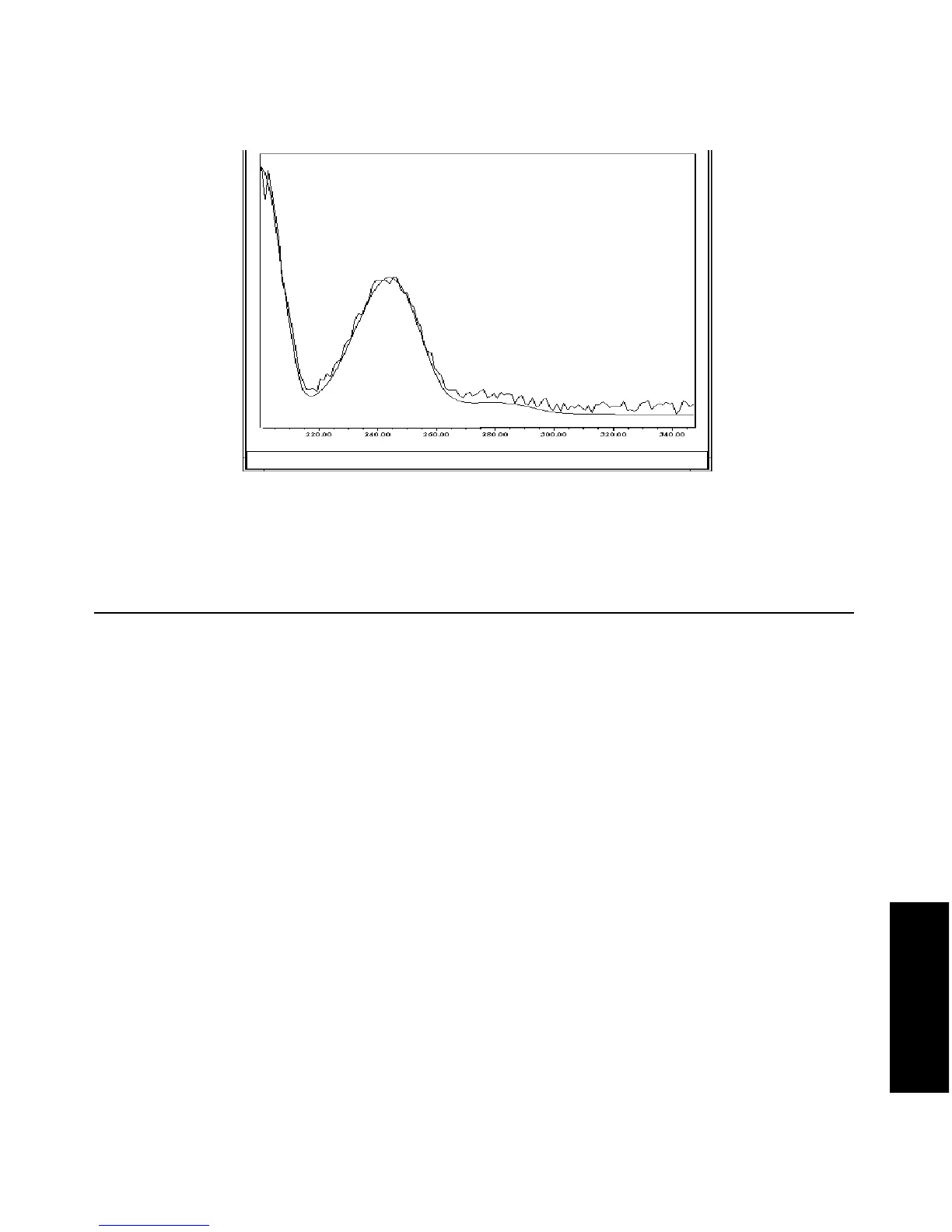
Figure 5-5 Absorbance Spectra of a Compound at Two Concentrations
5.4 Undesirable Effects
Shape differences between absorbance spectra can be caused by one or more of the
following undesirable effects:
• Detector noise
• Photometric error caused by high sample concentration
• Variation in solvent composition
These sources of spectral variation can cause chemically pure, baseline-resolved peaks to
exhibit a small level of spectral inhomogeneity. You can assess the significance of spectral
inhomogeneity by comparing a Spectral Contrast angle to a Threshold angle
(Section 5.4.4).
5.4.1 Detector Noise
Statistical and thermal variations add electrical noise to the absorbance measurements
made by the 2996 Detector. The noise manifests itself as fluctuations in the baseline,
known as baseline noise. The magnitude of any absorbance differences caused by
statistical and thermal variations can be predicted from the instrument noise in the baseline
region of a chromatogram.
Normalized Absorbance
Wavelength (nm)
Spectral Contrast Angle: 3.4°
Normalized Spectra of a Compound at Different
Concentrations

 Loading...
Loading...