Solvent miscibility
July 7, 2014, 715003736IVD Rev. C 89
•Temperature affects solvent miscibility. If you are running a
high-temperature application, consider the effect of the higher
temperature on solvent solubility.
•Buffers dissolved in water can precipitate when mixed with organic
solvents.
Using miscibility numbers (M-numbers)
Use miscibility numbers (M-numbers) to predict the miscibility of a liquid
with a standard solvent.
To predict the miscibility of two liquids, subtract the smaller M-number value
from the larger M-number value.
•When the difference between the two M-numbers is 15 or less, the two
liquids are miscible, in all proportions, at 15°C.
•A difference of 16 indicates a critical solution temperature from 25 to
75 °C, with 50 °C as the optimal temperature.
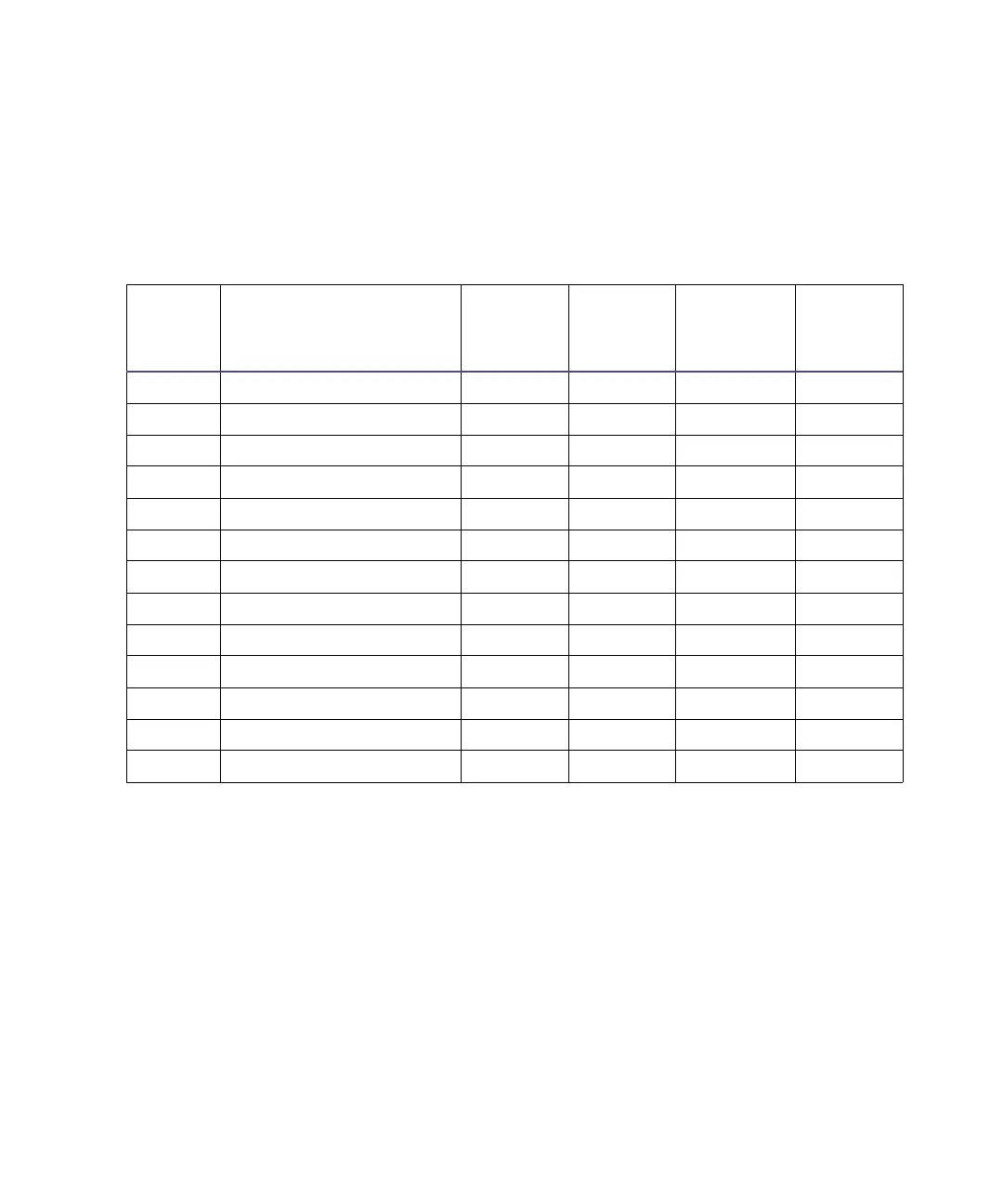
Solvent miscibility:
Polarity
index
Solvent
Viscosity
cP, 20 °C
(@1 atm)
Boiling
point °C
(@1 atm)
Miscibility
number
(M)
λ Cutoff
(nm)
0.0 N-hexane 0.313 68.7 29 ––
1.8 Triethylamine 0.38 89.5 26 ––
4.3 1-propanol 2.30 97.2 15 210
4.3 2-propanol 2.35 117.7 15 ––
5.2 Ethanol 1.20 78.3 14 210
5.5 Benzyl alcohol 5.80 205.5 13 ––
5.7 Methoxyethanol 1.72 124.6 13 ––
6.2 Acetonitrile 0.37 81.6 11, 17 190
6.2 Acetic acid 1.26 117.9 14 ––
6.4 Dimethylformamide 0.90 153.0 12 ––
6.5 Dimethylsulfoxide 2.24 189.0 9 ––
6.6 Methanol 0.60 64.7 12 210
9.0 Water 1.00 100.0 –– ––
 Loading...
Loading...