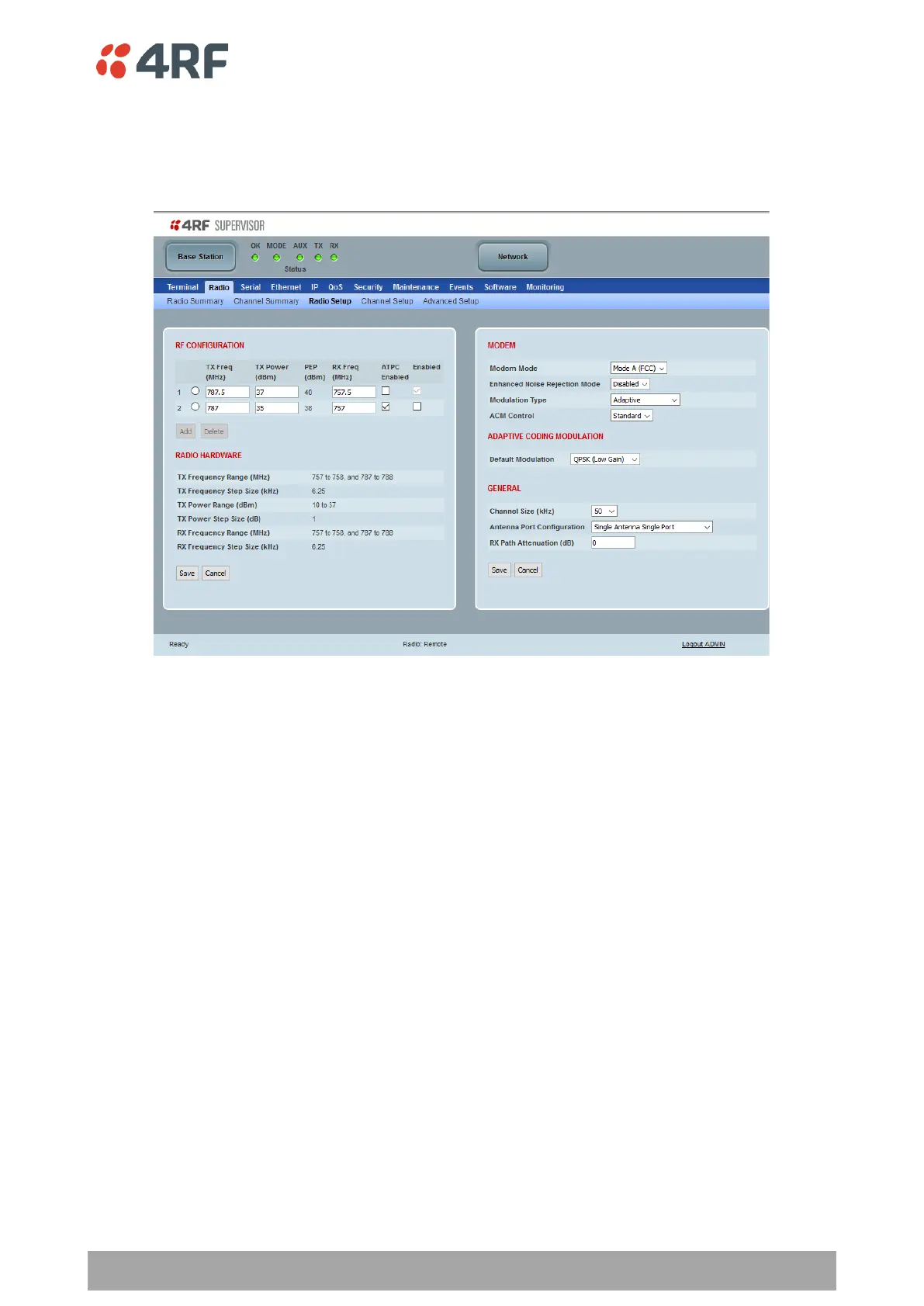
Radio > Radio Setup
Transmit frequency, transmit power and channel size would normally be defined by a local regulatory body
and licensed to a particular user. Refer to your site license details when setting these fields.
RF CONFIGURATION
RF configuration profiles allows for two sets of TX Frequency, RX Frequency, TX Power and ATPC. The
switch-over between the two profiles can be manual controlled (see Maintenance > RF on page 268) or
automatically controlled by alarm events (see Events > Event Action Setup on page 286).
ATPC Enabled
This parameter enables the radio Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC). ATPC reduces the TX power to
the minimum required while still providing reliable link capacity and performance at the remote radio. ATPC
considers margins for fading and multi path to achieve high availability.
The benefits of ATPC are:
• Enhanced frequency use and reduced interference
• Input power saving
ATPC will dynamically adjust both the base station and remote station transmitter power to maximise the
frequency reuse and reduce power consumption in the network.
A remote radio transmitter will adjust its transmitter power based on the RSSI being received at the base
station. As long as the SNR being received is greater than 30dB and the RSSI is above the current set point,
then the base station will send a recommendation for the remote radio to change its transmitter power.
This recommendation is sent every minute and is based on the lowest RSSI received during this period. The
transmitter power recommendations are a minimum of +/-1dBm up to a maximum change of +/-5dBm. The
SNR limit is used to prevent interference from limiting the throughput of the system.
 Loading...
Loading...