Aprisa SR+ User Manual 1.11.1
SR Compatible
The SR Compatible option enables over-the–air point-to-multipoint interoperation between an Aprisa SR+
network and New Aprisa SR radios. The default setting is unticked.
When the Aprisa SR+ ‘SR Compatible’ option is activated, the Aprisa SR+ locks its modulation to QPSK (as
per the New Aprisa SR modulation) and disables functionality which is not available in the New Aprisa SR for
full compatibility / interoperability operation.
This compatibility option allows the user a smooth migration to Aprisa SR+ when higher speeds of 120,
60 kbit/s (at 25, 12.5 kHz channel sizes), Adaptive Coding and Modulation, full duplex and more features
are required.
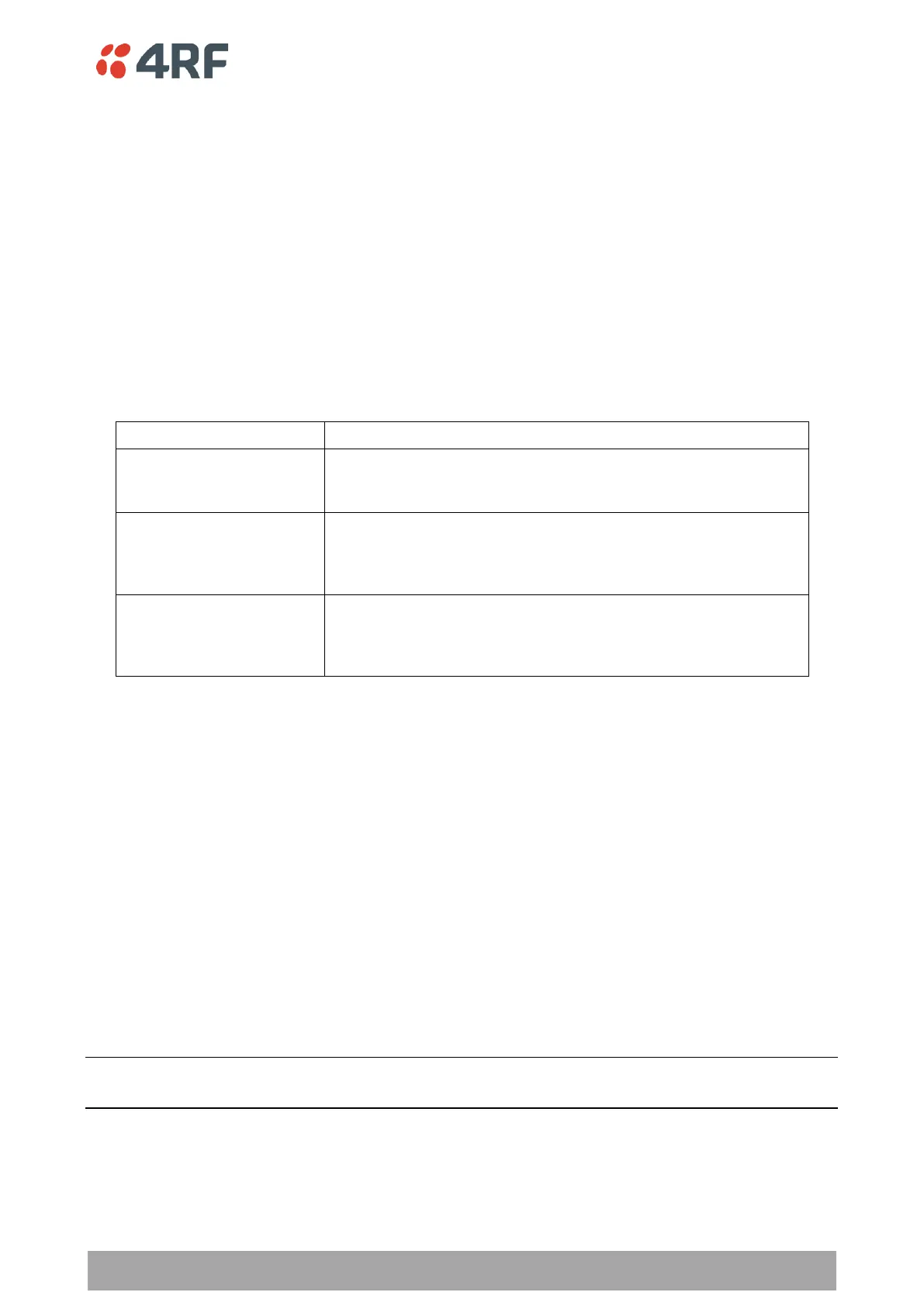
Ethernet Operating Mode
The Ethernet Operating Mode defines how Ethernet / IP traffic is processed in the radio. The default setting
is Bridge.
Bridge mode inspects each incoming Ethernet frame source and
destination MAC addresses to determine if the frame is forwarded
over the radio link or discarded.
Gateway Router mode inspects each incoming IP source and
destination IP addresses to determine if the packet is forwarded
over the radio link or discarded. In this mode, all Ethernet
interfaces have the same IP address and subnet.
Router mode inspects each incoming IP source and destination IP
addresses to determine if the packet is forwarded over the radio
link or discarded. In this mode, each Ethernet interface has a
different IP address and subnet.
Advanced
Enabled for Gateway Router and Router modes only. The default setting is unticked.
To enable Advanced routing, select the operating mode; Router or Gateway Router and tick the Advanced
checkbox.
Advanced Gateway Router mode (AGRM) or Advanced Router mode (ARM) act like a true router between the
Ethernet ports and RF interface port where the next hop is one of these ports. This means that the RF
interface is a public interface exposed to the user with IP and MAC address like the Ethernet interface.
In AGRM mode, all Ethernet interfaces have the same IP address and subnet.
In ARM mode, each Ethernet interface has a different IP address and subnet.
See ‘Advanced Gateway Router Mode (AGRM) and Advanced Router Mode (ARM)’ on page 40 for a detailed
explanation of advanced router modes.
Note: The Network Address Translation feature works only in Advanced Router or Advanced Gateway Router
operating mode (see ‘IP > NAT’ on page 194).
 Loading...
Loading...