ABB Switzerland Ltd 1KHW001489-EN ETL600
5.2.1. Power definitions
5.2.1.1. Mean power
The mean power of a signal with voltage x(t) is given by
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
=
∫
−
∞→
2
2
2
0
)(
1
lim
1
)(
T
T
T
mean
dttx
TR
xP
(1)
where R
0
is the impedance at the point where the voltage x(t) is
measured.
5.2.1.2. Peak power
The peak power of a signal with voltage x(t) is given by
]
∞<<∞−= ttx
R
xP
peak
),(max
1
)(
2
0
(2)
where R
0
is the impedance at the point where the voltage x(t) is
measured.
5.2.1.3. Peak envelope power (PEP)
The peak envelope power (PEP) of a signal with voltage x(t) is equal
to the mean power of a sine wave that has the same peak power as
x(t).
)(
2
1
)( xPxP
peakPE
=
]
∞<<∞−= ttx
R
),(max
2
1
2
0
(3)
where R
0
is the impedance at the point where the voltage x(t) is
measured.
The PEP has been defined by IEC60495 as a measure for the usable
output power of a PLC power amplifier.
5.2.2. Voltage definitions
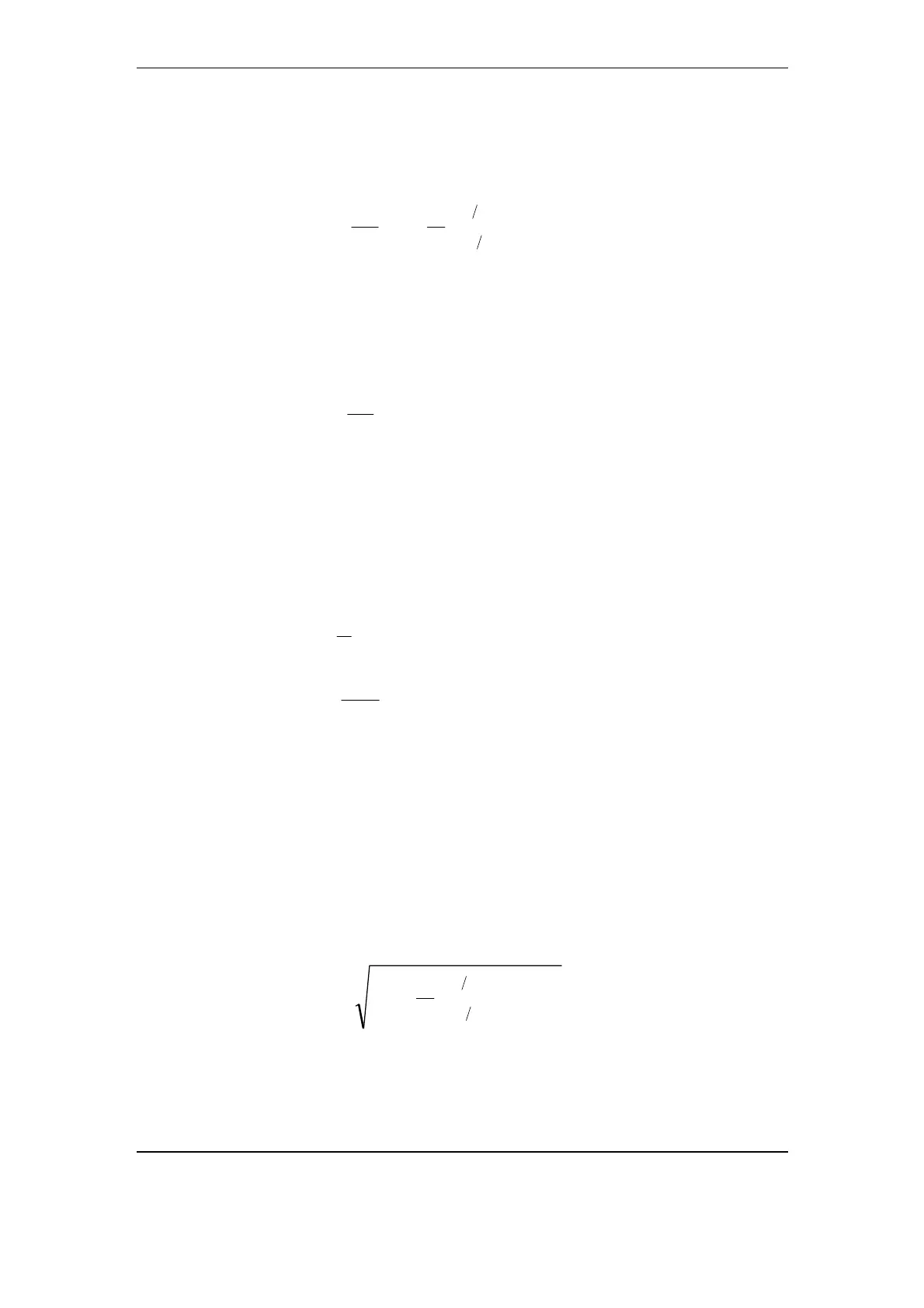
5.2.2.1. RMS voltage
The RMS (Root Mean Square) voltage of a signal with voltage x(t) is
given by
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
=
∫
−
→∞
2
2
2
)(
1
lim)(
T
T
T
RMS
dttx
T
xU
(4)
5-2 November 2005 Configuration and Set-up

 Loading...
Loading...