ABB Switzerland Ltd 1KHW001489-EN ETL600
9.6, 12, 14.4, 16, 19.2, 24, 28.8, 32, 36, 38.4, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 76.8,
80, 96, 112, 128, 144, 153.6, 160, 192, 224, 256, 288, 307.2,
320 kbps,
the upper limit being restricted by the choice of the DPLC bandwidth,
refer to Table 3-3. The MOD600 bandwidths of 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28
or 32 kHz are automatically selected according to the configured
bandwidth of the DPLC channel.
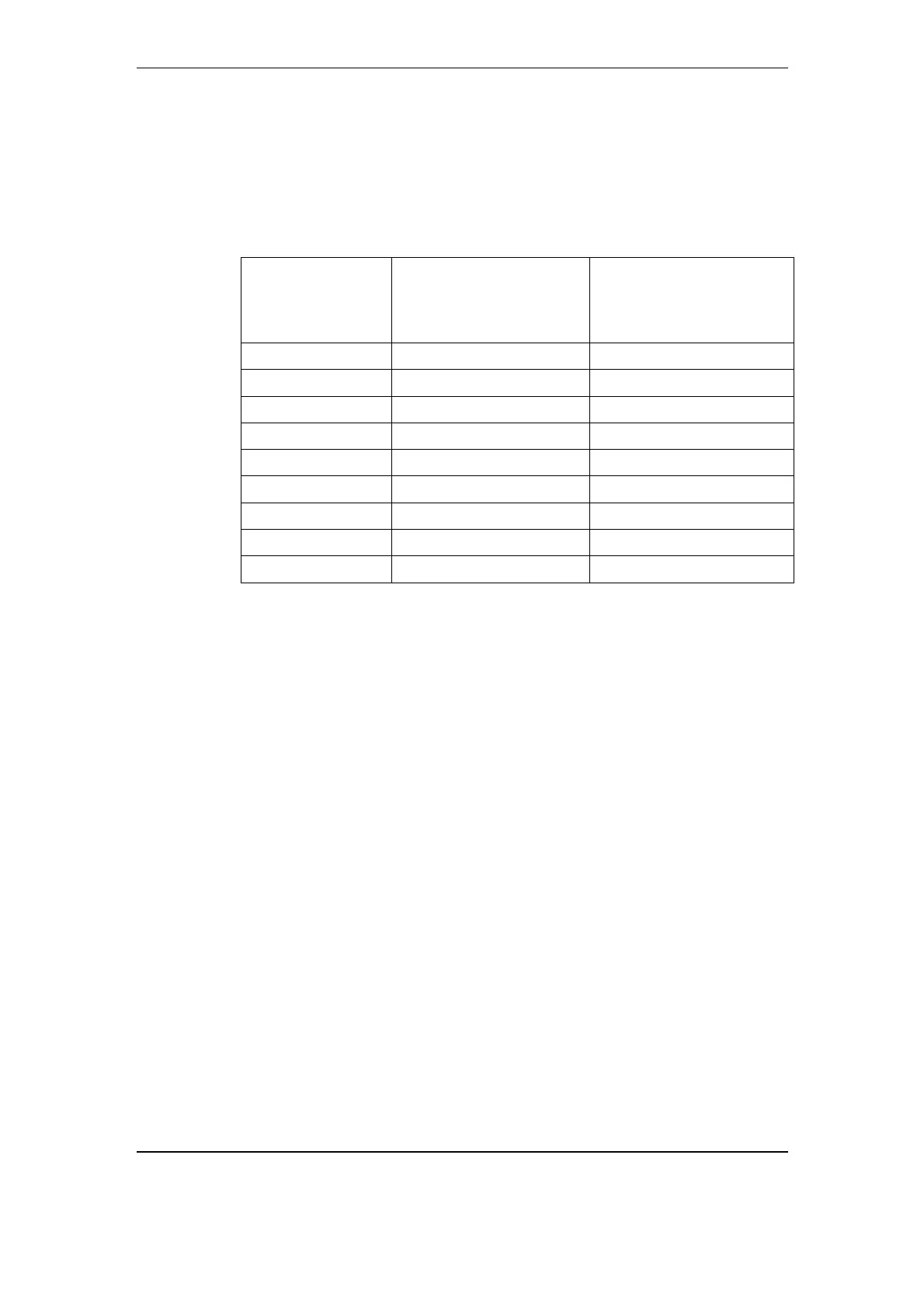
MOD600
bandwidth
[kHz]
Max. MOD600 datarate
with setting
“High Efficiency”
[kbps]
Max. MOD600 datarate
with setting
“Low delay”
[kbps]
3.5 40.0 28.8
4.0 40.0 32.0
8.0 80.0 64.0
12.0 112.0 96.0
16.0 160.0 128.0
20.0 192.0 160.0
24.0 224.0 192.0
28.0 256.0 224.0
32.0 320.0 256.0
Table 3-3 Max. MOD600 datarates
The fall-back/fall-forward option enables the datarate to be
automatically adjusted to ensure a sufficiently low BER under varying
transmission conditions. In this way a maximum data throughput is
achieved at any time. The quality of the communication channel is
continuously monitored and the most favorable of the five
programmable data transfer rates is selected accordingly. The BER is
estimated continuously and the datarate is reduced if the estimate
exceeds a preset limit. Respectively increased again as soon as the
quality of the communication channel improves sufficiently.
The modulation method used by MOD600 is block oriented: Data are
transmitted in packets of length N = 64, 128, 256 or 512 (orthogonality
interval). Data throughput and delay are increased with increasing
packet length. A guard interval of length L = 8, 16, 32 or 64 introduced
between the data packets allows for channel response and line echoes
to die off before the next data packet starts. Data throughput is
decreased while data delay is increased with increasing length of the
guard interval. The tradeoff between delay and data throughput is
evident from Table 3-3.
MOD600 has special means to combat against two kinds of
transmission channel impairments:
• Forward error correction (RS):
Two reduce the bit error probability by up to a factor of 1000 in
3-48 November 2005 Structure and Function
 Loading...
Loading...