8-15
Preset State and Memory Allocation
Memory Allocation
The analyzer attempts to allocate memory at the start of a calibration. If insufficient
memory is available, an error message is displayed. It is possible that the CMOS memory
might be fragmented due to the sequence of saving and deleting states of various sizes. So
another alternative would be to store the current state to disk and then press . The
analyzer runs a memory packer which might regain some previously inaccessible memory.
If memory is still inadequate, delete an instrument state and restart the calibration.
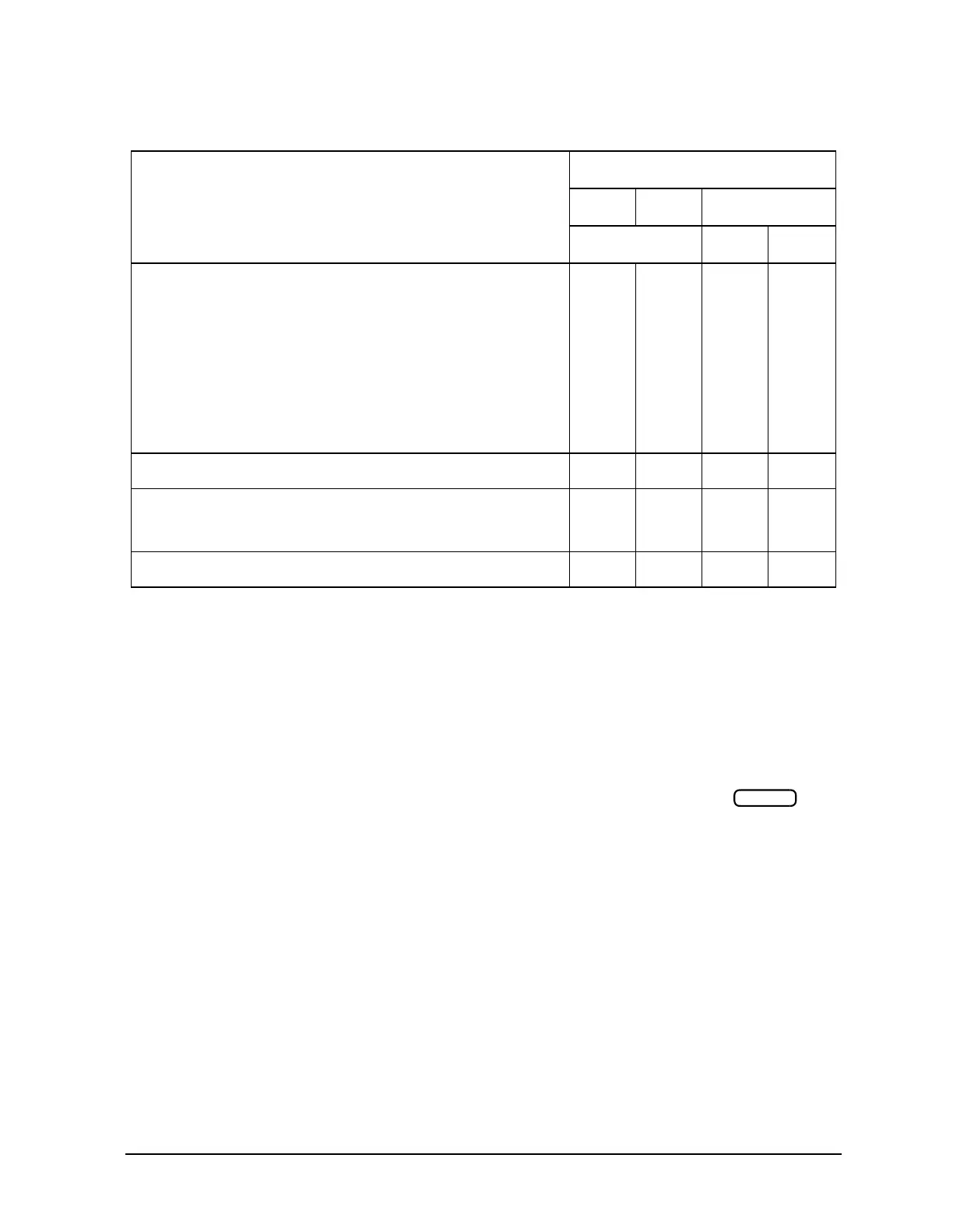
Table 8-5 Memory Requirements of Calibration and Memory Trace Arrays
Variable
Data Length (Bytes)
a
Approximate Totals (Bytes)
401pts 801pts 1601 pts
1 chan 1 chan 2chans
Calibration Arrays
Response
Response and
isolation
1-Port
2-Port
Interpolated cal
N × 6 + 52
N × 6 × 2 + 52
N × 6 × 3 + 52
N × 6 × 12 + 52
Same as above in addition to
regular cal
2.5 k
5 k
7 k
29 k
5 k
10 k
14 k
58 k
10 k
19 k
29 k
115 k
19 k
38 k
58 k
230 k
Power Meter Cal
b
(N
c
× 2 × number channels
d
) +208
1 k 1.8 k 3.4 k 6.6 k
Measurement Data
Memory trace array
b
N × 6 + 52 2.5 k 4.9 k 9.7 k 19 k
Instrument State
e
6 k6 k6 k6 k
a. N = number of points
b. This variable is allocated once per active channel.
c. The number of points that was set at the time the cal was turned on.
d. If the channels are coupled, this number is always 1. If the channels are uncoupled, this
number refers to the number of channels that have power meter cal on.
e. This value may change with different firmware revisions.
Preset

 Loading...
Loading...


















