Common Attributes for Advanced Process Control and Drives Instructions
538 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM006K-EN-P - November 2018
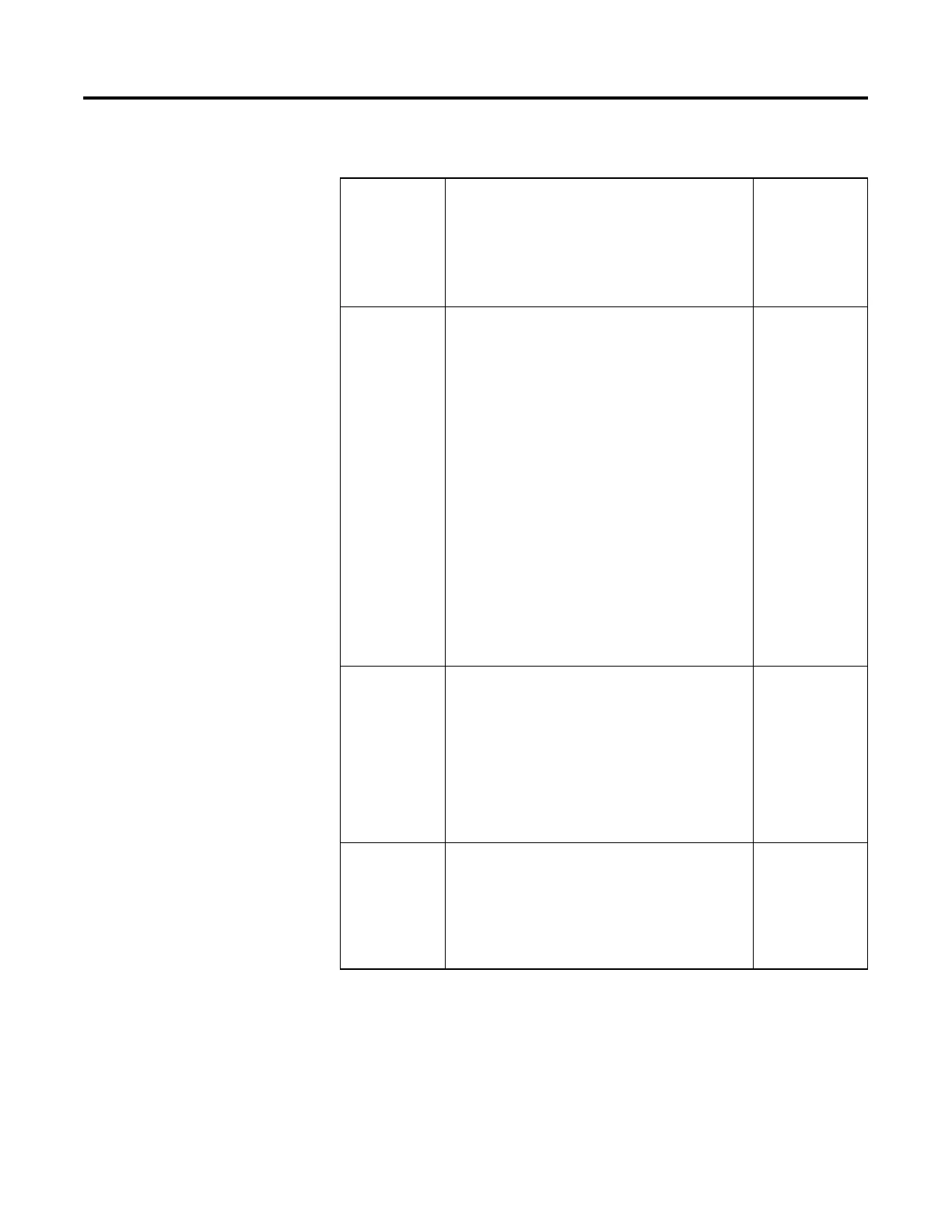
Status Flags
Status Flag Description
(For CompactLogix 5380, CompactLogix 5480, ControlLogix
5580, Compact GuardLogix 5380, and GuardLogix 5580
controllers)
Description
(For CompactLogix
5370, ControlLogix
5570, Compact
GuardLogix 5370,
and GuardLogix 5570
controllers)
S:FS
First scan flag
The first scan flag is set by the controller:
• The first time a program is scanned after the controller goes to
Run mode
• The first time a program is scanned after the program is
uninhibited
• When a routine is called from an SFC Action and the step that
owns that Action is first scanned.
Use the first scan flag to initialize data for use in later scans. It is also
referred to as the first pass bit.
The first scan flag is set
by the controller:
• The first time a
program is scanned
after the controller
goes to Run mode
• The first time a
program is scanned
after the program is
uninhibited
• When a routine is
called from an SFC
Action and the Step
that owns that
Action is first
scanned.
Use this flag to initialize
data for use in later
scans. It is also referred
to as the first pass bit.
S:N
Negative flag
The controller sets the negative flag when the result of a math or
logical operation is a negative value. Use this flag as a quick test for a
negative value.
The controller sets the
negative flag when the
result of a math or
logical operation is a
negative value. Use this
flag as a quick test for a
negative value.
Using S:N is more
efficient than using the
CMP instruction.
S:Z
Zero flag
The zero flag is set by the controller when the result of a math or
logical operation is zero. Use this flag as a quick test for a zero value.
The zero flag clears at the start of executing an instruction capable of
setting this flag.
The controller sets the
zero flag when the
result of a math or
logical operation is zero.
Use this flag as a quick
test for a zero value.

 Loading...
Loading...











