Process Control Instructions
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM006K-EN-P - November 2018 79
Description
The PID algorithm regulates the CV output in order to maintain the PV at the SP
when the instruction executes in Cascade/Ratio or Auto modes.
When ControlAction is set, the calculated value of EPercent and PVPIDPercent
is negated before being used by the control algorithm.
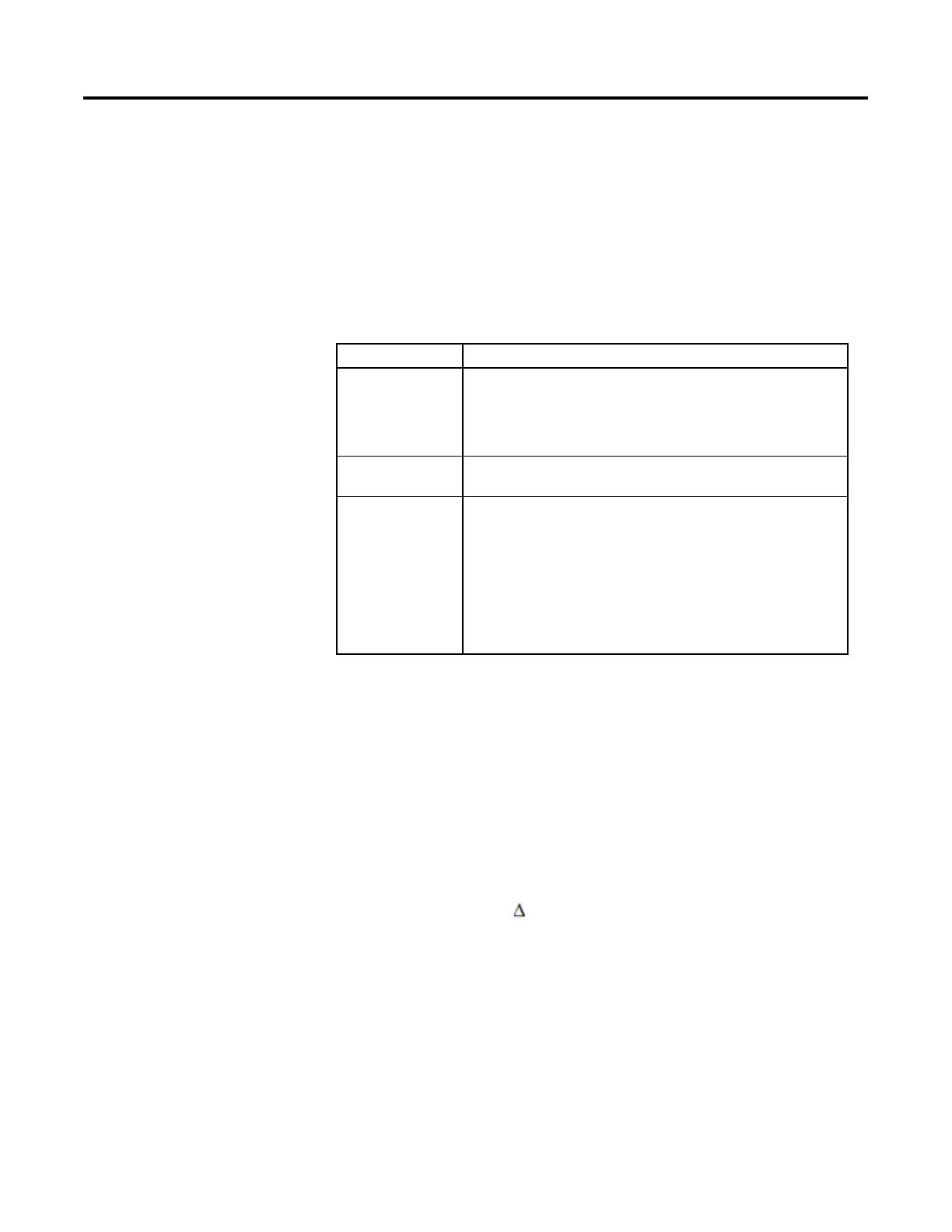
The following table describes how the instruction calculates the PID terms.
PID Term Method of Calculation
proportional The proportional term is calculated using:
• PV when PVEProportional is set or
• Error when PVEProportional is cleared
Set PGain = 0 to disable proportional control.
integral The integral term is calculated using Error. Set IGain = 0 to disable integral control.
Also, setting PGain = 0 when DependIndepend is set will disable integral control.
derivative The derivative term is calculated using:
• PV when PVEDerivative is set or
• Error when PVEDerivative is cleared
Set DGain = 0 to disable derivative control. Also, setting PGain = 0 when
DependIndepend is set will disable derivative control.
Derivative smoothing is enabled when DSmoothing is set and disabled when
DSmoothing is cleared. Derivative smoothing causes less CV output "jitter" as a result of
a noisy PV signal but also limits the effectiveness of high derivative gains.
Computing CV
The PID control algorithm computes the value for CV by summing Delta PTerm,
Delta ITerm, Delta
DTerm, and CV from the previous execution of the instruction, for example CV
n-
1
. When CVsetPrevious is set,
CVn-1 is set equal to CVPrevious. This lets you preset CV
n-1
to a specified value
before computing the value of CV.
CalculatedCV = CV
n-1
+ D PTerm + DITerm + DDTerm
PIDE Algorithms
The PIDE instruction uses a velocity form PID algorithm similar to that used in
most DCS systems. Some advantages to a velocity form algorithm include:
• Bumpless adaptive gain changes – You can change gains on the fly without
initializing the algorithm.
• Multi-loop control schemes – You can implement cross limiting between
loops by manipulating the CV
n-1
term.

 Loading...
Loading...











